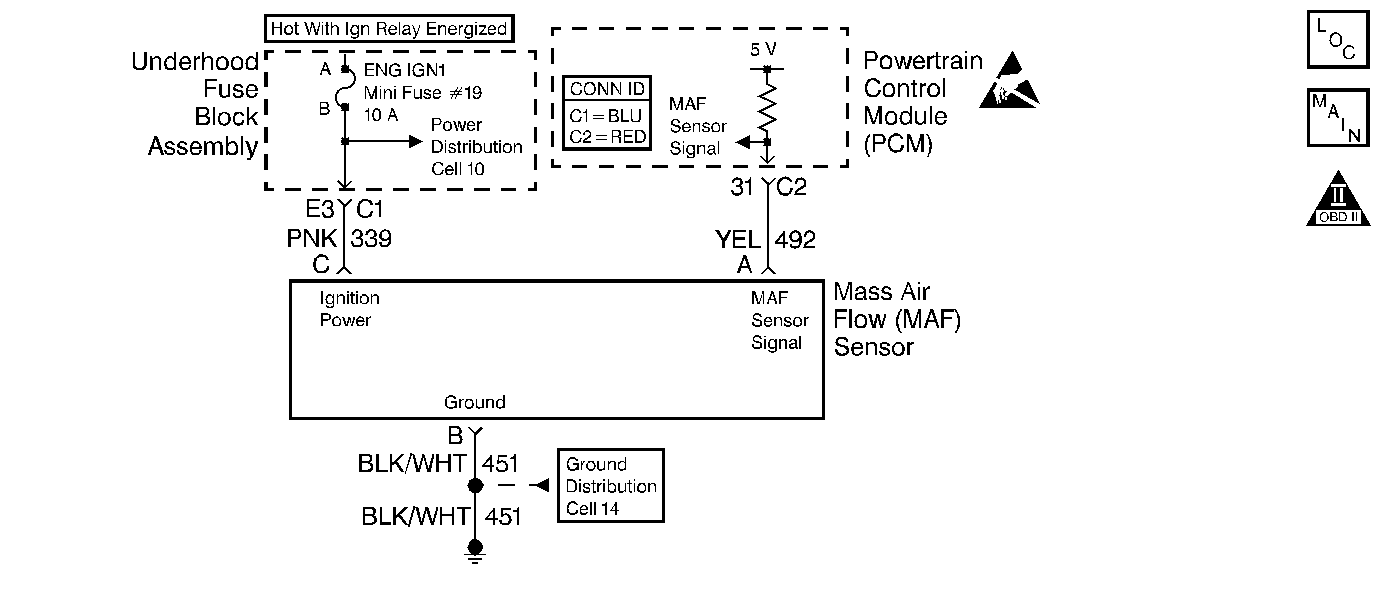
Circuit Description
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air ingested by the engine. The direct measurement of the air entering the engine is more accurate than calculating the airflow from the MAP, the IAT and the engine speed (speed/density). The MAF sensor has a battery feed, ground, and a signal circuit.
The MAF sensor used on this engine is a hot wire type. This engine uses the MAF sensor to measure air flow rate. The MAF output frequency is a function of the power required to keep the air flow sensing elements (hot wires) at a fixed temperature above the ambient temperature. Air flowing through the sensor cools the sensing elements. The amount of cooling is proportional to the amount of air flow. The MAF sensor requires a greater amount of current in order to maintain the hot wires at a constant temperature as the air flow increases. The MAF sensor converts the changes in current draw to a frequency signal read by the PCM. The PCM calculates the air flow (grams per second) based on this signal.
The PCM monitors the MAF sensor frequency. The PCM can determine if the sensor is stuck low, stuck high, not providing the airflow value expected for a given operating condition, or that the signal appears to be stuck based on a lack of signal variation expected during the normal operation. This diagnostic monitors for too low of an airflow rate. When the PCM detects that the MAF sensor frequency is below a predetermined value, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is operating greater than 0.5 second. |
| • | The engine is at least 300 RPM. |
| • | The ignition voltage is at least 8.0 volts. |
| • | All conditions stable for 2.0 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The Mass Air Flow frequency is less than 10 Hz. |
| • | All conditions met for greater than 1.0 second. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure records. |
| • | The PCM utilizes speed density (RPM, MAP, IAT) for fuel management. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM\TAC module connector surfaces before
servicing the PCM\TAC module. Inspect the PCM\TAC module connector gaskets
when diagnosing/replacing the modules. Ensure that the gaskets are installed
correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion into the PCM\TAC
modules. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component
harness connector, use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616
. Using this kit prevents damage
to the harness/component terminals. Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
| • | The following may cause an intermittent: |
| - | Poor Connections; Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
| - | Mis-routed harness |
| - | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| - | Broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Any un-metered air may cause this DTC to set. Inspect for the following: |
| - | An engine vacuum leak |
| - | The PCV system for vacuum leaks |
| - | An incorrect PCV valve |
| - | The engine oil dip stick not fully seated |
| - | The engine oil fill cap loose or missing |
| • | For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests whether the MAF sensor ignition feed circuit is shorted to a ground. If the fuse is open, repair the circuit as necessary and replace the fuse.
-
Monitoring the MAF sensor frequency will determine if the fault is present or the malfunction is intermittent.
-
Using the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This isolates when the DTC failed.
-
This step tests whether the 5.0 volts is available to the MAF sensor signal circuit.
-
This step tests if the signal circuit is shorted to another 5.0 volt reference circuit. If another DTC sets, repair the circuits that are shorted together. If no DTCs set it may be necessary to road test the vehicle.
-
Inspect the fuse 19 for being open. If the fuse is open, inspect the MAF sensor ignition feed circuit for a short to ground.
-
This step verifies whether B+ is available to the MAF sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Is the ENG-IGN1 fuse open? | -- | |||
Is the MAF sensor frequency below the specified value? | 10 Hz | |||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5V | |||
|
Important: If the engine does not start when the MAF sensor signal circuit is grounded, and no additional DTC sets, monitor the scan tool parameters for a sensor value that is not within range. This will aid in locating a short to another 5.0 volt circuit.
Do any additional DTCs set? | -- | |||
7 | Attempt to start and idle the engine. Do any additional DTCs set? | -- | ||
8 |
Does the DMM display a voltage? | -- | ||
9 |
Does the DMM display OL? | -- | ||
10 | Test for continuity of the MAF sensor signal circuit to battery ground using the DMM J 39200 . Refer to Testing for Continuity in Wiring Systems. Does the DMM display OL? | -- | ||
Does the DMM display OL? | -- | |||
Connect the test lamp J 35616-200 between the MAF sensor ignition feed circuit and the ground at the MAF sensor harness connector. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||
13 | Connect the test lamp J 35616-200 between the MAF sensor ignition feed circuit and the battery ground. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||
14 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
15 | Repair the short to voltage in the MAF sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Repair the open in the MAF sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
17 | Repair the short to ground in the MAF sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
18 | Repair the circuits that are shorted together. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
19 | Repair the MAF sensor ground circuit for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
20 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
21 |
Does the DMM display continuity from the MAF signal circuit to any other circuit? | -- | ||
22 | Repair the circuits that are shorted together between the MAF sensor signal circuit and the circuit for which the DMM displayed continuity. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
23 | Replace the MAF sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
24 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
25 |
Important: Program the replacement PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module/Throttle Actuator Control Module Replacement . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
26 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
27 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
