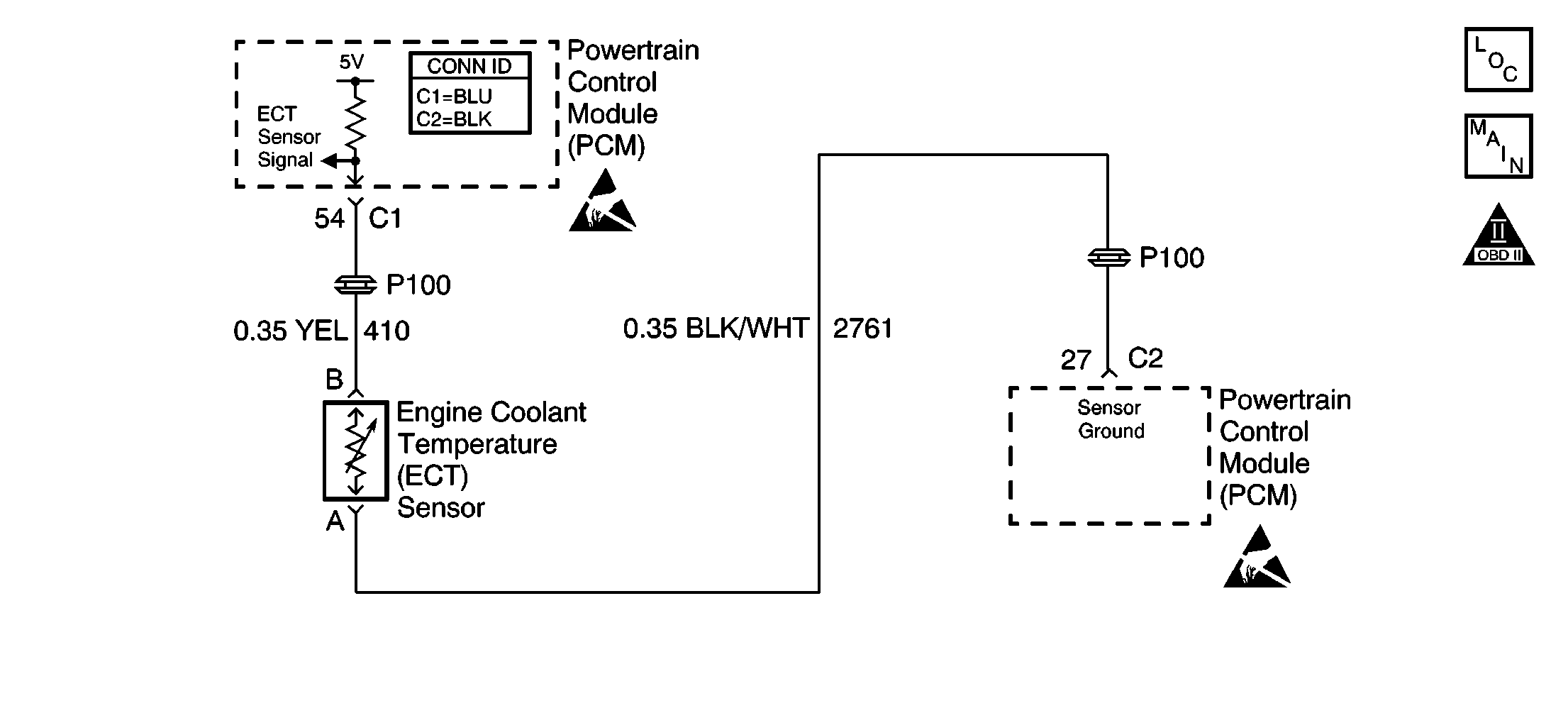
Circuit Description
The purpose of the engine cooling system is to maintain an efficient engine coolant temperature (ECT) level during all engine operating conditions. This is accomplished by using a thermostat to regulate the flow of engine coolant from the engine to the radiator. The thermostat allows the engine coolant to warm up faster by not allowing the coolant to flow through the radiator until the coolant has reached the thermostat regulating temperature. An ECT sensor monitors the temperature of the engine coolant. The Powertrain Control Module(PCM) uses the ECT sensor input for the following conditions:
| • | The engine control |
| • | The enabling criteria for some diagnostics |
The air flow coming into the engine is accumulated and is used to determine if the engine has been driven within the conditions that would allow the coolant to heat up to the normal thermostat regulating temperature. The diagnostics that use the ECT for enabling criteria may not run when expected if the following conditions exists:
| • | The ECT does not increase normally. |
| • | The coolant does not reach the thermostat regulating temperature. |
Conditions For Running The DTC
| • | The following DTCs are not set: P0105, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0130, P0131, P0132, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0300, P0325, P0336, P0420, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0452, P0453, P0480, P0502, P0503, P0506 or P1441. |
| • | The engine has been running for more than 30 seconds and less than 20 minutes. |
| • | The minimum intake air temperature (IAT) is more than -7°C (27°F) |
| • | The ECT at start up is less than 35°C (95°F) |
Conditions For Setting The DTC
| • | The average air flow is more than 10 g/sec (automatic transmission). |
| • | The average air flow is more than 15 g/sec (manual transmission). |
| • | The vehicle has traveled more than 0.5 miles over 25 mph. |
| • | Enough air flow has entered the engine and the ECT has not increased to 40°C (104°F) for 30 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate after 2 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns on. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn off after 3 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
A skewed ECT sensor will cause this DTC to set.
An intermittent may be caused by the following conditions:
| • | A poor electrical connection |
| • | A rubbed-through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Inspect for a poor electrical connection or a damaged PCM harness. Inspect the ECT sensor signal circuit and the ground circuit terminals for the following conditions: |
| - | Any incorrect mating |
| - | Any broken locks |
| - | Any incorrectly formed connectors |
| - | Any damaged terminals |
| - | A poor terminal to wire connection |
| - | A damaged harness |
| • | Perform an intermittent test. If the electrical connections and the harness check OK, monitor a DMM connected between the ECT sensor signal circuit and the ground circuit terminals while moving the related electrical connectors and the wiring harness. If a malfunction is induced, the resistance reading will change. This may help to isolate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Use the Temperature vs. Resistance table in order to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer to Temperature Versus Resistance . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Allow the engine to fully cool. The ECT sensor and the IAT sensor will read close to the ambient temperature in order to check for a possible skewed ECT sensor.
-
Measure the ECT with a thermometer in order to determine what the actual value the ECT should be. Consider whether the engine has been operating and if the coolant has been warmed without opening the thermostat.
-
This step simulates DTC P0118. The PCM and the wiring are OK if the PCM senses a change.
-
If the ECT sensor, the PCM, and the wiring have tested OK, inspect for proper thermostat and cooling fan operation.
-
The replacement PCM must be reprogrammed and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn procedure must be preformed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 | Are any other DTCs set? | -- | Go to Step 3 | |
3 | Inspect the ECT with the scan tool. Is the ECT more than or equal to the specified value? | 73°C (165°F) | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 |
4 |
Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 5 | -- |
Are the readings within the specified value of each other? | 5° | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 | |
Does the sensor accurately reflect the actual ECT? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 12 | |
7 |
Is the ECT less than the specified value? | -30°C (-22°F) | Go to Step 8 | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
Connect a fused jumper between the ECT sensor signal circuit and the ground circuit at the connector. Is the ECT more than the specified value? | 130°C (266°F) | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 10 | |
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 | |
11 |
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
12 |
. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
13 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
