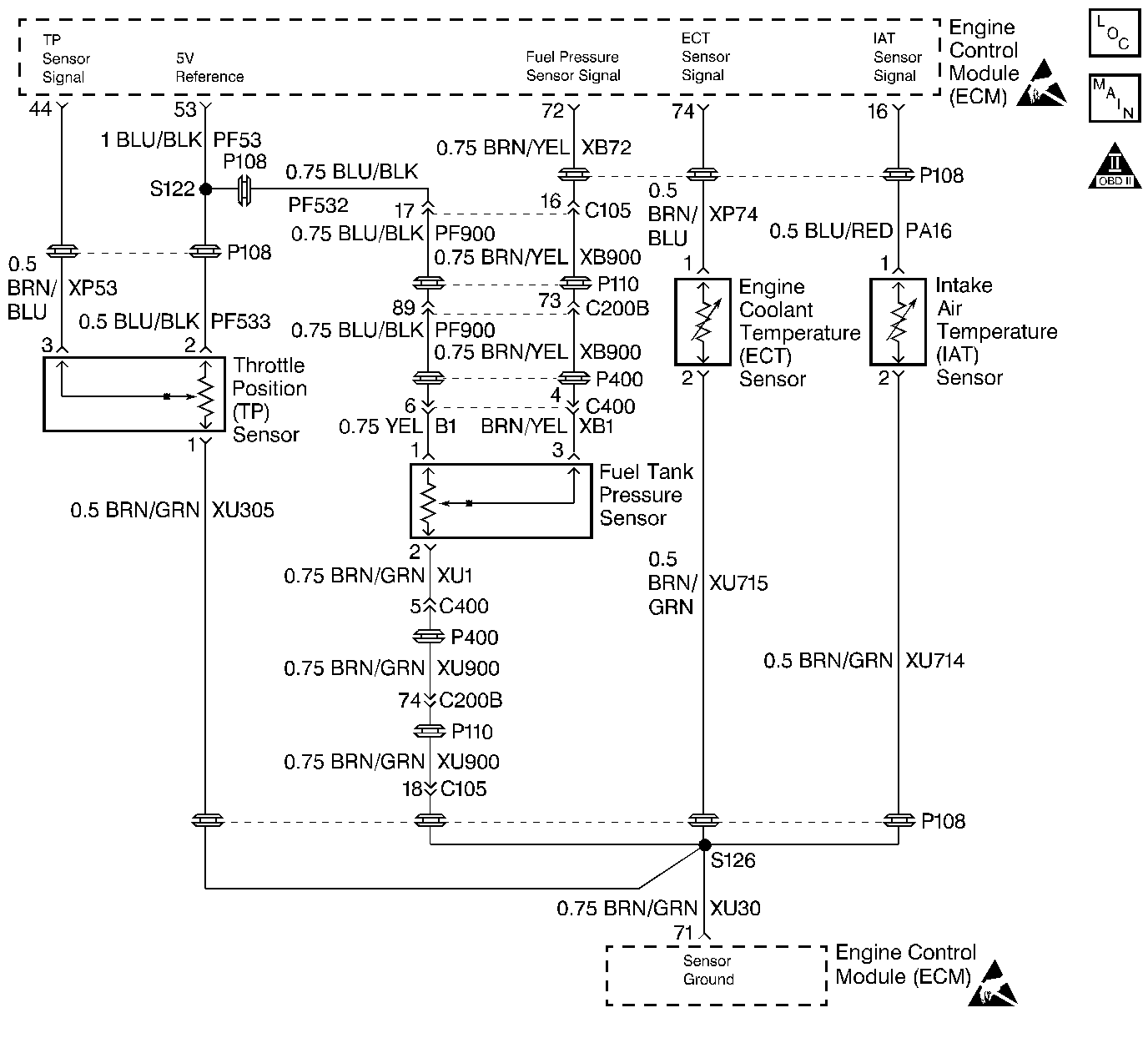
Circuit Description
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor contains a semiconductor device which changes the resistance based on temperature (a thermistor). The ECT sensor is located in the coolant crossover pipe at the center rear of the engine. The ECT sensor has a signal circuit and a ground circuit. The ECM applies a voltage (about 5.0 volts) on the signal circuit to the sensor. The ECM monitors any changes in this voltage caused by changes in the resistance of the sensor in order to determine the engine coolant temperature.
When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, and the ECM's signal voltage is only pulled down a small amount through the sensor to ground. Therefore, the ECM will sense a high signal voltage (low temperature). When the engine coolant is warm, the sensor resistance is low, and the signal voltage is pulled down a greater amount. This process causes the ECM to sense a low signal voltage (high temperature).
Conditions for Running the DTC
Engine running
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Difference between the calculated engine coolant temperature and the actual engine coolant temperature is greater than 20°C (11°F)
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616 for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Check the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the ECM or at the component. Inspect the harness connectors for the following: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection. |
| - | Refer to Engine Control Module Diagnosis , Checking Terminal Contact, for the proper procedure. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving any of the related connectors and the wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help in order to locate the fault. |
| If the sensor signal is only affected when the harness is moved at a component, and there is no problem with the harness or the connections, the component may be damaged. |
| • | Check for a stuck open thermostat. A stuck thermostat, during very cold ambient conditions, will cause the engine temperature to increase too slowly and could result in this DTC being set. |
| • | When checking the ECT sensor, the Temperature vs Resistance may be used in order to test the sensor at various temperature levels in order to evaluate the possibility of a shifted (mis-scaled) sensor. A shifted sensor could result in poor driveability complaints. |
| Refer to Symptoms for the Intermittents. |
| • | If other DTCs are set that share the same ground circuit, check the point where the circuits ground to the chassis or the engine block. |
If the engine has been allowed to sit overnight, the engine coolant temperature and the engine intake air temperature values should display within a few degrees of each other. If the temperatures are not within 3°C (5°F), refer to Temperature vs Resistance
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Determines if the ECM is capable of recognizing the changes in the circuit voltage.
-
Determines if the ECM is capable of recognizing the changes in the circuit voltage.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Is the ECT below the specified value? | -43°C (-45°F) | Go to DTC P0115 | ||
Is the ECT above the specified value? | 139°C (282°F) | Go to DTC P0115 | ||
4 | Replace the ECT sensor. Refer to Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
5 |
Is this DTC set? | -- | ||
6 | Were there any additional DTCs noted during the Powertrain OBD System Check that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | The System is OK |
