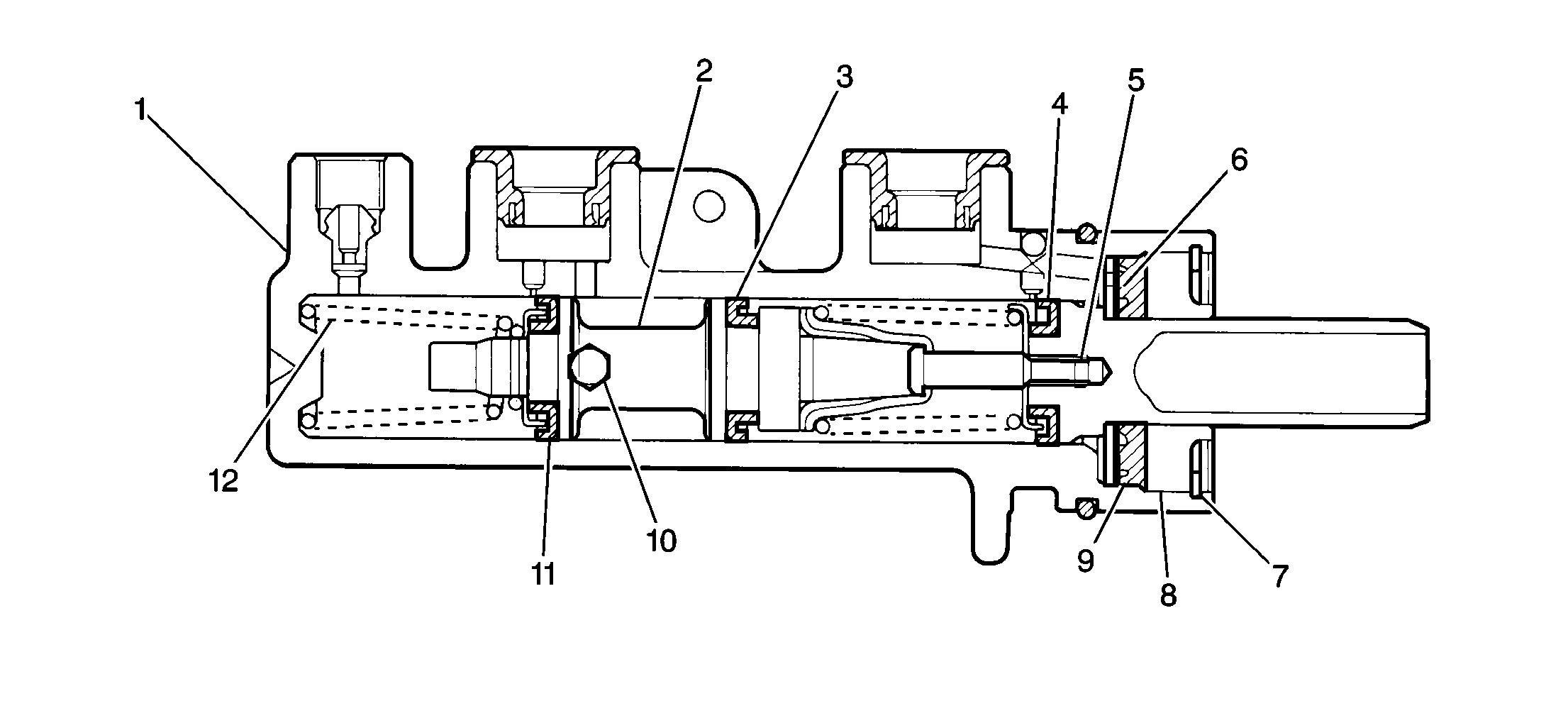
The master cylinder (1) assembly consists of an aluminum body and a plastic brake fluid reservoir. Internally, the master cylinder houses two pistons (one primary (4) and one secondary (2)) and three piston cups (3, 4, 11). The master cylinder is mounted on the brake booster assembly.
When the brake pedal is pressed, the primary piston compresses the volume of the primary chamber, increasing the hydraulic pressure in the chamber. This pressure, along with the return spring force (13), causes the secondary piston to compress the volume of the secondary chamber.
The hydraulic pressure in the primary chamber acts on the rear brakes -- both right and left. The pressure produced in the secondary chamber acts on the right and left front brakes.
On vehicles equipped with the Antilock Brake System (ABS), the master cylinder hydraulic lines are connected to the hydraulic modulator. For more information regarding ABS, refer to ABS Description in Antilock Brake System.
Reservoir and Cap
The reservoir is attached to the top of the master cylinder which is located under the hood on the left-side of the bulkhead. The reservoir is constructed of transparent plastic and is marked with the MAX level on the outside.
Fluid Level Switch
The brake fluid level switch is located in the master cylinder reservoir. If the master cylinder fluid level becomes too low, it will cause the BRAKE indicator to illuminate. This condition will alert the driver that a low fluid level condition exists in the master cylinder reservoir.
