Refer to
Power, Ground, MIL, DLC
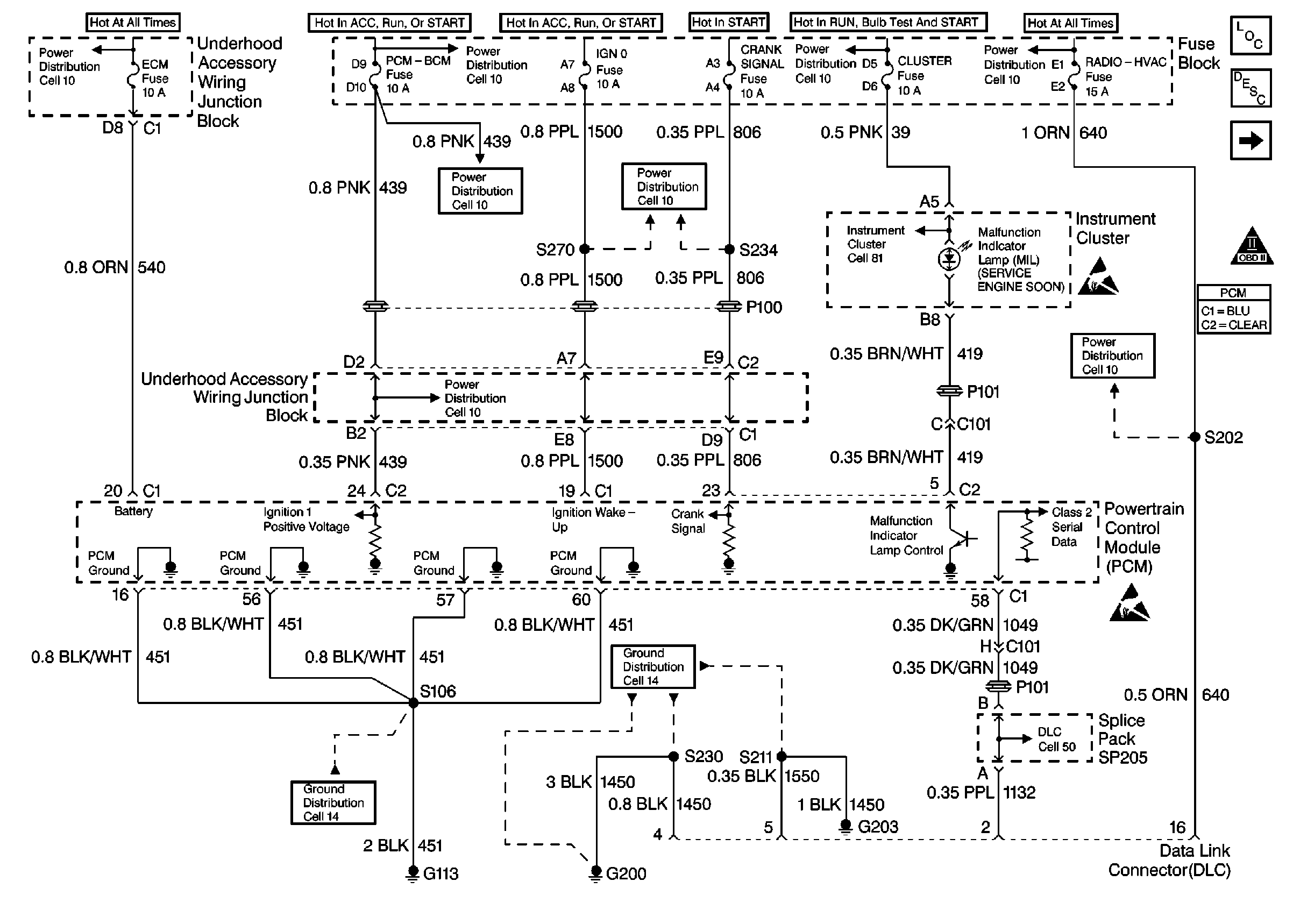
Circuit Description
The Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check must be the starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Before using this procedure, you should perform a careful visual/physical check of the PCM and engine grounds for being clean and tight. The Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check is an organized approach to identifying a problem created by an electronic engine control system malfunction.
MIL Operation
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is located on the instrument panel (CHECK ENGINE) or (SERVICE ENGINE SOON). The MIL performs the following functions:
| • | It informs the driver that a problem has occurred and that the vehicle should be taken for service as soon as possible. |
| • | As a bulb check and system check, the MIL will illuminate with the ignition switch ON and the engine not running. when the engine is started, the MIL will turn OFF. If the MIL remains ON, the self-diagnostic system has detected a problem. If the problem goes away, the MIL will turn OFF in most cases, but a diagnostic trouble code will remain stored. |
| • | If the MIL is illuminated, then the engine stalls, the MIL will remain Illuminated so long as the ignition switch is ON. |
| • | If the MIL is not illuminated and the engine stalls, the MIL will not illuminate until the ignition switch is cycled OFF, then ON. |
Perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check first, when the following conditions are present:
| • | When the MIL does not turn ON when the ignition switch is turned to the RUN position |
| • | When the MIL remains ON while the engine is running |
| • | When you suspect a driveability problem |
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation. Check for poor connections or a damaged harness. Inspect the PCM harness and connectors for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection, and damaged harness.
If multiple DTCs are stored, diagnose each DTC according to the following priority:
| • | PCM Error DTCs (P0601, P0602). |
| • | System Voltage (P0560, P1635, P1639). |
| • | Component Level DTCs (Switches, sensor range/performance, sensor high voltage, sensor low voltage, ODMs, etc....). |
| • | System level DTCs (Fuel trim, Misfire, EGR flow, TWC System, Idle Control System, HO2S Response or HO2S Transition Time Ratio). |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table:
-
The MIL should be ON steady with the key ON / engine OFF. If not, the No Malfunction Indicator Lamp table should be used to isolate the malfunction.
-
This test ensures that the PCM is capable transmitting Class 2 serial data to the DLC and that the Class 2 data circuit is not open or shorted. If a problem is encountered and a malfunctioning scan tool is suspected, try the scan tool on another vehicle to verify operation. If a DLC problem exists, the DLC Diagnosis table should be used to diagnose the condition.
-
If the engine will not start, the Engine Cranks But Will Not Run table should be used to diagnose the condition.
-
The scan tool may display DTCs which are diagnosed in 4L60-E Automatic Transmission Diagnosis. Refer to DTC List for a complete list of DTCs supported by this vehicle application. If multiple DTCs are stored, diagnose each DTC according the following priority:
-
A scan tool parameter which is not within the typical range may help to isolate the area which is causing the problem.
| • | PCM malfunction DTCs (P0601, P0602, P0604, P0606). |
| • | System voltage DTCs (P0560, P1635, P1639). |
| • | Component level DTCs (switches, sensor range/performance, sensor high voltage, sensor low voltage, ODMs, etc.). |
| • | System level DTCs (fuel trim, misfire, EGR flow, TWC system, EVAP system, idle control system, HO2S response or HO2S transition time ratio). |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Is the MIL illuminated? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool display PCM data? | -- | |||
Attempt to start the engine. Did the engine start and continue to run? | -- | |||
With a scan tool, display Diagnostic Trouble Codes. If any DTCs are stored, save the freeze frame and fail record information using the scan tool: Are any DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | ||
Compare PCM data values displayed on the scan tool to the Engine Scan Tool Data List . Are the displayed values normal or close to the typical values? | -- | System OK | Go to Component System Checks |
