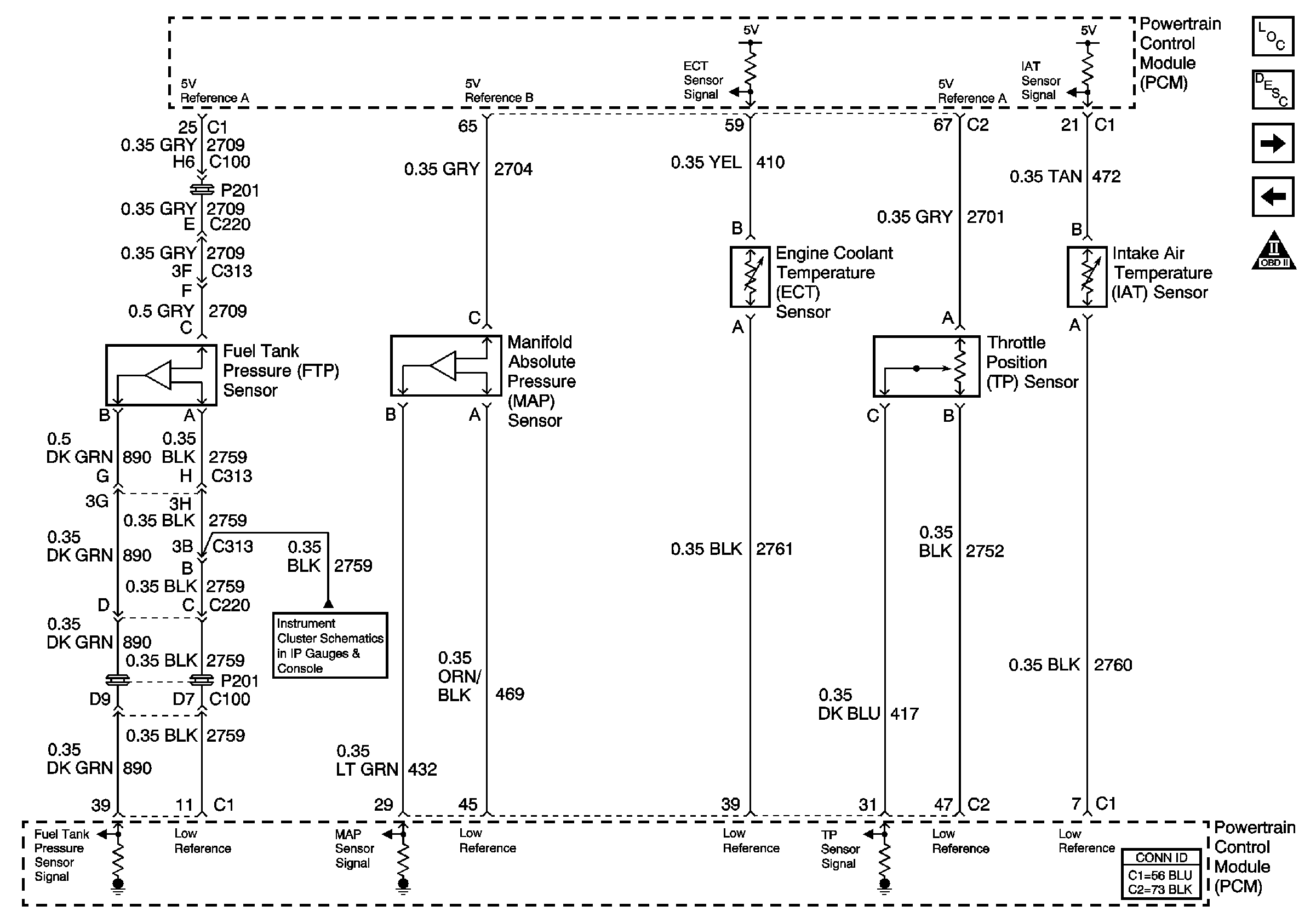
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor signal in order to detect vacuum decay and excess vacuum during the enhanced evaporative emission (EVAP) diagnostic. The PCM supplies a 5-volt reference and ground to the sensor. The FTP sensor signal voltage increases as the fuel tank pressure decreases (negative pressure or vacuum, high voltage). The FTP sensor signal voltage decreases as the fuel tank pressure increases (positive pressure, low voltage). When the FTP sensor signal voltage goes above a predetermined value, DTC P0453 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The key is ON.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The fuel tank pressure sensor voltage is more than 4.9 volts |
| • | All conditions present for greater than 5.0 seconds |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test ran and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic ran and passed. |
| • | The History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table:
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference:
| ||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||
Did DTC P1639 fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||
3 |
Is the FTP sensor voltage more than the specified value? | 4.3 V | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||
4 |
Does the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||
5 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the FTP sensor voltage is greater than the specified value? | 0.0 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||
6 | Test the signal circuit of the FTP sensor for a short to voltage between the body pass-through connector and the PCM. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||
7 | Probe the low reference circuit of the FTP sensor at the body pass-through with a test lamp connected to battery voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||
8 | Test the low reference circuit of the FTP sensor for an open between the body pass-through connector and the PCM. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||
10 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the PCM . Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 | ||||||
11 | Replace the FTP sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- | ||||||
12 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- | ||||||
13 |
Does the DTC run and pass? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||
14 | With a scan tool, observe the stored information, Capture Info. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||