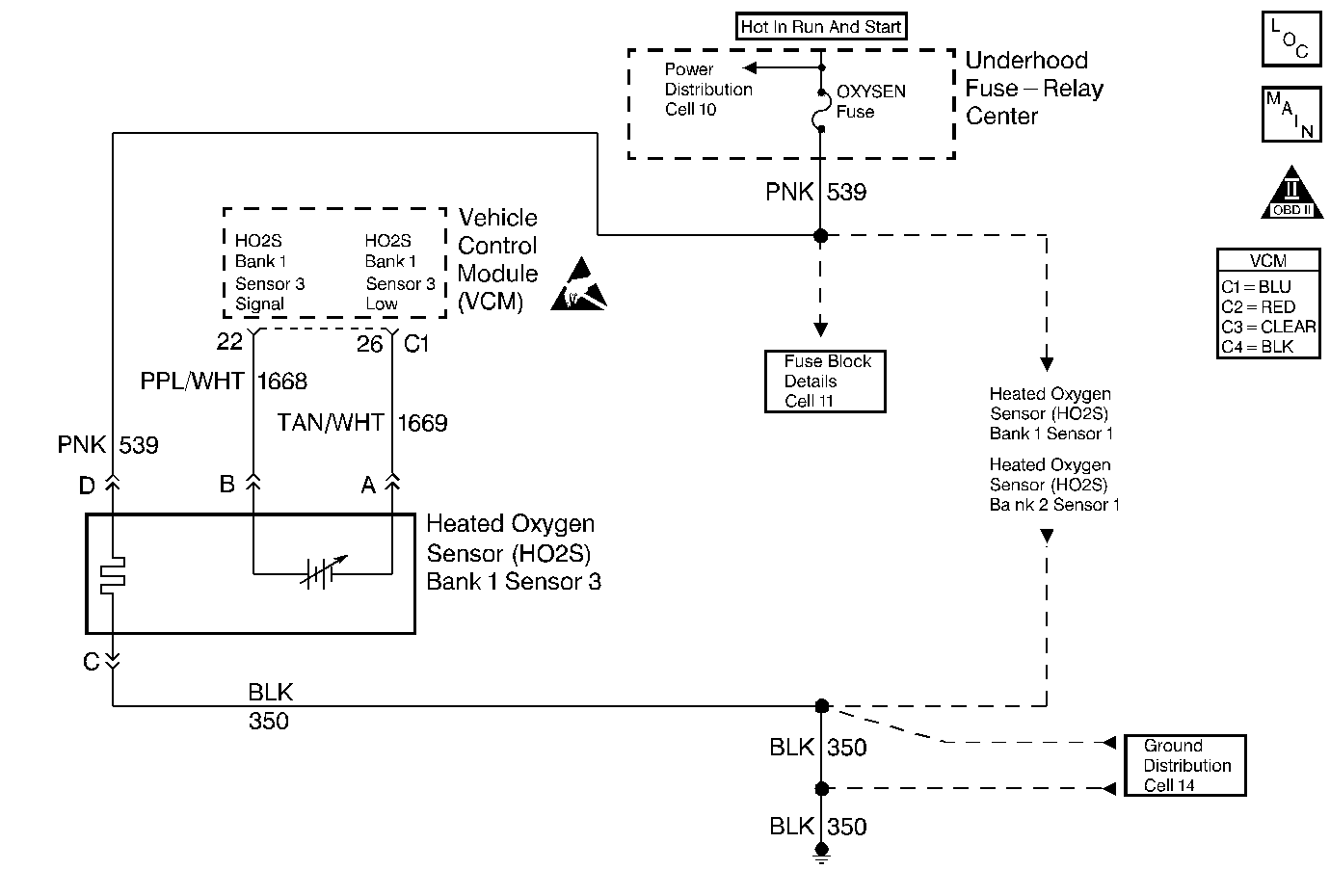
Circuit Description
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is a sensor designed to create a voltage relative to the oxygen content in the engine exhaust stream. The control module supplies the HO2S with signal high and low circuits. Ignition voltage and ground are supplied to the HO2S heater by independent circuits. The oxygen content of the exhaust indicates when the engine is operating lean or rich. When the HO2S detects that the engine is operating rich, the signal voltage is high, and decreases the signal voltage as the engine runs leaner. This oscillation above and below the bias voltage, sometimes referred to as activity or switching, can be monitored with the HO2S signal voltage.
The HO2S contains a heater that is necessary in order to quickly warm the sensor to operating temperature. The heater also maintains the operating temperature during extended idle conditions. The HO2S needs to be at a high temperature in order to produce a voltage. When the HO2S reaches operating temperature, the control module monitors the HO2S bias, or reference, voltage. It also monitors the HO2S signal voltage for Closed Loop fuel control. During normal Closed Loop fuel control operation, the control module will add fuel, or enrich the mixture, when the HO2S detects a lean exhaust content. The control module will subtract fuel, or "lean-out" the mixture, when the HO2S detects a rich exhaust condition.
Certain vehicle models utilize an oxygen sensor behind the catalytic converter in order to monitor catalyst efficiency.
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) determines if the HO2S is functioning properly. It checks for an adequate number of HO2S voltage transitions above and below the bias range of 300-600 mV. This DTC sets when the vehicle control module (VCM) fails to detect a minimum number of voltage transitions above and below the bias range during the test period. Possible causes of this DTC are:
| • | An open or a short to voltage on either the HO2S signal or HO2S low circuits |
| • | A malfunctioning HO2S |
| • | A problem in the HO2S heater or its circuit |
| • | A faulty HO2S ground |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No active TP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active EVAP system DTCs |
| • | No active IAT sensor DTCs |
| • | No active MAP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active ECT sensor DTCs |
| • | No active MAF sensor DTCs |
| • | No intrusive tests (i.e., EGR or Catalyst) in progress |
| • | No device control active |
| • | The system voltage is between 11.7-18 volts |
Rich Test
| • | The system is in closed loop |
| • | The air/fuel ratio is between 14.5-14.8 |
| • | The throttle position is between 0-50 percent |
Decel Fuel Cut-Off (DFCO) Rich Test
| • | DFCO mode active |
| • | The system is in closed loop |
| • | The elapsed time since test enabled is greater than 2 seconds |
Decel Fuel Cut-Off (DFCO)
| • | DFCO mode active |
| • | The system is in closed loop |
| • | Elapsed time since test enabled is greater than 2 seconds |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Rich Test
The O2 sensor voltage is greater than 993 mV for more than 110 seconds.
Decel Fuel Cut-Off (DFCO) Rich Test
The O2 sensor voltage is greater than 468 mV for more than 40 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Set
A current DTC P0144 causes the system to operate in an Open Loop. With a current DTC P0144 set, the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) illuminates after 2 test failures.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Never solder the HO2S wires. For proper wire and connector repair refer to Wiring Repairs .
Check the following items:
| • | The fuel pressure: If the pressure is too high, the system will run rich. The VCM can compensate for some increase; however, if the pressure gets too high, the DTC may set. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| • | A rich injector. Perform a poppet nozzle test. Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test . |
| • | A leaking injector. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| • | Fuel contaminated oil |
| • | EVAP canister purge: Check for a fuel saturation. If full of fuel, check the canister control and hoses. Refer to Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis . |
| • | Leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to the regulator for fuel. |
| • | The TP sensor: An intermittent TP sensor output causes the system to run rich due to a false indication of the throttle moving. |
| • | False rich indication due to silicon contamination of the heated oxygen sensor. A DTC P0144 accompanied by a lean driveability conditions and a powdery white deposit on the sensor indicates a false rich indication. |
| • | Faulty HO2S: the HO2S is internally shorted, the HO2S voltage displayed on a scan tool will be over 1.0 volt (1000 mV). Try disconnecting the HO2S, if the displayed voltage goes from over 1000 mV to around 450 mV, replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
In order to determine if the engine is lean during power enrichment operate the vehicle under higher throttle/acceleration conditions while monitoring scan tool HO2S voltage and the power enrichment parameter. A lean condition will cause HO2S voltage to be less than 598 mV during power enrichment.
-
Monitor the HO2S voltage of the opposite bank sensor. If the voltage activity of the opposite bank sensor is similar to the voltage activity of the suspect sensor check for lean conditions that would affect both cylinder banks. An opposite bank sensor with normal HO2S voltage activity indicates the suspect HO2S needs replacement or a lean condition exists only on the suspect HO2S cylinder bank.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info function to save the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear DTC Information function is used. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
Is the HO2S voltage fixed less than the value specified? | 86 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any engine conditions as necessary. Did you perform a repair? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
Is the HO2S voltage within the specified value range? | 351 mV-551 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The HO2S may be detecting a lean exhaust condition. Check for one of the following conditions:
Repair any engine conditions as necessary. Did you perform a repair? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
Is the resistance at the specified value on both tests? | ∞ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
7 | Repair the HO2S signal HIGH circuit shorted to ground or shorted to the HO2S LOW circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
