Refer to Engine Controls Schematic
CKP, CMP, ICM and Knock Sensor
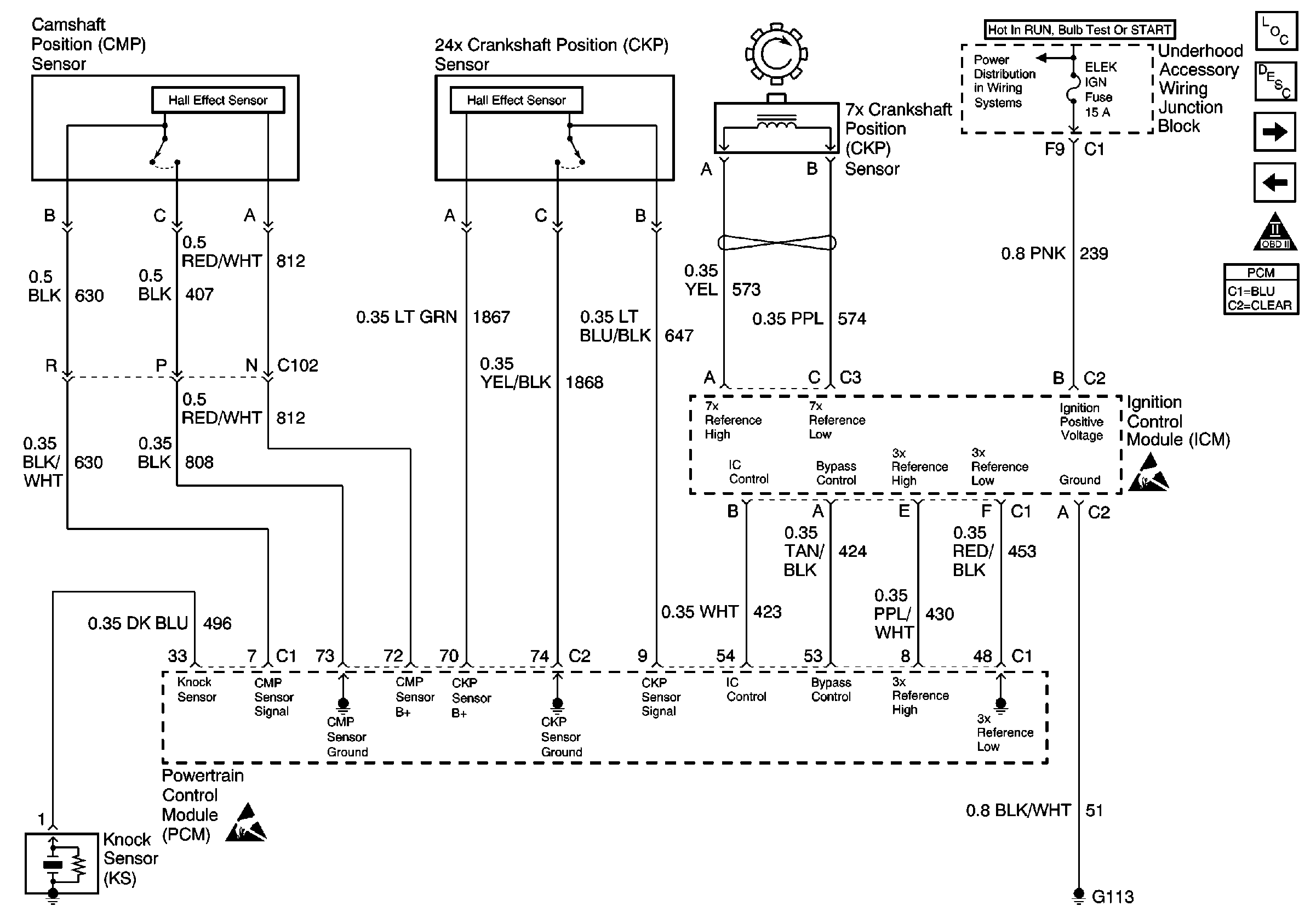
.
Circuit Description
The 24X reference signal is used to improve idle spark control at low engine speeds. The PCM uses the 24X reference signal to calculate engine RPM and crankshaft position at engine speeds below 1600 RPM. The PCM constantly monitors the number of pulses on the 24X reference circuit and compares the number of 24X reference pulses to the number of 3X reference pulses and CAM signal pulses being received. If the PCM receives an incorrect number of pulses on the 24X reference circuit, DTC P0336 will set and the PCM will use the 3X reference signal circuit for fuel and ignition control. The engine will continue to start and run using the 3X reference and CAM signals only.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running (3X reference pulses are being received) for a minimum of 3 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ratio of 24X reference pulses to 3X reference pulses received by the PCM is incorrect.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0336 can be caused by secondary components leaking high voltage into the ignition module. Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | Incorrect harness routing near secondary ignition components. |
| • | Ignition coil arcing to wiring harness or Ignition Control Module (check ignition coils for cracks, carbon tracking, or other signs of damage). |
| • | Secondary ignition wires arcing to wiring harness. |
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table:
-
If sent here from DTC P0327 proceed with DTC P0336 Diagnostic even if P0336 has not failed this ignition.
-
The 24X RPM on the scan tool should change each time the signal circuit is touched.
-
If the fuse blows in the jumper wire, there is a short to ground on the signal circuit.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is being replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
|
Important: A short to ground on the CMP sensor ignition circuit can cause P0336 and P0327 to set. Test this circuit for a short to ground before proceeding with this diagnostic table.
Does scan tool indicate DTC P0336 failed this ignition? | -- | Go To Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 |
Does 24X RPM vary with engine speed up to approximately 1600 RPM? | -- | Go To Diagnostic Aids | |
4 |
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | B+ | ||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
6 |
Does testlamp illuminate? | -- | ||
7 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
Does 24X RPM change EACH time the signal circuit is touched? | -- | |||
Did the fuse in the jumper wire blow? | -- | |||
10 | Test the signal circuit of the 24X CKP sensor for a short to voltage or an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
11 | Test the signal circuit of the 24X CKP sensor for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
12 | Inspect for poor connections at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Continuity , and Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
13 |
Important: : Replacement PCM must be reprogrammed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
14 | Inspect for poor connections at the 24X CKP sensor. Refer to Testing for Continuity , and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
15 | Replace 24X CKP sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
