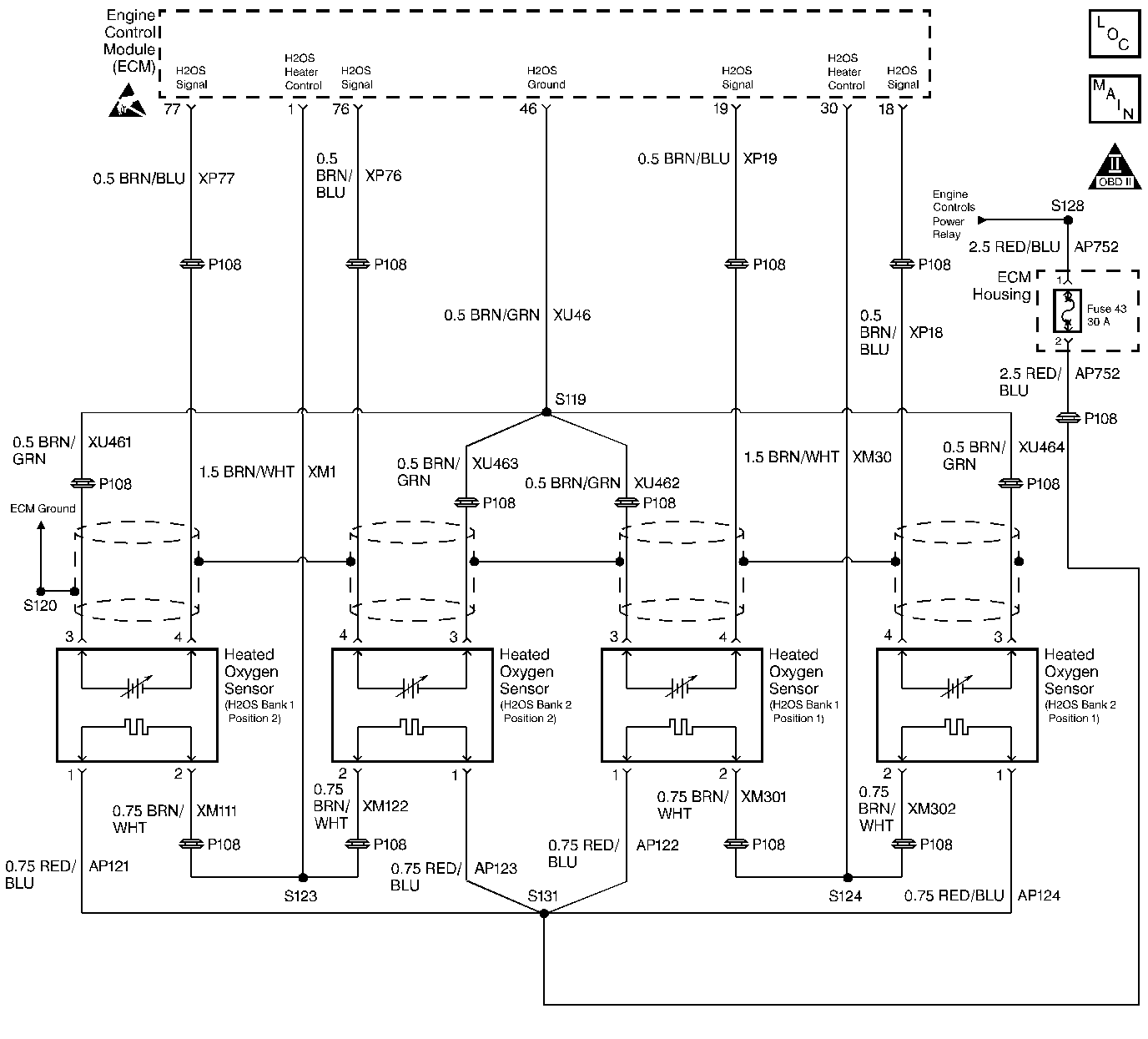
Circuit Description
Using the heated oxygen sensors for fuel control decreases the amount of time required to enter the Closed Loop operation. The heated oxygen sensors use the post-catalyst in order to ensure that a sufficient amount of heat is maintained for more accurate catalyst monitoring.
When the HO2S is cold, the signal voltage at the ECM is approximately 450 mV. When the ignition is turned to the on position, the Switched B+ is supplied to the HO2S heaters via the Engine Controls Power Relay. The ECM controls the heater operation by first modulating the ground circuit when the sensors are cold, and then turning the heaters on continuously after a predetermined amount of time. This prevents the possibility of thermal shock to the sensors by controlling the sensor's rate of heating. As the heater reaches the operating temperature, the HO2S voltage responds by changing from the bias voltage range to the normal operation. On a cold start, the ECM will track how much time the HO2S voltage takes to go above or below the bias range threshold. If the ECM determines that the HO2S voltage takes too much time to enter the normal operating range, this DTC will set. The time it takes the HO2S to reach the normal operating temperature is based on the amount of air that flows into the engine and the start-up coolant temperature.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is running at the normal operating temperature. |
| • | The above conditions continuously are present for 180 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM calculated HO2S heater resistance is greater than 9.56 ohms or less than 2.45 ohms.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616 for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals. |
| • | Heated oxygen sensor wiring. Check for the following conditions: |
| - | The sensor pigtail or the harness may be mis-positioned and contacting the exhaust system. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wire connection |
| • | Corrosion and water intrusion |
| • | Refer to Electrical Diagnosis in Engine Electrical, Checking Terminal Contact for proper procedure. An oxygen supply inside the HO2S is necessary for proper operation. This supply of oxygen is provided through the HO2S wires. All of the HO2S wires and connections should be inspected for any breaks or any contamination. If any wiring repairs need to be made, refer to Electrical Diagnosis in Engine Electrical, Electrical Diagnosis, Repair Procedures. |
| • | If the above are OK, the HO2S may have an intermittent fault. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The lamp may flash on and off if the operating conditions are correct for the ECM to be modulating the control circuit. This still indicates that the control circuit and the ECM are functioning. The engine must be running before the ECM will ground the control circuit.
-
The feed circuit to the HO2S heater fuse is actually the rest of the Switched B+ circuit from the Engine Controls Power Relay. Check for an open circuit between the feed side of the fuse and the splice in the harness. An inoperative Engine Controls Power Relay will cause a no-start and no MIL. If this is the case, go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | ||
2 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
4 | Check the HO2S heater fuse. Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
5 | With test light J 34142-B connected to ground, check for power at the HO2S fuse. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
6 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
7 | Measure the resistance of the front HO2S heaters at the sensor pigtail with the DVM J 39200 . Is the resistance of each heater greater than the specified value? | 4.0 Ohms | Refer to Diagnostic Aids | |
8 |
Is continuity indicated? | -- | ||
9 | Check for a poor connection or poor terminal tension at the HO2S harness connector. Refer to Electrical Diagnosis in Engine Electrical, and Troubleshooting Procedures for hte proper procedure. Also, refer to Checking Terminal Contact in Engine Control Module Diagnosis . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the HO2S. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Repair the open/high resistance Switched B+ circuit between the fuse and the HO2S. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Repair the feed circuit to the fuse. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
13 | Repair the short to ground in the Switched B+ circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Replace the HO2S with the low resistance heater. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 | Repair the open/high resistance Heater Control circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Check for a poor connection or poor terminal tension at the ECM harness connector. Refer to Electrical Diagnosis in Engine Electrical, and Troubleshooting Procedures for hte proper procedure. Also, refer to Checking Terminal Contact in Engine Control Module Diagnosis . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
17 |
Important: This vehicle is equipped with a Theft Deterrent System which interfaces with the Engine Control Module (ECM). Program the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
18 |
Is this DTC set? | -- | ||
19 | Were there any additional DTCs noted during the Powertrain OBD System Check that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | The System is OK |
