Refer to
Power, Ground, MIL, and DLC
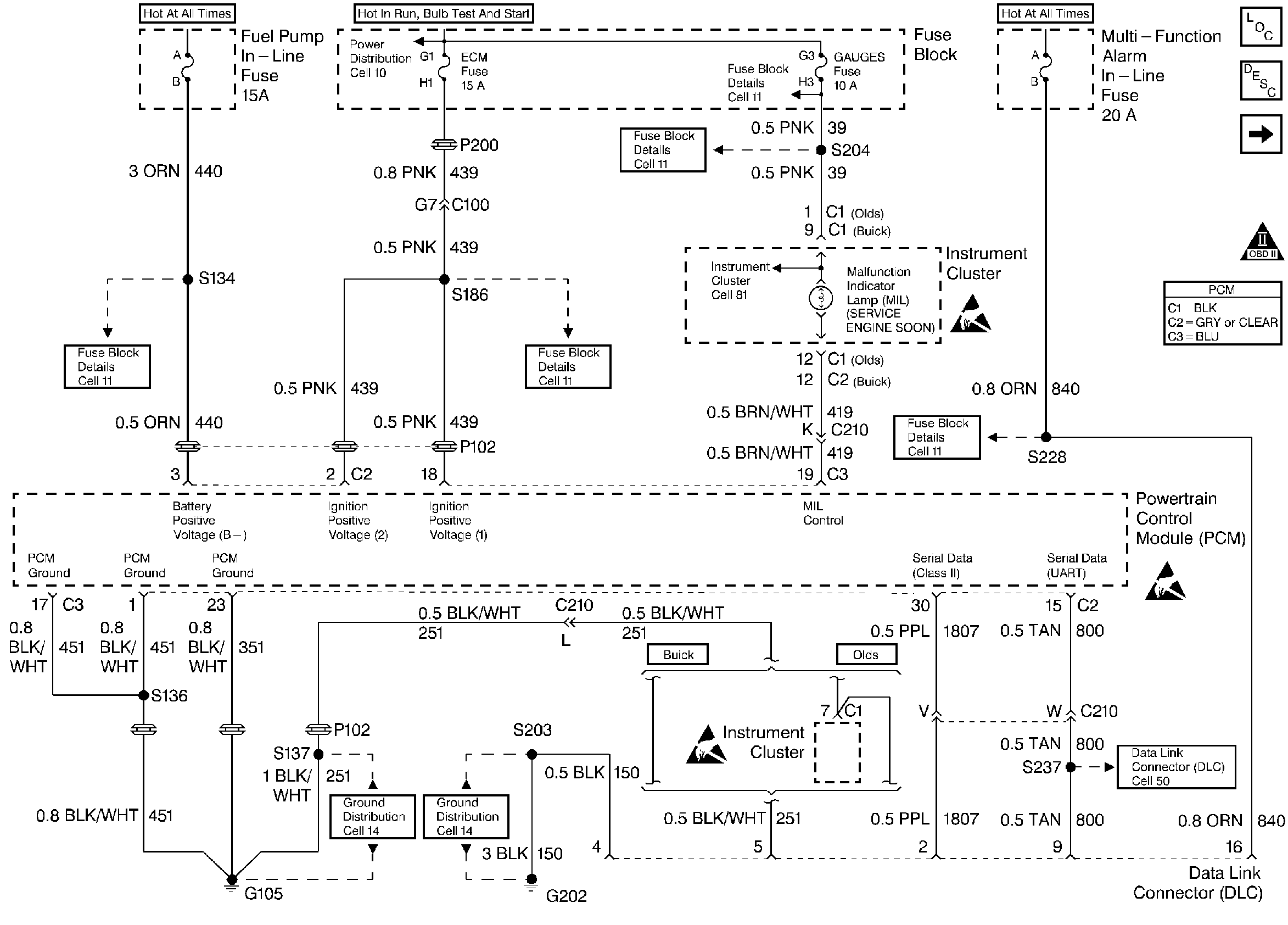
for wiring view.
Circuit Description
Important: Do not perform this check if no driveability complaint exists.
The Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check is an organized approach to identifying a problem created by an electronic engine control system malfunction. The Powertrain OBD system check is the starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. This directs the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. Understanding the table and using it correctly will reduce diagnostic time, and prevent the replacement of good parts.
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Do not clear DTCs unless directed by a diagnostic procedure. Clearing DTCs will also clear valuable freeze frame and failure records data.
| • | Check for any published service bulletins relating to exhibited symptoms or component operation. |
| • | Inspect all related wiring and connections at the PCM. These may cause an intermittent malfunction. |
| • | Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing an intermittent complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminals to wiring connections |
| - | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| - | Corrosion |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
When the ignition is initially turned ON, the MIL will momentarily flash ON then OFF and remain ON until the engine is running if no Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) are stored.
-
The diagnostic tables in this section are designed for use with a properly functioning scan tool. Serial data communication must be corrected before beginning any other diagnostic procedures. Class ll Serial Data will not transmit if the system voltage is below 9.0 volts or above 16.0 volts.
-
If multiple DTC's are stored, refer to the DTC Tables in the following order:
-
By storing the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool, an electronic copy of the data is created when the fault occurred and stored on the scan tool which can be referred to later. Type D DTC's do not store freeze frame data. If this option is not available, manually record the information for later reference.
-
After the engine is at normal operating temperature, comparison of actual control system data with the typical values is a quick way to determine if any parameter is not within limits. Keep in mind that a base engine problem (i.e. advanced cam timing) may substantially alter sensor values.
Check the following sensors for proper operation:
| • | PCM Error DTC's. |
| • | System voltage DTC's. |
| • | Component level DTC's (DTC's that indicate a faulty part). |
| • | System level DTC's (DTC's that indicate a system fault). |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor for initial coolant temperature reading close to ambient, then observe the raise in temperature to operating temperature while the engine is warming up. |
| • | Throttle Position (TP) sensor for proper sweep from 0% to 100%. |
| • | Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor for quick changes during changes in various engine loads. |
| • | The Oxygen Sensor (O2S 1) for proper rich/lean and lean/rich sweeps operation. |
| • | The Idle Air Control (IAC) valve for proper idle control and observe for proper transition while operating high load components such as a/c control. |
| • | Checking the sensors for proper operation during warm up can be a crucial step in correctly diagnosing any driveability concern. Careful observation of these sensors during engine warm up may reveal a slow responding sensor or a sensor that malfunctions only within a small portion of its range. |
| • | Check for any published service bulletins relating to exhibited symptoms or components operation. |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Is the MIL ON? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool display PCM data? | -- | |||
3 | Using the scan tool, command the MIL OFF. Does the MIL turn OFF? | -- | ||
Check for DTC's with the scan tool. Were any last test fail, history, or MIL request DTC's set? | -- | |||
Using a scan tool, record the freeze frame and failure records information. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | -- | |
6 | Does the engine start and continue to run? | -- | ||
Are the display values normal or within typical ranges? | -- | Go to Symptoms | Go to the applicable diagnostic section |
