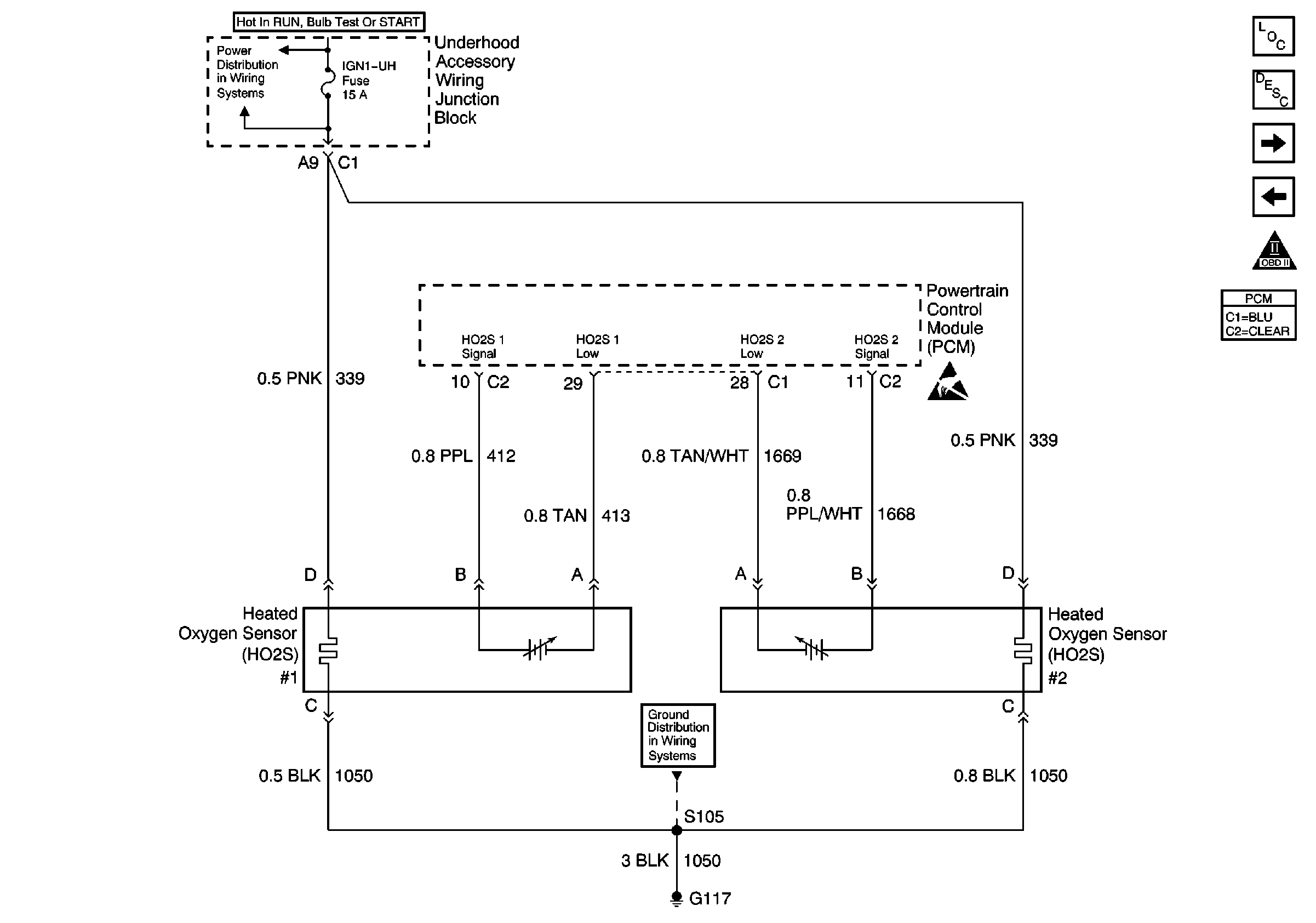
Refer to Engine Controls Schematic
HO2S #1 and HO2S #2
.
Circuit Description
To control emissions of Hydrocarbons (HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx), a three way catalytic converter is used. The catalyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction which oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas, converting them into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide. The catalyst also reduces NOx, converting it to nitrogen. The PCM has the ability to monitor this process using the HO2S 1 and the HO2S 2 heated oxygen sensors. The HO2S 1 sensor produces an output signal which indicates the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gas entering the three way catalytic converter. The HO2S 2 sensor produces an output signal which indicates the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst this in turn indicates the catalysts ability to convert exhaust gases efficiently. If the catalyst is operating efficiently, the HO2S 1 signal will be far more active than that produced by the HO2S 2 sensor. If the HO2S 2 signal voltage remains excessively high for an extended period of time, DTC P0138 will be set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active TP, MAP, MAF, ECT, IAT Sensor, fuel injector circuit, EVAP, AIR DTCs present. |
| • | System voltage between 9.0 and 18.0 volts. |
| • | Throttle angle between 5% and 40%. |
| • | Closed loop commanded air/fuel ratio is between 13.0 and 16.5. |
| • | Commanded AIR pump OFF. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
HO2S 2 signal voltage remains above 999mV during normal closed loop operation for greater than 5 minutes.
OR
HO2S 2 signal voltage remains above 200 mV during deceleration fuel mode operation for greater than 100 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | Fuel pressure. An excessively rich fuel mixture can cause a DTC P0138 to be set. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| • | Rich injectors. Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test . |
| • | Leaking injector. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| • | Evaporative emissions (EVAP) canister purge. Check for fuel saturation. If full of fuel, check canister control and hoses. Refer to Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis . |
| • | MAF sensor. Disconnect the MAF sensor and see if rich condition is corrected. If so, replace MAF sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . |
| • | Test for a leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by inspecting the vacuum line to regulator for the presence of fuel. |
| • | TP sensor. An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system to go rich, due to a false indication of the engine accelerating. |
| • | Shorted Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S). If the HO2S is internally shorted the HO2S voltage displayed on the scan tool will be over 1.0 volts. Try disconnecting the affected HO2S and jumper the HO2S low circuit to ground with the key ON, engine OFF. If the displayed HO2S voltage changes from over 1000 mV to around 450 mV, replace the HO2S. Silicon contamination of the HO2S can also cause a high HO2S voltage to be indicated. This condition is indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion of the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. If contamination is evident, replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
| • | Open HO2S Signal or Low Circuit or Faulty HO2S. A poor connection or open in the HO2S signal or low circuit can cause the DTC to set during deceleration fuel mode. An HO2S which is faulty and not allowing a full voltage swing between the rich and lean thresholds can also cause this condition. Operate the vehicle while monitoring the HO2S voltage with a scan tool. If the HO2S voltage is limited within a range between 300 mV to 600 mV, check the HO2S signal and low circuit wiring and associated terminal connections. If the wiring and connections are OK, replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table:
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Important: During this step, observe the pre-catalyst HO2S voltage parameters. If the pre-catalyst parameters remain above 600mV refer to Diagnostic Aids.
Does the HO2S 2 voltage measure above the specified value? | 999 mV or 200 mV during deceleration fuel mode | ||
Does scan tool indicate DTC P0138 failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
4 | Disconnect HO2S 2 and jumper HO2S low circuit to ground. Does the scan tool indicate HO2S 2 voltage measure near the specified value? | 450 mV | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
5 |
Does the DMM indicate a voltage more than the specified value? | 999 mV | ||
6 | Repair short to voltage in the HO2S 2 signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
|
Important: : Replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||
8 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
