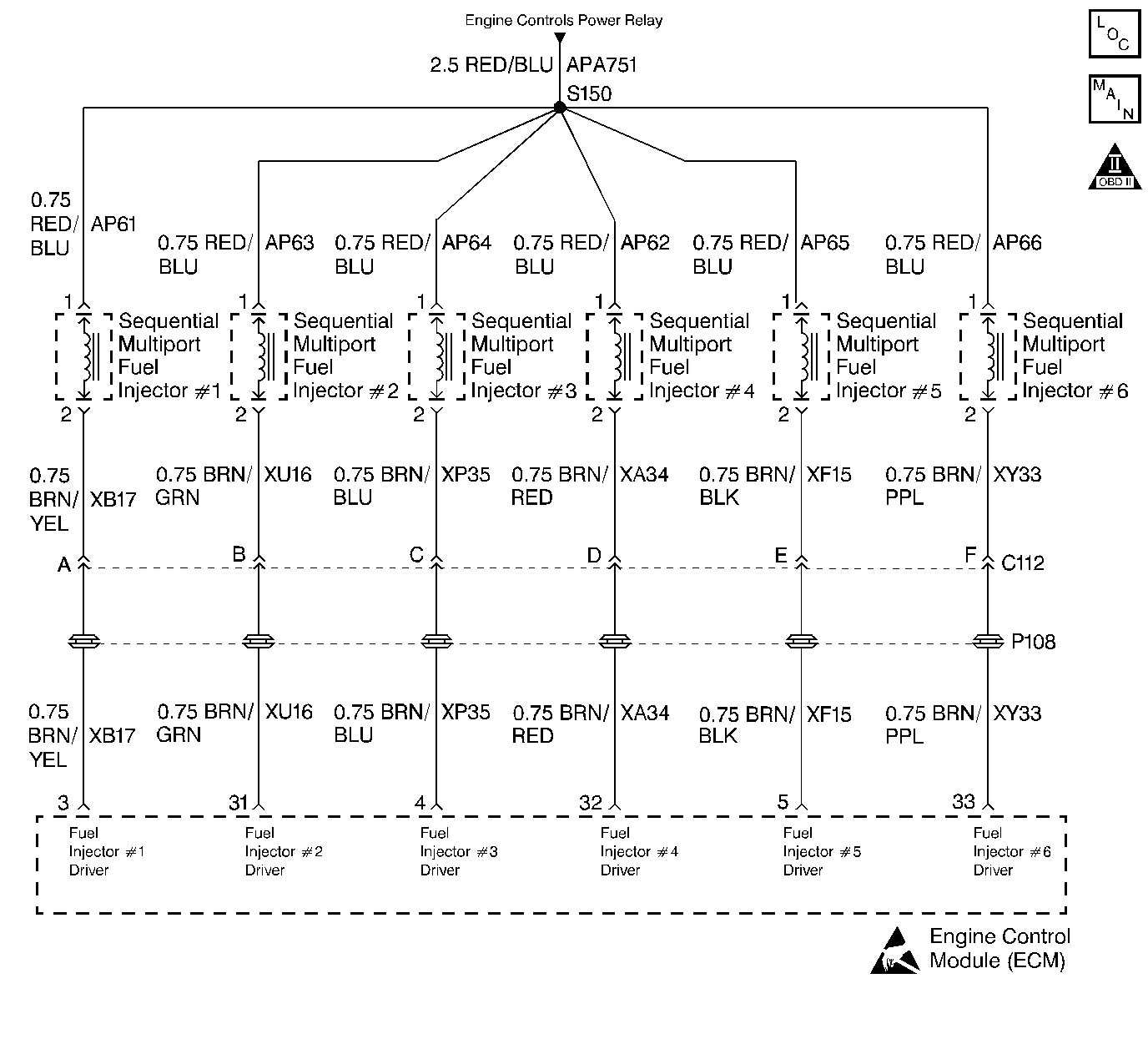
Circuit Description
The ECM will enable an injector on the intake stroke of each cylinder. Each individual cylinder fuel control is referred to as Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection (SFI).
The ignition voltage is supplied directly to the fuel injectors. The ECM controls each injector by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called a driver. The primary function of the driver is to supply the ground for the component being controlled. Each driver has a fault line which is monitored by the ECM. When the ECM is commanding a component on, the voltage of the control circuit should be low (near 0 volts). When the ECM is commanding the control circuit to a component off, the voltage potential of the circuit should be high (near battery voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage other than what is expected, this DTC will set.
The ECM will monitor the injector circuit for the following:
| • | Short to ground |
| • | Short to voltage |
| • | Open circuit |
| • | An internally shorted or excessively low resistance injector |
When the ECM detects any of the above malfunctions, this DTC will set and the affected driver will be disabled. The ECM will continue to test the circuit and if the fault goes away the driver will be reactivated.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition voltage is between 9.0 and 17.0 volts. |
| • | The engine speed is greater than 80 RPM. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
An injector circuit fault is detected.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616 for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the ECM or at the component. Inspect the harness connectors for any backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. Refer to Engine Control Module Diagnosis for the proper procedure. |
| • | Misrouted harness. Inspect the harness in order to ensure that the harness is not routed too close to high voltage wires such as the spark plug leads, or too close to any high current devices such as the alternator, the motors, the solenoids etc. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving the related connectors and the wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help in order to locate the fault. |
Refer to Symptoms for the Intermittents.
The number(s) below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Determines if a malfunction is present.
-
The main injector connector is located at the back of the intake plenum toward Bank 2.
-
If the Switched B+ circuit is restored, and the power feeds through the circuit and back to the test light, circuit continuity is verified. Replace the inoperative fuel injector.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | ||||||||
Is the counter incrementing? | 90°-110°C | Problem is intermittent. Refer to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Is the test light illuminated? | -- | |||||||||
4 |
Is the test light illuminated? | -- | ||||||||
5 |
Is the test light illuminated? | -- | ||||||||
6 | Crank the engine. Does the test light blink (approximately once per second)? | -- | ||||||||
Is continuity indicated? | -- | |||||||||
8 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
9 | Check for the following conditions:
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||
10 | Repair the open/high resistance injector control circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
11 | Repair the injector control circuit shorted to ground. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
12 | Repair the injector driver circuit shorted to voltage. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
13 | Replace the fuel injector. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
14 | Check for a poor connection or poor terminal tension at the ECM harness connector. Refer to Electrical Diagnosis in Engine Electrical, and Troubleshooting Procedures for the proper procedure. Also, refer to Checking Terminal Contact in Engine Control Module Diagnosis . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||
15 |
Important: This vehicle is equipped with a Theft Deterrent System which interfaces with the Engine Control Module (ECM). Program the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
16 |
Is this DTC set? | -- | ||||||||
17 | Were there any additional DTCs noted during the Powertrain OBD System Check that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | The System is OK |
