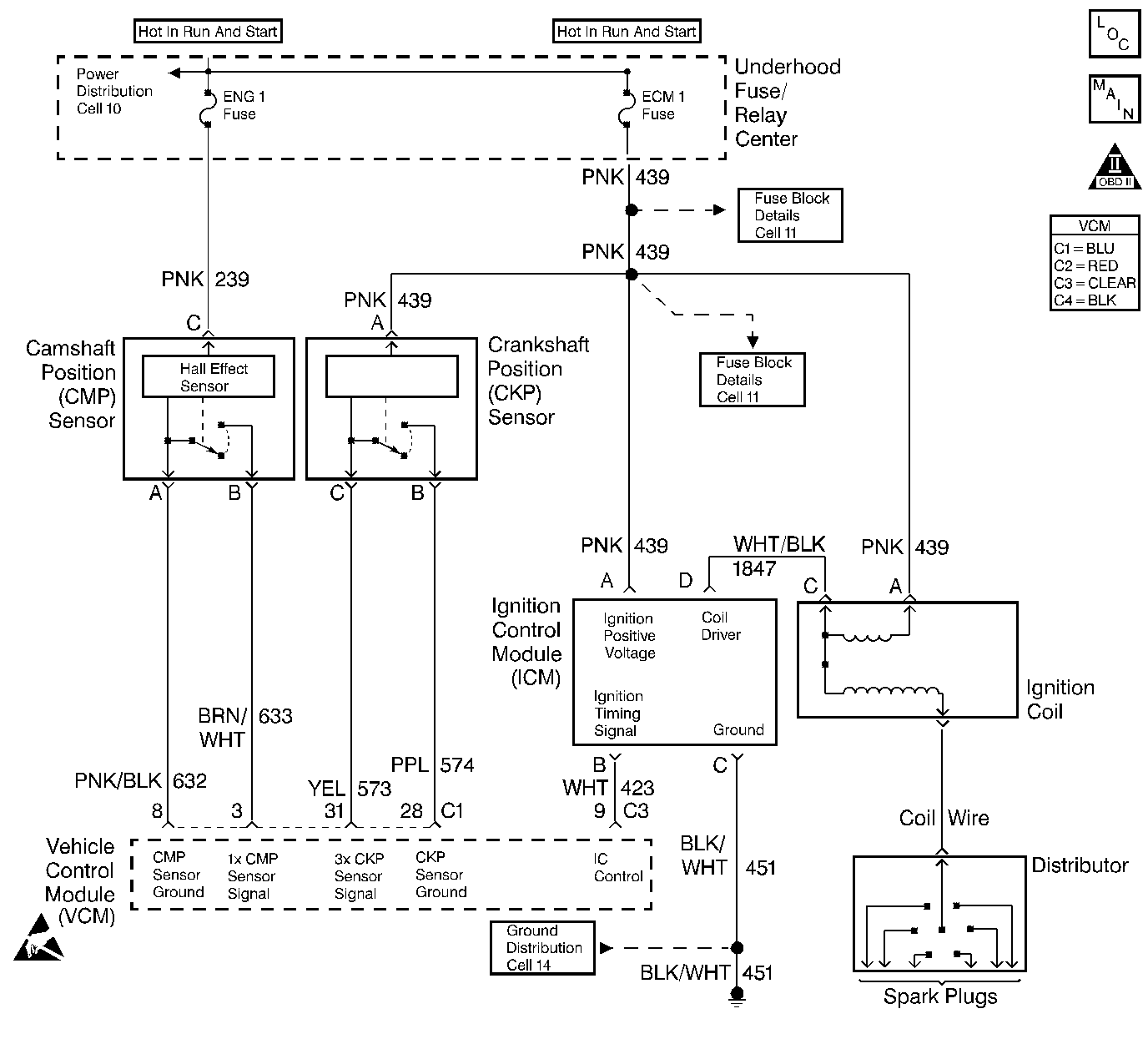
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is the primary input to determine if misfire is occurring. Engine misfire is detected by monitoring crankshaft speed variations between cylinders. If a crankshaft deceleration occurs during a combustion or power stroke, the control module will compare this change in crankshaft speed to the previous cylinder. If the crankshaft speed change is more than a maximum allowable speed, the misfire is detected. Misfire may occur in a specific cylinder or in all cylinders randomly.
When an engine is misfiring, brief decelerations in crankshaft rotational speed will be detected by the CKP. The control module determines which cylinder has misfired based upon the camshaft position (CMP) sensor input. Misfire data is stored for each cylinder in separate accumulators. After 100 combustion events, the misfire totals are compared to a calibrated maximum number. If the misfire is excessive, this diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Important: If start-up ECT is below -7°C (20°F), misfire detection is delayed until ECT is greater than 21°C (70°F). If start-up ECT is greater than -7°C (20°F), misfire detection begins after a 5 second delay.
| • | No active VS sensor DTCs |
| • | No active TP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active MAF sensor DTCs |
| • | No active CKP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active CMP sensor DTCs |
| • | The fuel level is greater than 10 percent |
| • | The engine speed is between 450-5,000 RPM |
| • | The system voltage is between 11-16 volts |
| • | The positive throttle position is steady within 2 percent for 100 ms |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The VCM detects a deceleration in the crankshaft speed characteristic of either an emission type misfire or a catalyst damaging type misfire.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
If the VCM determines that the engine misfire is significant enough to have a negative impact on emissions, the VCM turns ON the MIL after the misfire has been detected on 2 non-consecutive trips under the same operating conditions. If the misfire is severe enough that catalytic converter damage could result, the MIL flashes while the misfire is present.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
The Misfire Index counts the number of misfires. The scan tool can monitor the Misfire Index. There is a current and history misfire counter for each cylinder. Use the current misfire counter in order to determine which cylinder is misfiring, or use the history misfire counter for misfires that are not currently present.
Many different condition could cause an intermittent misfire.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Check the IC control circuit for an intermittent short to ground. |
| • | Check the spark plug wires and the coil wire for the following conditions: |
| - | Ensure that the spark plug wires are securely attached to the spark plugs and the distributor cap. |
| - | Check the wire routing in order to ensure that crossfiring is not occurring. |
| - | If the misfire occurs when the weather is damp, the problem could be due to worn plug wires. |
| - | Test for this condition by spraying the wires with water while the is engine running. Watch for spark to jump from the wires. If a spark is visible, replace the wires. |
| • | Check for contaminated fuel, or a low fuel level. Inspect the fuel for the following conditions: |
| • | Check the fuel condition and quality. Dirty or contaminated fuel could cause a misfire condition. |
| • | If the fuel level is low, contaminants in the bottom of the fuel tank could enter into the fuel metering system. |
| • | For more information, refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis . |
| • | Sticking intake or exhaust valves on an engine with a misfire when cold. |
| • | Check HO2S for abnormal voltage readings. |
| • | Check for a vacuum leak as a possible cause of the engine misfire. |
For more information, refer to fuel supply system.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If DTCs P0337 (Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Input) or P0338 (Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit - High Input) are set, this could result in a misfire condition.
-
In order to duplicate the conditions under which the misfire occurred, it may be necessary to drive the vehicle and monitor the scan tool DTC Set This Ignition Cycle variable.
-
When checking the spark at the spark plug wires, the spark should be consistent. A few sparks then nothing is no spark.
-
At this point, the ignition system is OK and the problem may be in the fuel system or an engine mechanical problem.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, record the Freeze Frame and the Failure records for reference with a scan tool. This data will be lost when you use the Clear DTC Information function. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
Install the scan tool. Review the Failure Records data. Are there any other DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | ||||||||||
3 | Perform the CKP System Variation Learning Procedure. Refer to Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn . Is the action complete? | -- | ||||||||||
4 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||||||||||
Duplicate the conditions when the misfire occurred, using the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records, . Does the scan tool indicate this DTC failed this ignition? | -- | |||||||||||
6 |
Are all of the misfire counters increasing. | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
Does the tester indicate spark is consistent on all tested ignition wires? | -- | |||||||||||
8 | Remove the spark plug(s) from the cylinder(s) that indicate a misfire and check for the following conditions:
Are any of the listed conditions present? | -- | ||||||||||
Check the spark plug(s) for the following:
Are any of the listed conditions present? | -- | Go to Engine Mechanical | ||||||||||
10 | Perform a cylinder compression test. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Engine Mechanical | |||||||||
11 |
Did the misfire(s) change cylinder(s)? | -- | ||||||||||
12 |
Does the lamp flash on all tested circuits while cranking the engine? | -- | ||||||||||
13 | Misfire is intermittent. Are any additional DTC's stored? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
14 | Replace the spark plugs. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
15 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||
16 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTC's? | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
