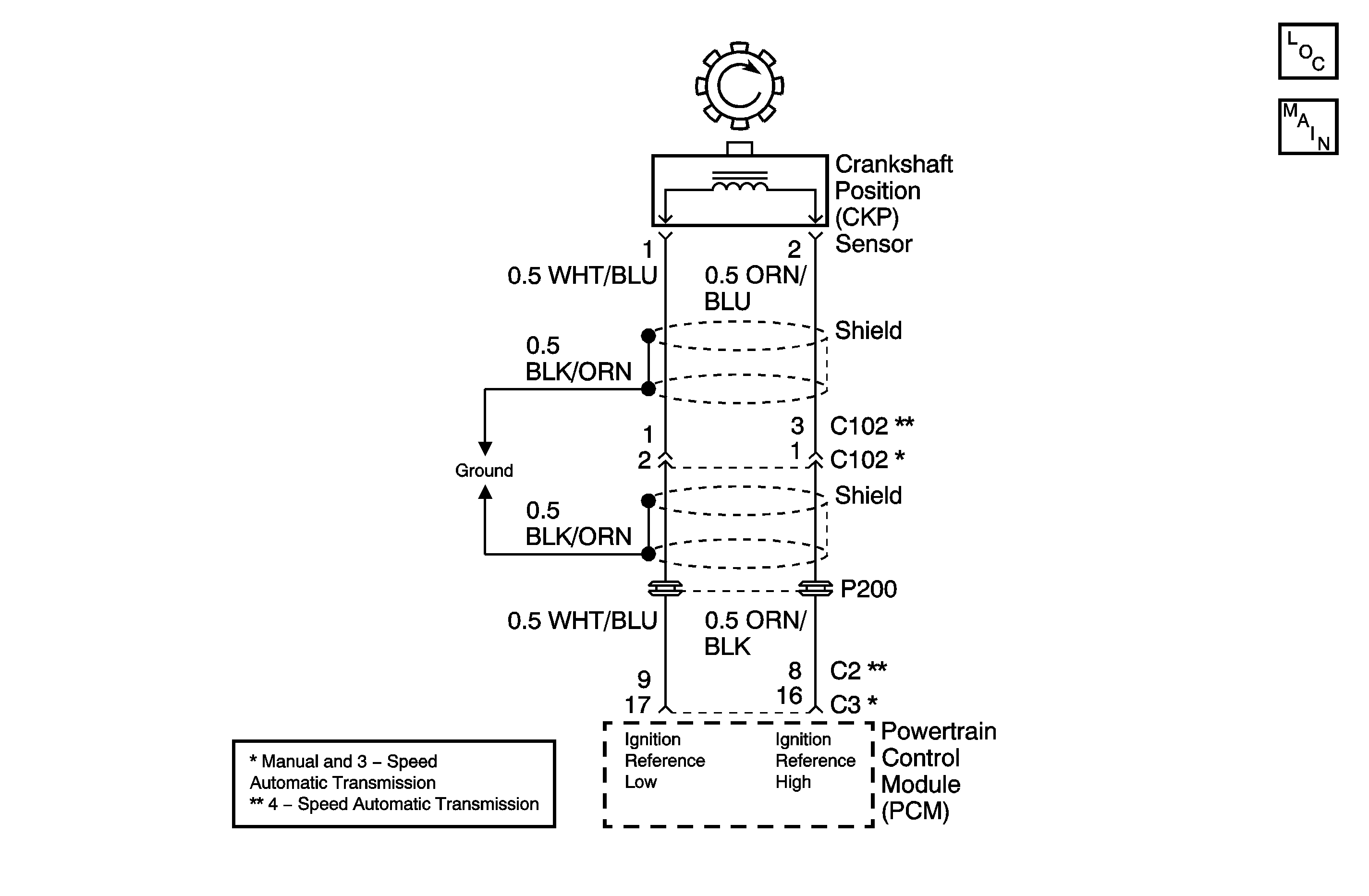
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is used to indicate crankshaft position so that the powertrain control module (PCM) can determine which cylinder is misfiring when a misfire is present.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No signal from the CKP sensor with the PCM receiving 20 pulses from the CMP sensor.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn off after three consecutive drive cycles without a fault present. |
| • | A DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The DTCs can be cleared by using a scan tool or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | The CKP sensor performance may be affected by temperature. Check the sensor's operation and internal resistance at various temperatures. |
| • | Check the wiring harness boot covering the CKP sensor electrical connectors for water intrusion. Water entry into the CKP sensor electrical connections may cause an intermittent loss of the CKP sensor signal. |
| • | Check the CKP sensor signal rotor for foreign material or damaged teeth. |
| • | A DTC P0335 that sets while driving and checks OK may be caused by inadequate CKP sensor circuit shielding. Check that the CKP sensor circuit is properly shielded and that the drain wire has a good ground. |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the CKP sensor circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connector locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals. |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
If no problem is found with the CKP sensor or the circuitry, check the crankshaft timing belt pulley for foreign material or damaged teeth.
If the DTC P0335 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining vehicle operating conditions since the DTC was first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain (OBD) System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
Determine if a fault is present. Review the Freeze Frame data to determine when the DTC set. Always record this information.
-
If the CKP sensor is within the specified value, measure the resistance from each terminal (CKP sensor side) to ground. The CKP sensors resistance should be 1M ohms or more, if not replace the CKP sensor.
-
Check for an open or a short in the CKP sensors high and low reference circuits between the PCM and the CKP sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
Is a DTC P0335 set? | -- | Fault Not Present-Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Is the resistance within the specified value? | 360 to 460 ohms at 20°C (68°F) | |||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
5 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
6 | Replace the CKP sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
