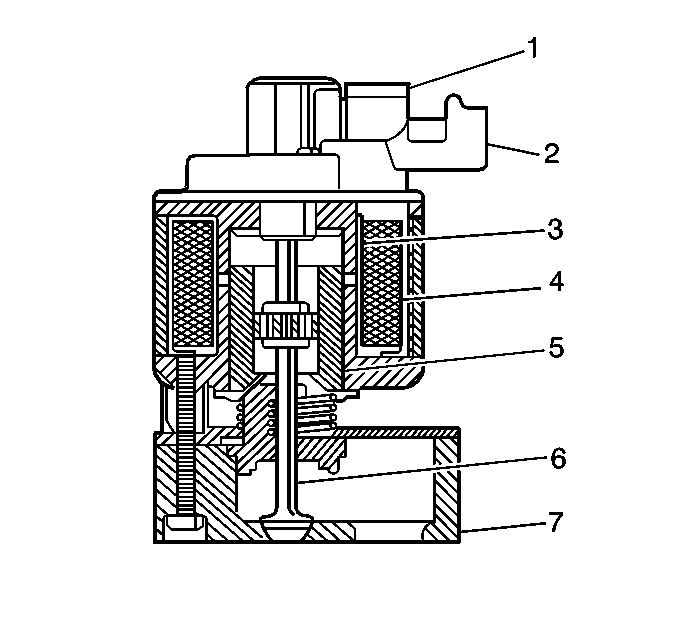
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System is used to reduce the amount of nitrogen
oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by high combustion temperatures. At temperatures
above 1 371°C (2,500°F), oxygen and nitrogen combine to form oxides
of NOx. Introducing small amounts of exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber
displaces the amount of oxygen entering the engine. With less oxygen in the air/fuel
mixture, the combustion pressures are reduced and, as a result, combustion temperatures
are decreased restricting the formation of NOx. The EGR system will only operate under
specific temperature, barometric pressure and engine load conditions in order to prevent
driveability concerns and to increase engine performance.