Refer to
EVAP and EGR Controls
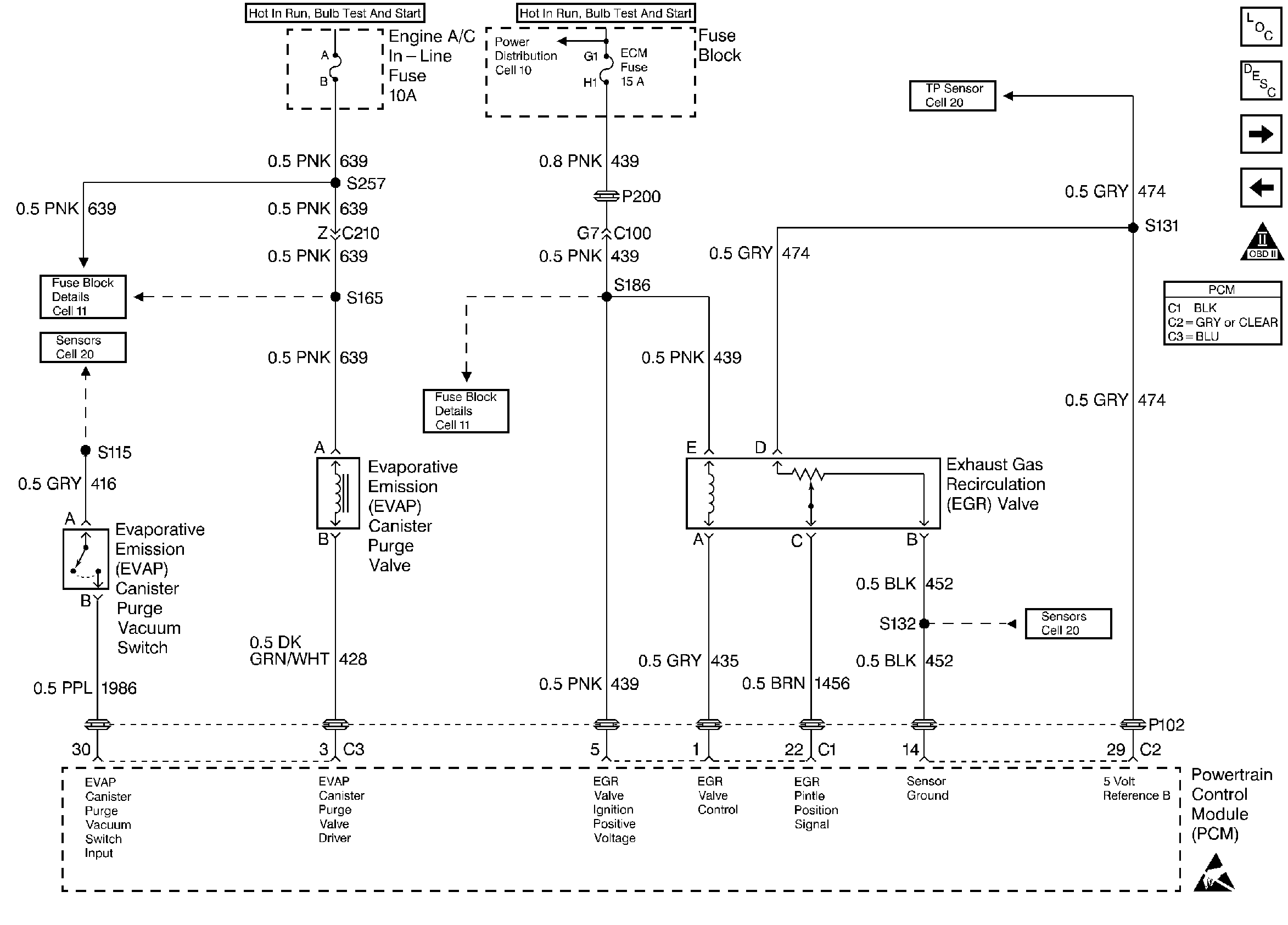
for wiring view.
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are reduced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with a PCM controlled pintle. The PCM controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors. The PCM then commands the EGR valve to operate when necessary by controlling a ground signal through the PCM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the Desired EGR Position. Ignition voltage is supplied to the valve through a fuse.
The PCM monitors the results of its command through a feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the EGR valve pintle position is sent to the PCM. This feedback signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR Position .
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTC's P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0200, P0300-P0304, P0335, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0502, P0503, P0506, P0507, and P1441 not set. |
| • | Engine speed is between 1000 and 2200 RPM (manual). |
| • | Engine speed is between 900 and 1800 RPM (automatic). |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than 80° C (176° F). |
| • | Barometric Pressure (BARO) is greater than 60 kPa. |
| • | Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) is between 13 and 32 kPa. |
| • | Idle Air Control (IAC) hasn't changed more than 5 counts. |
| • | Throttle Position less than 1 %. |
| • | Vehicle speed is above 20 MPH. |
| • | Decel EWMA is greater than +2 kPa. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) illuminates. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time when the diagnostic fails. This information stores in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The Decel EWMA (Exponentially Weighted Moving Average) value can be a great aid in determining if a problem exists and to verify repairs. The Decel EWMA is an average of the difference in the expected MAP change and the actual MAP change caused by opening the EGR valve during a deceleration, and is used to determine when the MIL is illuminated. By driving the vehicle up to approximately 60 mph (97 km/h) and decelerating to 20 mph (32 km/h), it can be determined if the EGR system is OK, partially restricted or fully restricted. |
| • | A more negative number (less than -3) indicates that the system is working normally whereas a positive number indicates that the system is being restricted and that the expected amount of EGR flow is incorrect. A number that falls between negative 3 and positive 2 indicates that the system is partially restricted but not restricted enough to fail. The Decel EWMA value should always be a -3 or lower. If the Decel EWMA number becomes more positive (towards 0 or more), then the EGR system is becoming restricted. Look for possible damage to the EGR pipe or for a restriction caused by carbon deposits in the EGR passages or on the EGR valve. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored on the scan tool for later reference.
-
Commanding the EGR valve open determines whether the EGR system is totally restricted or partially restricted.
-
Visually and physically inspect the EGR passages and valve for excessive carbon deposits or damage.
-
Be sure all gasket material is removed from the EGR mounting surface. Even a small amount of material may cause a DTC P0401 to set. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Replacement System for on vehicle service of the EGR valve.
-
This step verifies if the fault is present and also verifies if a repair corrected the problem. Refer to Diagnostic Aids for an explanation on Decel EWMA. If the Decel EWMA value stays near 0 or a positive number after several tests have been run, then a small restriction may still exist. Be sure to check the EGR pipe for damage or dents and the EGR valve for any excessive carbon build up. Only 1 test per ignition cycle will run unless a DTC P0401 has been cleared or the battery has been disconnected.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||
Does the engine stall or attempt to stall? | 50 % | |||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
Replace the EGR valve. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
|
Caution: Perform this step ONLY in an area where the vehicle can be operated as described without risk to other vehicles or passengers.
Is the Decel EWMA value greater than the specified value? | 10 seconds 60 mph (97 km/h) 20 mph (32 km/h) 0 | |||
6 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | ||
7 | Check if any additional DTC's are set. Are any DTC's displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
