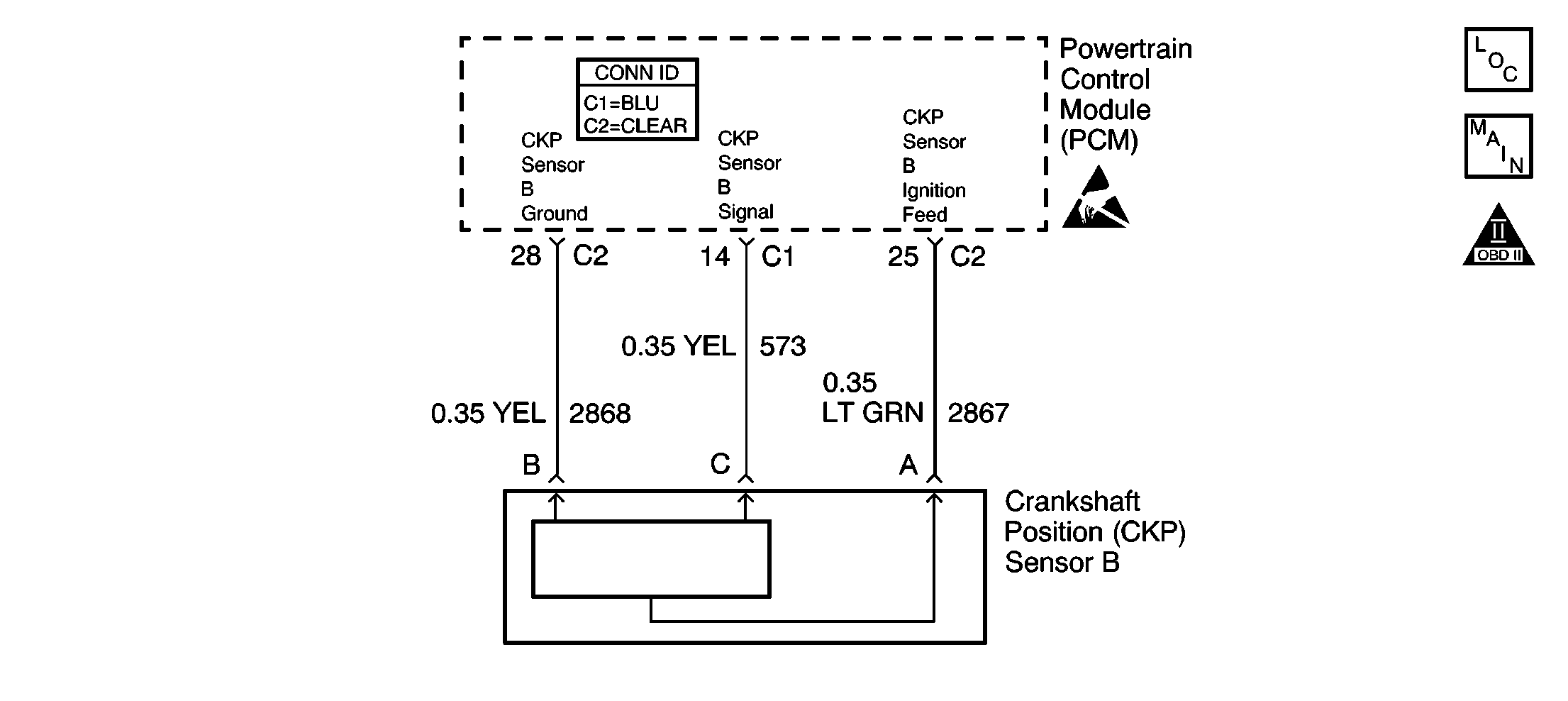
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) uses dual crankshaft position (CKP A and CKP B) sensors to determine crankshaft position. The PCM supplies an ignition voltage and a ground for each sensor. During engine rotation, a slotted ring, machined into the crankshaft, causes the sensors to return a series of ON and OFF pulses to the PCM. The PCM uses these pulses to decode the position of the engine crankshaft.
The PCM uses two basic methods of decoding the engine position: Angle Based; and Time Based (using either CKP A or CKP B sensor input). During normal operation, the PCM uses the angle based method. In order to operate in this mode, the PCM must receive signal pulses from both CKP sensors. The PCM uses the signal pulses to determine an initial crankshaft position, and to generate MEDRES (24X reference) and LORES (4X reference) signals. Once the initial crank position is determined, the PCM continuously monitors both sensors for valid signal inputs. As long as both signal inputs remain, the PCM will continue to use the angle based mode.
When either CKP signal is lost, the PCM will compare the MEDRES signal to the camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal. If the PCM detects a valid CMP signal, and the MEDRES to CMP signal correlation is correct, the PCM determines that CKP sensor A is at fault. However, if the MEDRES to CMP correlation is incorrect, the PCM determines that CKP sensor B is at fault. If the PCM determines that CKP sensor B is at fault, DTC P0385 will set. The PCM will switch from angle based mode to Time Based mode A using CKP sensor A signal input.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Engine speed is more than 20 RPM . |
| • | MAF is more than 2.5 gps. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects a loss of CKP sensor B signal.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM stores the conditions present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
If the condition is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Ignition system DTCs set with the ignition switch in the START position if the starter relay or the starter is inoperative. When the PCM enables starter operation, the PCM also initiates the diagnostic test routines for DTCs P0335, P0340, and P0385. If a condition exists which prevents the engine from cranking, the PCM will not receive signal input from the CKP and CMP sensors, and the DTCs will set.
If DTC P0615 is set, diagnose DTC P0615 first. If DTC P0335, P0340, and/or P0385 are set and no trouble is found, check for the following:
| • | Is there a no-crank condition or an intermittent no-crank condition? |
| • | Was an attempt made to crank the engine with the shift lever not in P/N? |
Procedures for Selecting Crank Position Sensing Decode Mode
When diagnosing the crankshaft position sensors, it may be necessary to enable a specific decode mode (Angle, Time A, or Time B). To enable a specific crank decode, using the scan tool, perform the following steps:
| • | Turn the ignition to the RUN/ON position. |
| • | Select Engine Output Controls. |
| • | Select Crank Position Sensing Decode Mode. |
| • | Select the desired mode (Angle, Time A, or Time B) and press SELECT STATE. |
| • | Command the decode mode by pressing COMMAND STATE. |
The commanded state remains valid for the current ignition cycle. A specific decode mode can not be commanded with the engine running, or after commanding a desired decode mode. To command a different decode mode, you must cycle the ignition OFF and ON.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||
2 |
Important:
Does the scan tool indicate the CKP Sensor Status as ANGLE? | -- | ||||||||||||
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate a CKP Sensor Status change to TIME A or an engine stall occur? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||
4 |
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | ||||||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
6 |
Does the scan tool indicate an RPM while repeatedly touching sensor signal circuit? | -- | ||||||||||||
7 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
9 | Replace the CKP Sensor B. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
10 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
11 |
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P0385 passed? | -- | System OK |
