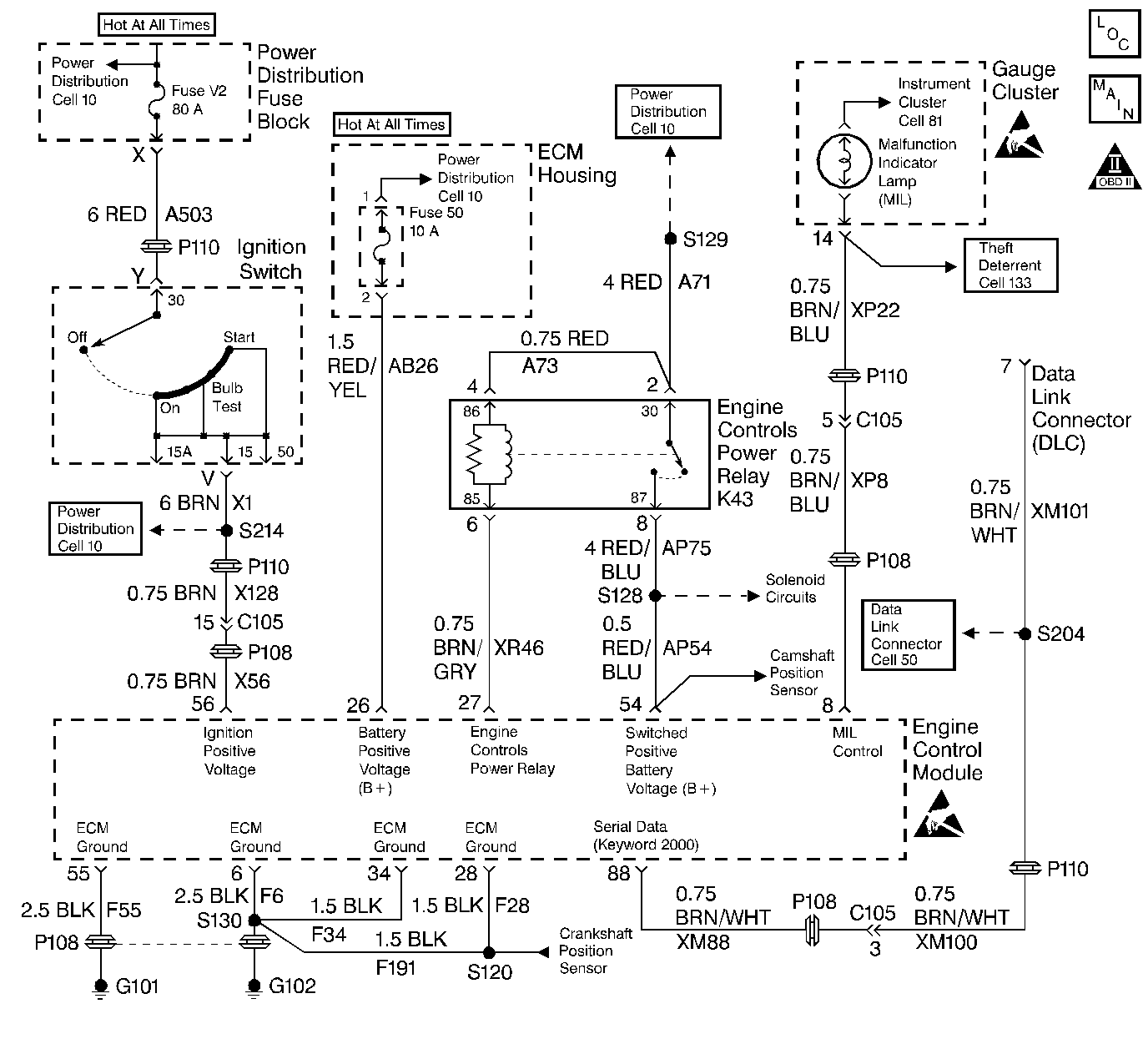
Description
Important: This vehicle is equipped with a Theft Deterrent System which interfaces with the Engine Control Module (ECM). When the diagnostics call for a replacement of the ECM, reprogram the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming .
The Powertrain OBD System Check is an organized approach to identifying a problem that was created by an electronic engine control system malfunction. The Powertrain OBD system check must be the starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. The Powertrain OBD system check directs the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing a complaint. Understanding and using the table correctly will reduce the diagnostic time and prevent the replacement of good parts.
Do Not perform this check if a driveability concern is not present.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Do not perform the Powertrain OBD System Check unless one of the concerns noted is present. Failure to follow this procedure could lead to misdiagnosis of the system.
-
The diagnostic tables in this section are designed for use with a scan tool. If the scan tool is inoperative, this condition must be corrected before beginning any other diagnostic procedures. Do Not clear the DTCs unless you are instructed to do so by a diagnostic procedure.
-
Checking for applicable service bulletins before proceeding with diagnosis is recommended.
-
If any multiple DTCs are stored, diagnose in the following order of priority:
| 1. | The ECM failure DTCs (P0601, P0602). |
| 2. | The System Voltage DTCs. |
| 3. | The Component level DTCs (the Sensors, the Solenoids, the Relays etc.). The multiple DTCs within this category should be diagnosed in numerical order starting with the lowest numbered DTC. |
| 4. | The System level DTCs (the Misfire, the Fuel Trim, etc.). |
| 5. | The Transmission DTCs. The transmission DTCs are not located in this section. Refer to Transmission for transmission diagnostics. |
When there is a known exception, a DTC table may direct the technician to diagnose a different DTC first.
-
Capturing the stored Information will preserve the data that will be lost when you are instructed to clear the DTCs at the end of a diagnostic table, or if a ECM disconnect or replacement occurs during a diagnostic procedure. The Freeze Frame data stores in the scan tool's memory. Any non-emissions DTCs that are set should be written down at this time (the Freeze Frame only stores data for the emissions related DTCs). The captured Information should be reviewed at the end of the diagnostic table in order to catch the next DTC in the event that the multiple DTCs were stored. Follow the order of the priority as listed above.
-
Verify that no DTCs are set. If a DTC sets during this check, go back to step 7.
-
Compare the actual control system data with the values in the Engine Scan Tool Data List in order to determine if any parameter is not within limits. Keep in mind that a base engine problem (for example, advanced cam timing) may substantially alter the sensor values. If the actual data does not correspond with the values in the Engine Scan Tool Data List , but the corresponding DTC is not set, there are specific conditions that have to be met before some diagnostics will run. This information is in the supporting text for the DTC table. If a system fault is suspected (the EVAP operation, the HO2S operation, etc.) refer to the DTCs that apply to that system. The DTC tables are not designed to be used unless a DTC is set, however, many tables begin with a functional test of the related component. This information can be a useful aid in diagnosis.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Check for one or more of the following conditions:
Is one or more of the conditions present? | -- | The System is OK Refer to Test Description. | ||||||||
Does the scan tool display data? | -- | Go to No Scan Tool Data | ||||||||
3 | Does the engine crank? | -- | Go to Electrical Diagnosis in Engine Electrical, Starting and Charging System | |||||||
4 | Turn on the ignition with the engine off. Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Illuminated? | -- | ||||||||
5 | Does the engine start and run? | -- | ||||||||
Check for bulletins that may address the concern. Was a bulletin repair made? | -- | Verify repair | ||||||||
Check for the DTCs with the scan tool. Are there any DTCs displayed? | -- | |||||||||
Use the scan tool in order to capture the Freeze Frame info. Also note any DTCs that are set but are not in the Freeze Frame buffer (non-emissions related). Refer to Test Description. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | -- | |||||||
Start the engine. Is the MIL on with the engine running? | -- | |||||||||
Compare the scan tool data with the values shown in the Engine Scan Tool Data List Are the values normal or within typical ranges? | -- | Go to Symptoms | Refer to Test Description |
