Circuit Description
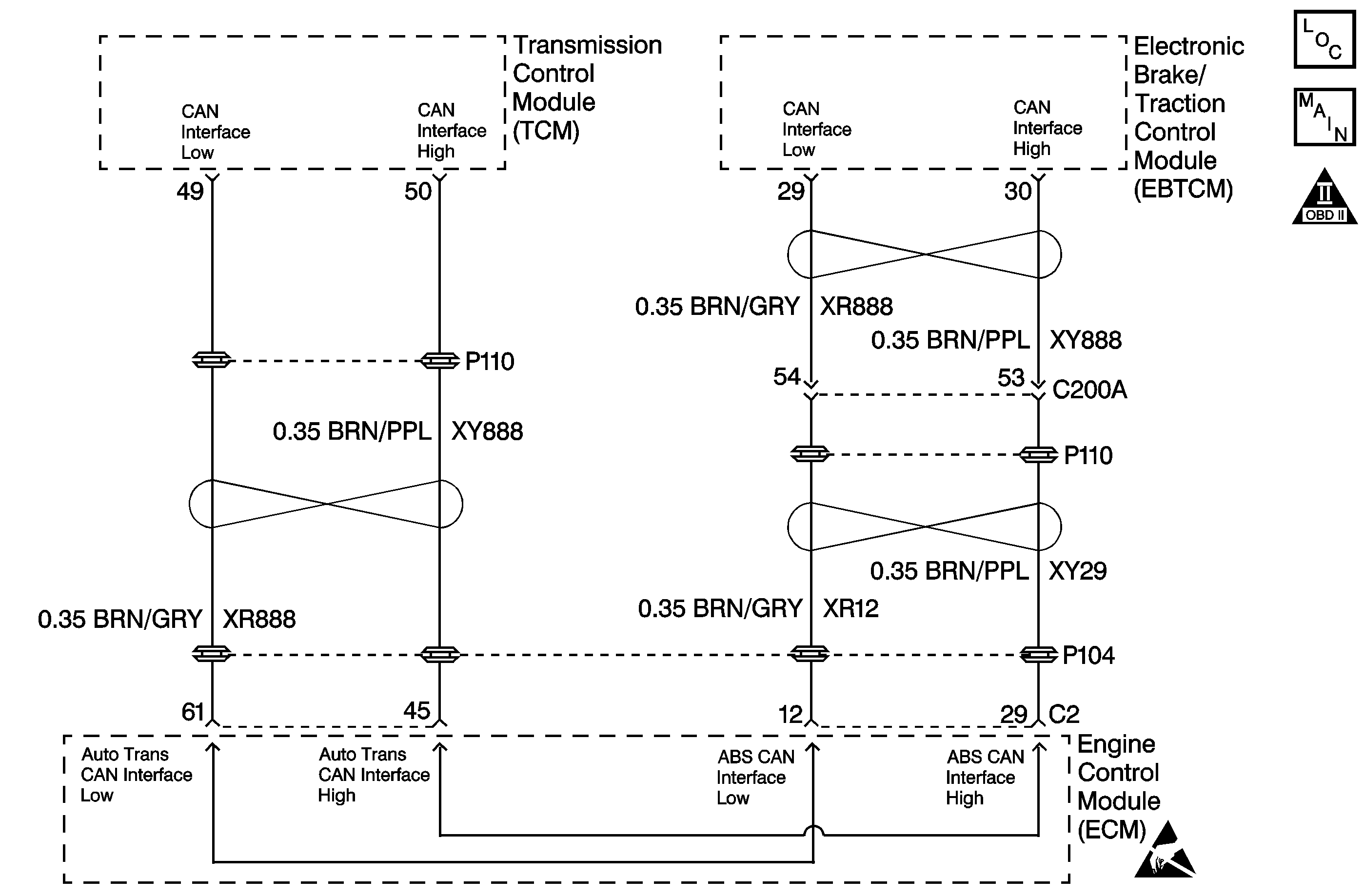
The controller area network (CAN) is used to receive and transmit data between the engine control module (ECM), the electronic brake/traction control module (EBTCM), and the transmission control module (TCM) . Each module sends signals by toggling the circuit either high or low to produce pulse-width signals, which the other modules decode. Circuits XR888 and XY888 are the CAN information lines used to transmit the data between the modules.
The CAN data stream contains status messages for relevant operating parameters, as well as state-of-health messages.
When the TCM detects the loss of communication on either CAN bus line for a specified amount of time, then DTC U2100 will set. DTC U2100 is a type B DTC.
Condition for Running the DTC
The ignition switch is in the RUN position.
Condition for Setting the DTC
The TCM detects the loss of communication on either CAN bus line for 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The TCM flashes the sport mode lamp and sends a MIL request to the ECM on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | The ECM records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame at the time of the MIL request from the TCM. |
| • | The transmission operates in the default mode (maximum line pressure, command 4th gear, inhibit TCC, freeze shift adapts). |
Conditions For Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns off the MIL after three consecutive drive trips during which the TCM sends no MIL request. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are present by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
| • | The TCM cancels the DTC default mode actions when the ignition switch is Off long enough in order to power down the TCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the J 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the TCM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the TCM or at the component. Inspect the harness connectors for any backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems for proper procedure. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving any related connectors and any wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help to locate the fault. |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check in Engine Controls | |
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the Scan Tool in order to record the Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Failure Records from the ECM/TCM. Did DTC U2100 reset? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 |
Does the Scan Tool transmit live transmission data values? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
4 | Check circuit XR 888 and XY 888 for an short to ground. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Did you find the condition? | -- | ||
5 | Check circuit XR 888 and XY 888 for an open. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Did you find the condition? | -- | ||
6 | Repair the wiring as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
7 | Replace the TCM. Refer to Transmission Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
8 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Does the Scan Tool transmit live transmission data values? | -- | System OK |
