The MAF sensor measures the amount of air coming into the engine. This direct airflow measurement is more accurate than the calculated airflow information obtained from the other sensor inputs. The MAF sensor also houses an integrated intake air temperature
(IAT) sensor. The MAF sensor uses the following circuits:
| • | An ignition voltage circuit |
| • | An IAT low reference circuit |
The MAF sensor that is used on this vehicle is a hot film type and is used in order to measure the air flow rate. The air flow through the sensor passes over a temperature sensor, is then heated, and then passes over another temperature sensor. The difference
in air temperature before and after the heater is measured. The air temperature difference is proportional to the amount of air flow. This air temperature difference also allow for determination of whether the air is flowing in the forward or reverse directions.
As the air flow increases the delta temperature between the two sensors increases. The MAF sensor converts the temperature difference into a frequency signal that the ECM monitors. The ECM calculates the air flow based on this signal.
The ECM monitors the MAF sensor signal frequency and can determine if the sensor signal is too low or too high. The ECM can also detect airflow that is inappropriate for a given operating condition based on the signal frequency.
The scan tool displays the MAF sensor value in grams per second (g/s) and hertz (Hz). Values should change rather quickly on acceleration, but should remain fairly stable at any given engine speed. If the ECM detects a condition with the MAF sensor circuits,
the following DTCs set:
| • | P0100 Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit |
| • | P0101 Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Performance |
| • | P0102 Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage |
| • | P0103 Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit High Voltage |
Intake Manifold Tuning (IMT) Valve Solenoid
The characteristic torque curve of a normally aspirated engine depends mainly on how the engines average pressure changes over the engine speed band. The average pressure is proportional to the volume of the air mass present in the cylinder when the inlet
valve is closed. The design of the inlet system determines how large an air mass can be drawn into a cylinder at a given engine speed.
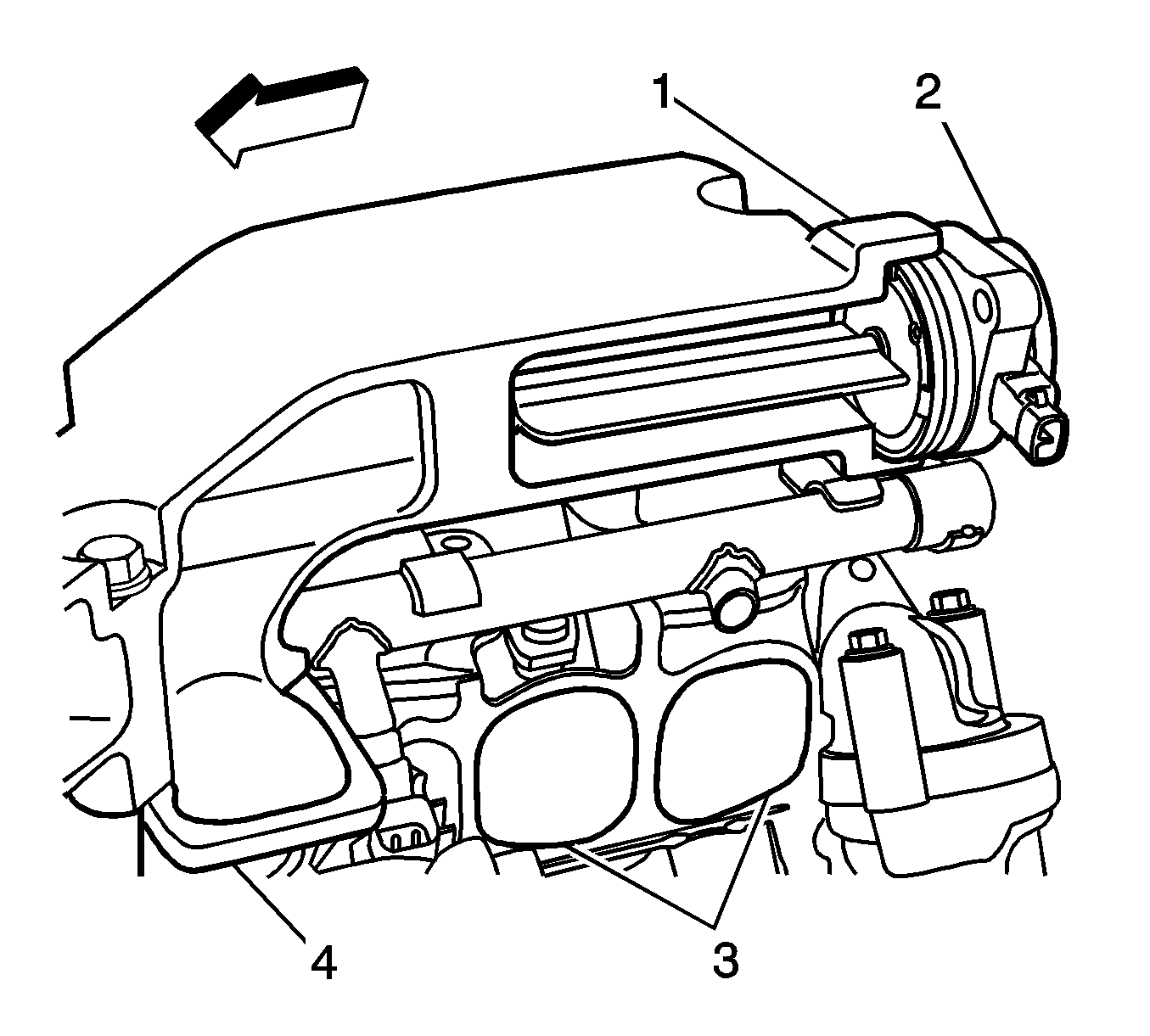
An intake manifold tuning (IMT) Valve (2) is used to change the intake manifold runner configuration. When the IMT valve is open, the intake manifold is configured to one large plenum (4). When the IMT valve is closed, the intake manifold
is configured to two smaller plenums (3). The two intake manifold runner sizes result in different torque curves which improves performance at low and high engine speeds. The IMT valve is located in the intake manifold (1). The IMT valve solenoid
is supplied with ignition 1 voltage and is controlled by the engine control module (ECM).

