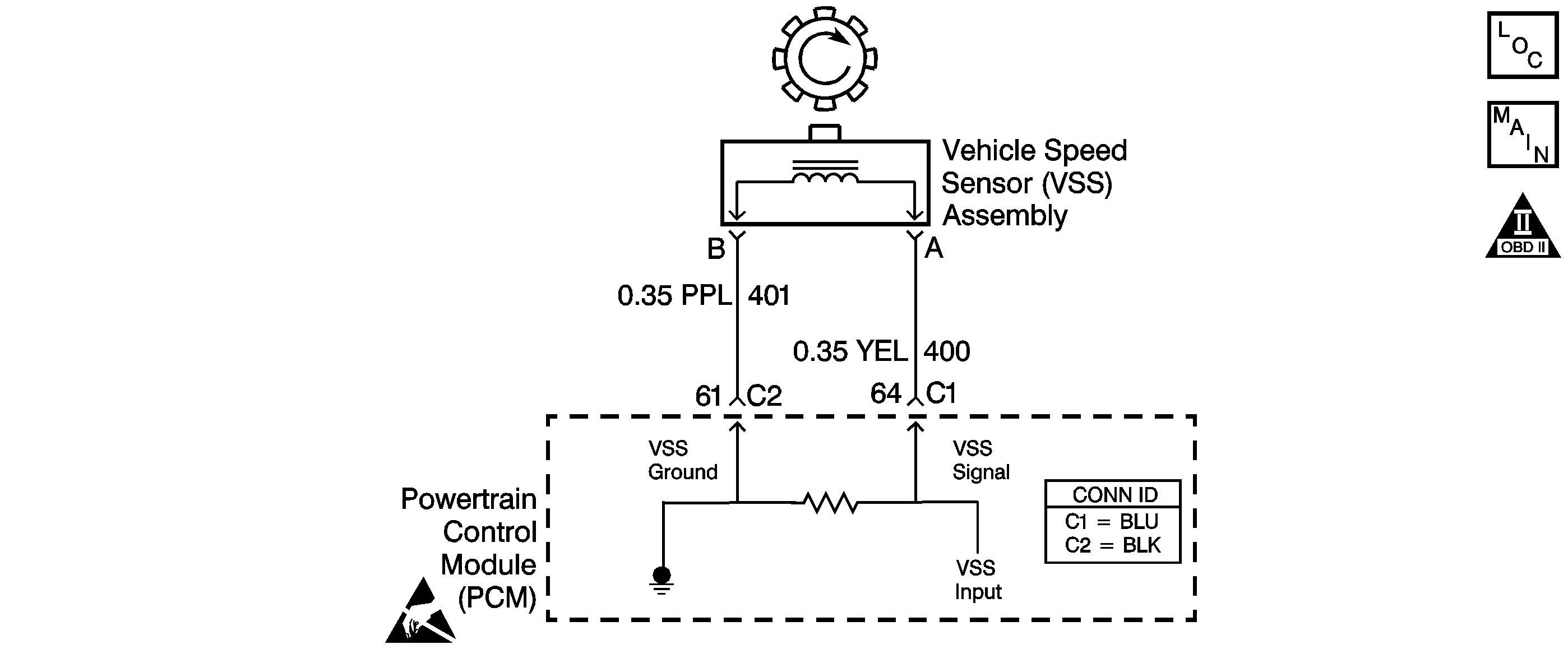
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) assembly provides vehicle speed information to the powertrain control module (PCM). The VSS assembly is a permanent magnet (PM) generator. The PM generator produces an AC voltage as the speed sensor rotor teeth on the transmission governor assembly pass through the sensor's magnetic field. The AC voltage level and the number of pulses increases as the speed of the vehicle increases. The output voltage varies from a minimum of 0.5 volts AC at 25 RPM to more than 100 volts AC at 200 RPM. The PCM converts the pulsing voltage to vehicle speed. The PCM uses the vehicle speed signal to calculate torque converter clutch (TCC) scheduling.
When the PCM detects a low vehicle speed and there is a high engine speed in a drive range, then DTC P0502 sets. DTC P0502 is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No MAP DTCs P0106, P0107 or P0108 |
| • | No TP DTCs P0121, P0122 or P0123 |
| • | The TP angle is greater than 15%. |
| • | The engine speed is 2000-4800 rpm. |
| • | MAP is greater than 50 kPa. |
| • | The transmission is in a drive range. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The vehicle speed is less than 3.2 km/h (2 mph) for 3 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which conditions for setting the DTC are met . |
| • | TCC will not apply. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions when the Conditions for Setting the DTC are met. The PCM stores this information as Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
| • | The PCM stores DTC P0502 in PCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the Conditions for Setting the DTC are met. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and passes. |
| • | A scan tool can clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | The PCM clears the DTC from PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without an emission-related fault occurring. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect for electromagnetic interferences (EMI) induced on circuit 400 and circuit 401 by an improperly routed harness. |
| • | Inspect the connectors at the PCM, the VSS and all other circuit connecting points for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the circuit wiring for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the following components for proper operation: |
| - | Speed sensor assembly housing |
| - | Speed sensor rotor teeth |
| - | Governor assembly and drive gear |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests for a vehicle speed signal.
-
This step checks for the VSS assembly ability to produce an AC voltage.
-
This step checks for correct circuit resistance.
-
When the VSS assembly is disconnected, the circuit resistance should be infinite.
-
This step checks for improper voltage in the circuit.
-
This step inspects for possible mechanical problems.
-
Replace the PCM only after you have completed the preceding diagnostic steps.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain Diagnostic System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the Scan Tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Freeze Frame and Failure Records from the PCM. Notice: Support the lower control arms in the normal horizontal position in order to avoid damage to the drive axles. Do not operate the vehicle in gear with the wheels hanging down at full travel. With the drive wheels rotating, does the Scan Tool transmission output speed increase when the wheel speed increases? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||
Can a voltage value greater than the specified amount be obtained? | 0.5V AC | |||||||||||||
Is the circuit resistance within the specified range? | 139-376ohms | |||||||||||||
5 | Is the circuit resistance greater than the specified value? | 376 ohms | ||||||||||||
Is the circuit resistance less than specified? | 139 ohms | |||||||||||||
7 | Test the signal circuit (CKT 400) and the ground circuit (CKT 401) of the VSS. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
8 | Test the signal circuit (CKT 400) of the VSS. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
Does the DMM display system voltage? | -- | |||||||||||||
10 | Test the signal circuit (CKT 400) of the VSS for a short to power. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
11 | Inspect circuits 400 and 401 for an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
Refer to Transmission Overhaul in the 3T40-E Section of the Transmission Unit Repair Manual. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||
13 | Replace the VSS assembly. Refer to Vehicle Speed Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming in Engine Controls. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||
15 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Has the test run and passed? | -- | System OK |
