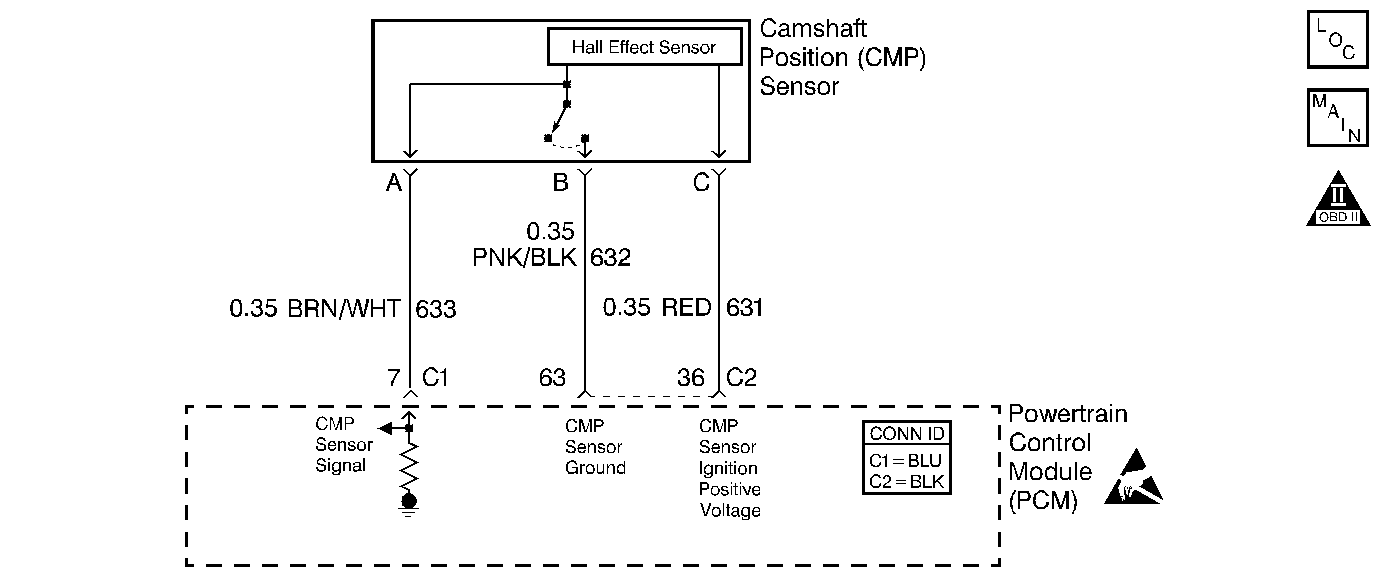
System Description
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors both the crankshaft and the camshaft position in order to detect an engine misfire. A rapid decrease in the crankshaft speed indicates an engine misfire. The PCM may require that several consecutive misfire conditions are detected before storing this DTC and before illuminating the MIL. During light misfire conditions, the PCM may require more than one trip to set this DTC. Under a severe misfire condition, the PCM flashes the MIL. A flashing MIL indicates that there is a misfire that is capable of damaging the catalytic converter. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic transmission, the torque converter clutch (TCC) disables momentarily in order to determine if the misfire was due to a rough road condition.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0105, P0107, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0171, P0172, P0325, P0335, P0341, P0342, P0502, P0503, P0506, P0507, P0601, P0740, P0742, P1133, and P1621 are not set. |
| • | The engine speed is between 469-5900 RPM. |
| • | The battery voltage is between 9-17 volts. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is between -7°C and +123°C (20°-254°F). |
| • | The engine has been running more than 5 seconds. |
| • | The throttle position (TP) has not increased more than 8 percent in 1 second. |
| • | The throttle position (TP) has not decreased more than 1.5 percent in 1 second. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The misfire total is more than 8 counts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) illuminates if the fault is active within the same conditions for two out of eighty ignition cycles and a misfire is present. |
| OR |
| The MIL illuminates after two consecutive ignition cycles during in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active |
| OR |
| The MIL illuminates immediately and flashes if a misfire is severe enough to cause any catalyst damage. |
| • | In vehicles with an automatic transmission only, the torque converter clutch (TCC) is disabled when a misfire is present. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC is stored. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles during which the diagnostic runs without a fault present under the Freeze Frame conditions that existed when the DTC failed. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor wheel. Remove the crankshaft sensor and inspect the reluctor wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity and examine the condition of the reluctor wheel.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
| • | The wiring for proper connections, pinches or, cuts. |
| • | The PCM grounds for being clean and tight. |
| • | The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper connections as shown on the vehicle emission information label. Inspect thoroughly for any type of leak or restriction. |
| • | Inspect the throttle body mounting area and the intake manifold sealing surfaces for air leaks. |
-
When all the accumulators indicate misfire, then the misfire is caused by something that affects the entire engine.
-
If the misfire is not present, operate the vehicle within the conditions recorded in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect the misfire. Depending on the engine load, the conditions may need to be maintained for up to 20 seconds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire counter will store the number of misfires that have occurred until the DTC is cleared.
-
Test the fuel for contamination such as water, alcohol, etc.
-
Tests the ignition system voltage output by using a spark tester.
-
Replace any spark plugs that are worn, cracked, or fouled. Refer to Ignition System in the supporting text if any plugs are fouled or damaged due to an engine mechanical malfunction.
-
Tests for voltage at the ignition feed circuit.
-
A basic engine problem that affects all cylinders, such as cam timing, throttle body leak, restricted air flow, etc., is the only possibility at this point.
-
Whenever the fuel injector driver circuit is shorted to ground, the lamp will be ON steady. When the driver circuit is shorted to voltage or open, the lamp will be OFF.
-
Because the voltage is supplied to the fuel injector on a single circuit, the malfunction may only be a faulty electrical connection or an open in the fuel injector electrical harness. An open before the harness may result in a Cranks But Will Not Run complaint.
-
The replacement PCM must be programmed and the Crankshaft Position System Variation learn procedure must be performed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
2 |
Are any injector control circuit DTCs set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | |||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||
4 |
Are any misfire current counters incrementing? | -- | ||||||||
Was a misfire present in all cylinders? | -- | |||||||||
Are any misfire current counters incrementing? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
7 |
does the fuel pressure read within the specified range? | 284-325 kPa (41-47 psi) | Go to Fuel System Diagnosis | |||||||
Test the fuel for contamination. Refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis . Is the fuel OK and uncontaminated? | -- | |||||||||
9 | Replace the contaminated fuel. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
Was spark observed on all four spark plug wires? | -- | |||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||
Does the fuel injector test lamp blink? | -- | |||||||||
13 | Perform the Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Between 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) . Did you find a problem? | -- | ||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | ||||||||
15 |
Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
16 | Replace any malfunctioning fuel injectors. Refer to Fuel Injector Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
17 | Test the affected fuel injector driver circuits for the following conditions:
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||||||||
Repair the condition as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | ||||||||
Repair the open in the ignition positive voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | ||||||||
20 | Measure the resistance of the spark plug wire where the spark plug tester did not spark. Does the resistance measure less than the specified value? | 1,000 ohms/inch | ||||||||
21 |
Notice: Do not leave the jumper wire connected to the PCM IC circuit connector for longer than 5 seconds at a time. Failure to do so may damage the ignition coil and/or the Ignition Control Module. Does the spark tester spark when the test lamp is removed from the IC circuit? | -- | ||||||||
22 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
23 |
Does the secondary coil resistance measure within the specified value? | 5,000-8,000 ohms | ||||||||
24 |
Did the test lamp blink while cranking the engine? | -- | ||||||||
25 |
Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||
26 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||||||||
28 | Replace the spark plug wire. Refer to Spark Plug Wire Harness Replacement in Engine Electrical. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
29 | Replace the ignition coil. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
30 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
