System Description
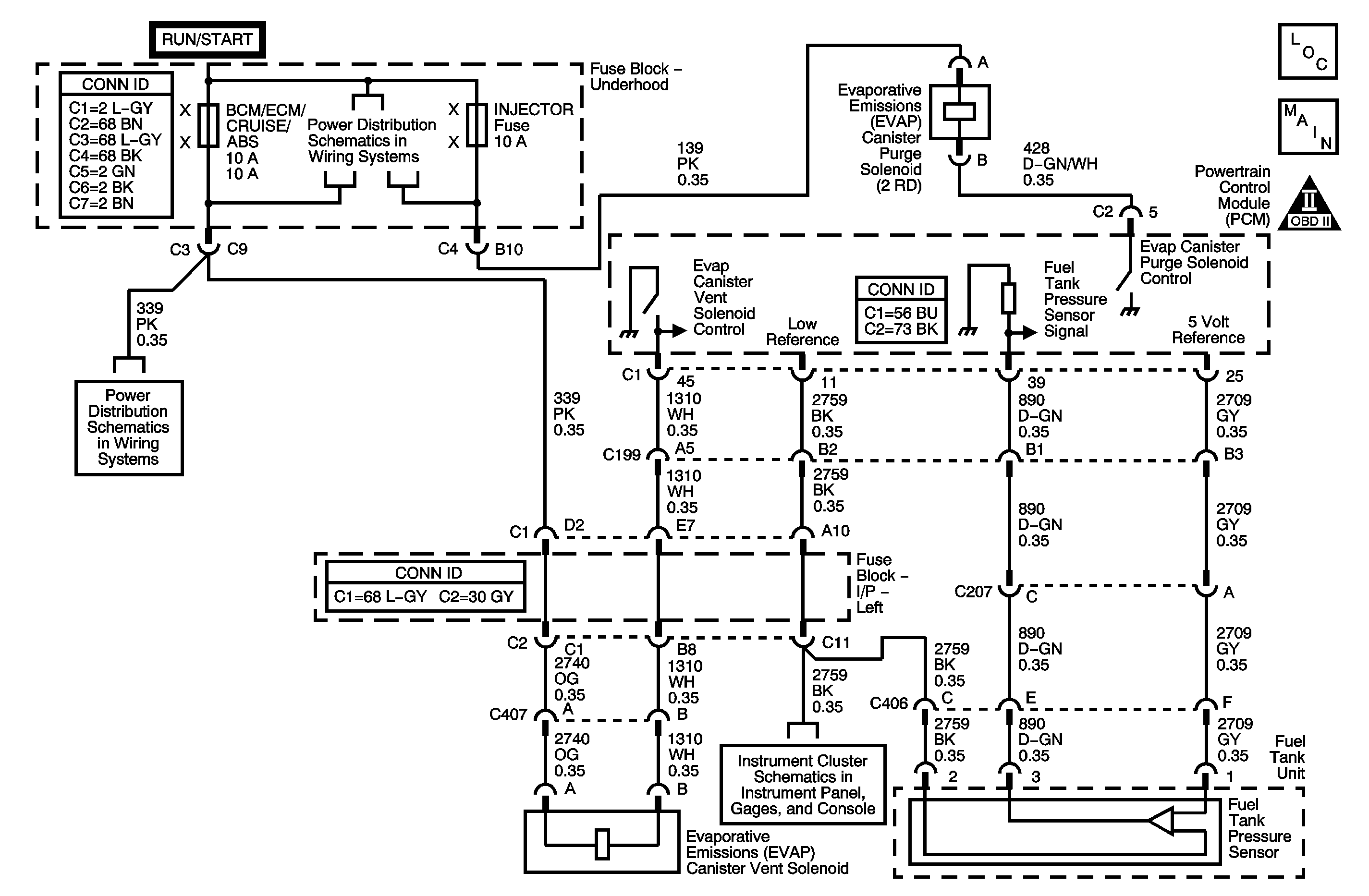
The evaporative emission (EVAP) system is used to store fuel vapors to reduce the amount of unburned fuel from escaping into the atmosphere. The EVAP canister purge solenoid valve is pulse width modulated (PWM) and is used to control the flow of fuel vapors from the EVAP canister to the intake manifold. The EVAP canister purge solenoid valve is commanded ON, PWM, whenever the EVAP system is in purge mode. Fuel vapors can be purged at anytime the powertrain control module (PCM) is in Closed Loop and the vehicle is not in a decel. The PCM controls the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve by controlling an internal driver that pulls the control circuit to ground. During one part of the EVAP diagnostic system test, the PCM will close the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve and the EVAP canister vent solenoid valve. DTC P0496 sets when the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor indicates that the pressure is lower than atmospheric, indicating the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve is stuck open.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0135, P0452, P0453, P0502, P0503, P0601, P0602, P1621 are not set. |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The EVAP canister vent solenoid valve is commanded ON, closed. |
| • | The EVAP canister purge solenoid valve is commanded OFF, closed. |
| • | The fuel level is between 15-85 percent. |
| • | The barometric pressure (BARO) is greater than 75 kPa. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) and intake air temperature (IAT) are between 4-30°C (39°-86°F) at engine startup. |
| • | The ECT and the IAT are within 8°C (15°F) of each other. |
| • | The vehicle speed is less than 113 km/h (70 mph). |
| • | The throttle position (TP) is between 10-35 percent. |
| • | DTC P0496 diagnostic runs once per ignition cycle, usually for 30 seconds if no faults exist, during the EVAP diagnostic system test. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | If the FTP sensor voltage is indicating less than 2.0 volts, continuous purge flow, during the EVAP diagnostic system test, DTC P0496 will set. |
| • | The above condition exists for 75 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores this information in the Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | A diagnosed EVAP canister purge solenoid valve or EVAP canister vent solenoid valve circuit fault may have caused this DTC to set. |
| • | The PCM uses the FTP sensor to detect the amount of vacuum pulled on the EVAP system during the leak diagnostic tests. Ensure that the fuel pressure sensor is not skewed by verifying the FTP sensor on the scan tool is between 2.35-2.85 volts with the ignition ON and the fuel cap removed. |
| • | The most likely cause of DTC P0496 is a stuck open EVAP canister purge solenoid valve. Command the EVAP purge solenoid valve ON, PWM, with the scan tool. The valve should click at an even rate. Replace the valve if the valve intermittently sticks. |
| • | A condition may exist where a leak in the EVAP system only exists under a vacuum condition. By using the scan tool Purge/Seal function to create a vacuum, seal the system and observe the FTP parameter for vacuum decay, this type of leak may be detected. |
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Evaporative Emissions Hose Routing Diagram and Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views | ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Does the vacuum gage indicate an increase in vacuum? | -- | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 3 |
3 |
Does the vacuum gage indicate an increase in vacuum? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 4 |
4 |
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter within the specified value? | 2.35-2.85 V | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 7 |
5 | Test the control circuit of the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve for a short to ground. Refer to Testing for Short to Ground and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the conditions? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 6 |
6 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 7 |
7 | Replace the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
8 | Replace the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
9 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 10 |
10 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |
