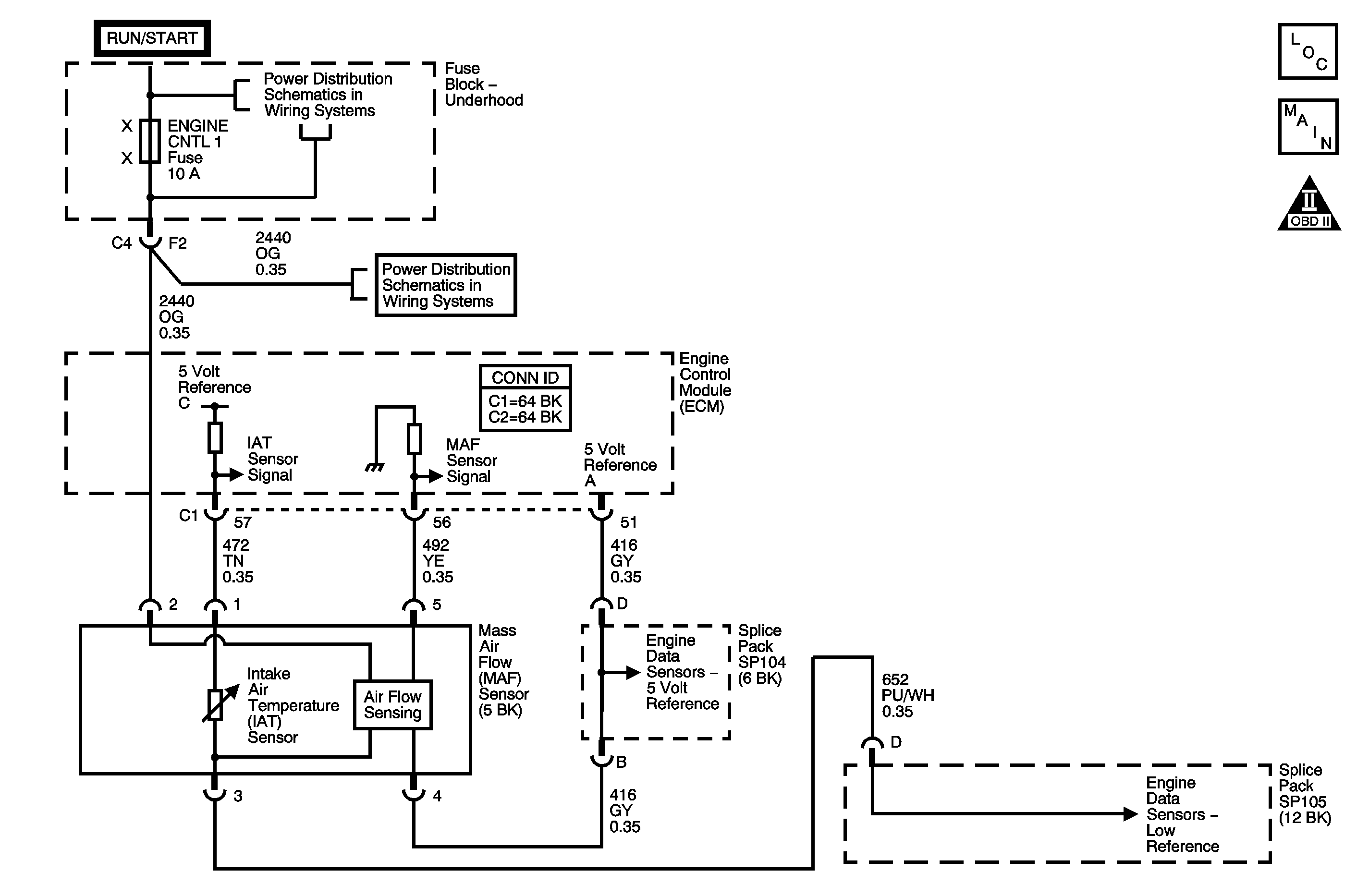
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is an air flow meter that measures the amount of air entering the engine. The engine control module (ECM) uses the MAF sensor signal in order to provide the correct fuel delivery for a wide range of engine speeds and loads. The MAF sensor signal is a function of the current required to keep the air flow sensing element at a fixed temperature. The air flowing through the sensor cools the sensing element. The amount of cooling is proportional to the amount of the air flow. As the air flow increases, more current is required in order to maintain the hot elements at a constant temperature. The MAF sensor converts the changes in current to a voltage signal that is read by the ECM. The ECM calculates the air flow based on this voltage signal. The MAF sensor uses the following circuits in order to operate:
| • | The ignition 1 voltage |
| • | The 5-volt reference |
| • | The MAF sensor signal |
| • | The low reference |
The 5-volt reference for the MAF sensor is also supplied to additional sensors. For two of the sensors the voltage is supplied on separate ECM terminals. The other sensors are connected at a splice pack. The 5-volt reference is shared by the following sensors:
| • | The MAF sensor |
| • | The camshaft position (CMP) sensor |
| • | The accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor 1 |
| • | The fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor |
| • | The air conditioning (A/C) refrigerant pressure sensor |
The low reference circuit of the MAF sensor is shared at a splice pack with the following components:
| • | TP sensor 1 |
| • | TP sensor 2 |
| • | The camshaft position (CMP) sensor |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
If the ECM detects the MAF sensor signal is more than the possible range of a properly operating sensor DTC P0103 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223 are not set. |
| • | The engine is running for more than 0.5 second. |
| • | The ignition 1 signal is more than 11 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The ECM detects that the MAF sensor signal is more than 4.8 volts for more than 2 seconds. |
| OR |
| • | The MAF sensor signal is more than a calculated value using throttle position (TP) and engine speed. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect for the following conditions: |
| - | A high resistance on the low reference circuit of the MAF sensor may cause this DTC to set intermittently and also result in poor engine performance. |
| - | An intermittent short to voltage on the low reference circuit of the MAF sensor may cause this DTC to set. It may also result in possible internal ECM damage. |
| - | Any water in the air induction system may cause this DTC to set. |
| - | Any contamination of the hot elements of the MAF sensor may cause this DTC to set. |
| • | If the condition is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step will determine if any mechanical faults have caused this DTC to set.
-
A very small amount of voltage will appear on this circuit when the ECM is operational. This is considered normal.
-
The measured resistance of the circuit will increase when the ECM is operational. This is considered normal.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Control Module Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views | ||||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||
2 |
Important:: If you were sent here from P0101 proceed to step 4.
Does the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||
3 |
Is the MAF sensor voltage more than the specified value? | 4.8 V | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||||
5 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0.00 V | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 7 | |||||||||||
|
Important:: Verify that the engine control module (ECM) has shut down prior to measuring the resistance of the low reference circuit of the MAF sensor. This can be verified by the loss of communication on the scan tool.
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 8 | |||||||||||
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 9 | ||||||||||
9 | Measure the resistance from the ECM case to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||
10 |
Important: Disconnecting the ECM connectors may eliminate the short to voltage if the signal circuit is shorted to another ECM circuit.
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||
11 | Repair the high resistance or an open in the ground circuit of the ECM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||||
12 |
Important:: A short to voltage on the low reference circuit of the MAF sensor may cause internal damage to the ECM. Verify proper system operation after completing the repair. Repair the short to voltage in the low reference circuit of the MAF sensor. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||||
13 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the MAF sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||||
14 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the ECM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||||
15 | Replace the MAF/IAT sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor/Intake Air Temperature Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||||
16 | Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | ||||||||||
17 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||
18 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||
