Refer to Engine Control Schematic
A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor, TP, MAP, ECT and IAT Sensor
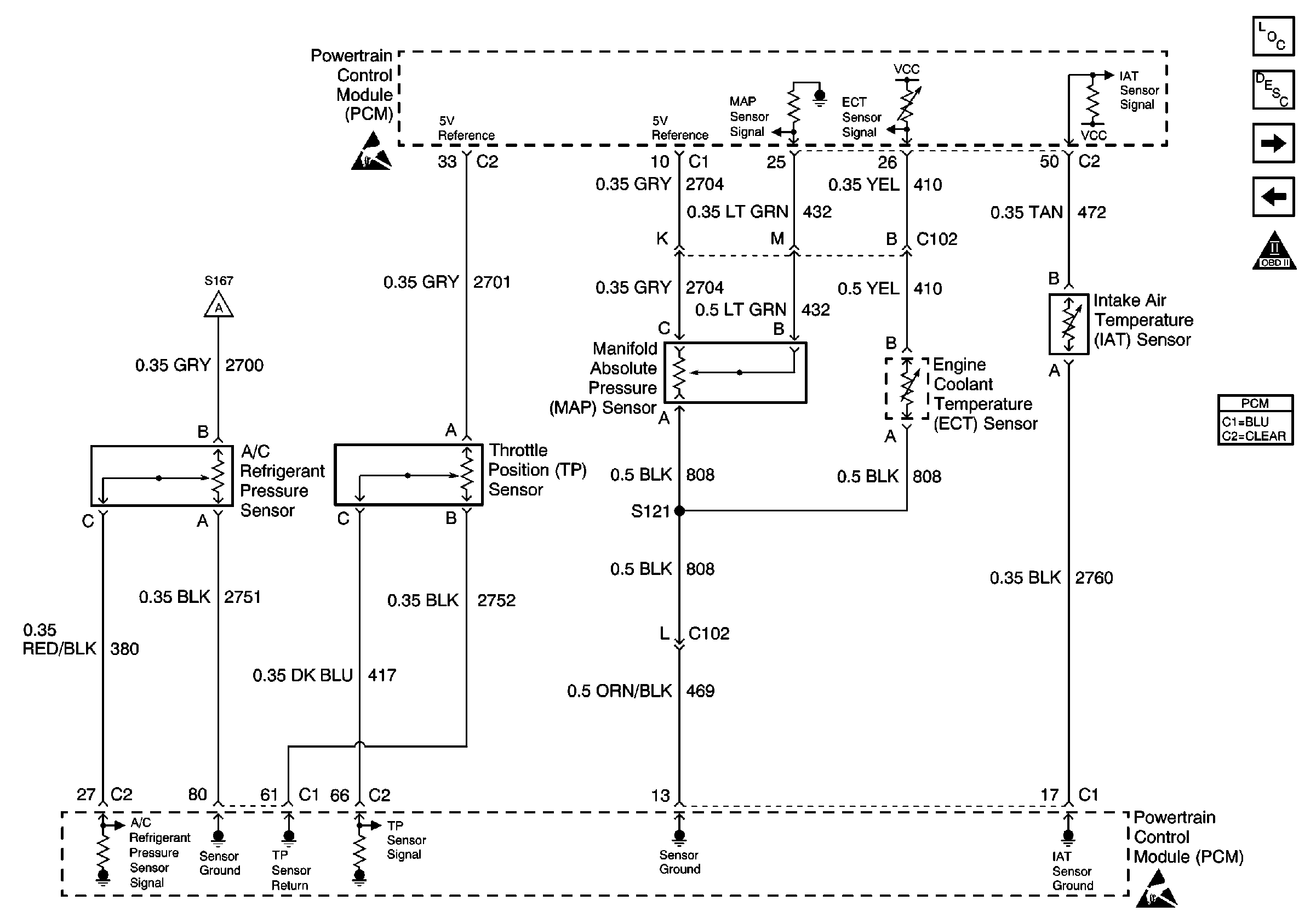
.
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The MAP sensor signal voltage to the PCM varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above 4 volts with the key ON, engine not running or at wide-open throttle (low vacuum). The MAP sensor is used to determine manifold pressure changes while the EGR flow test diagnostic is being run, refer to DTC P0401 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient . Also to update the barometric pressure reading (BARO), and as a enabling factor for other diagnostics. The PCM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the PCM detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively high, refer to DTC P0108 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Circuit High Voltage will be set. If the PCM detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, refer to DTC P0107 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage will be set.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Monitor the MAP sensor using a scan tool. If the MAP sensor does not respond to throttle changes, check the 3X reference circuits from the ignition control module to the PCM. |
| If the 3X reference signal is lost the PCM will only update the MAP sensor reading once per key cycle, when the engine is first started. |
| Depending on where the MAP sensor voltage (high voltage or low voltage) is when the engine is started, the high or low voltage MAP sensor DTCs will set. |
| • | Inspect for kinked and damaged vacuum hoses, ensure that a good vacuum source is available. Refer to Emission Hose Routing Diagram . |
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Poor terminal connection. |
| Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness. |
| Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the PCM and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. |
If the DTC is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Failure Records can be useful in determining when the DTC was last set.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||
2 |
Did you find and correct any of the conditions? | -- | ||||||||||||||
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the MAP sensor voltage parameter is greater than the specified value? | 0.0 V | ||||||||||||||
4 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the MAP sensor parameter is near the specified value? | 4.95 V | ||||||||||||||
5 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the MAP sensor voltage parameter is near the specified value? | 4.95 V | ||||||||||||||
6 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||
7 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||
10 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||
11 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
12 | Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||
13 |
Important: : Perform the set up procedure for the PCM. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
14 | With the engine idling, monitor the MAP sensor with a scan tool while increasing engine RPM. Does the MAP sensor value change? | -- | System OK |
