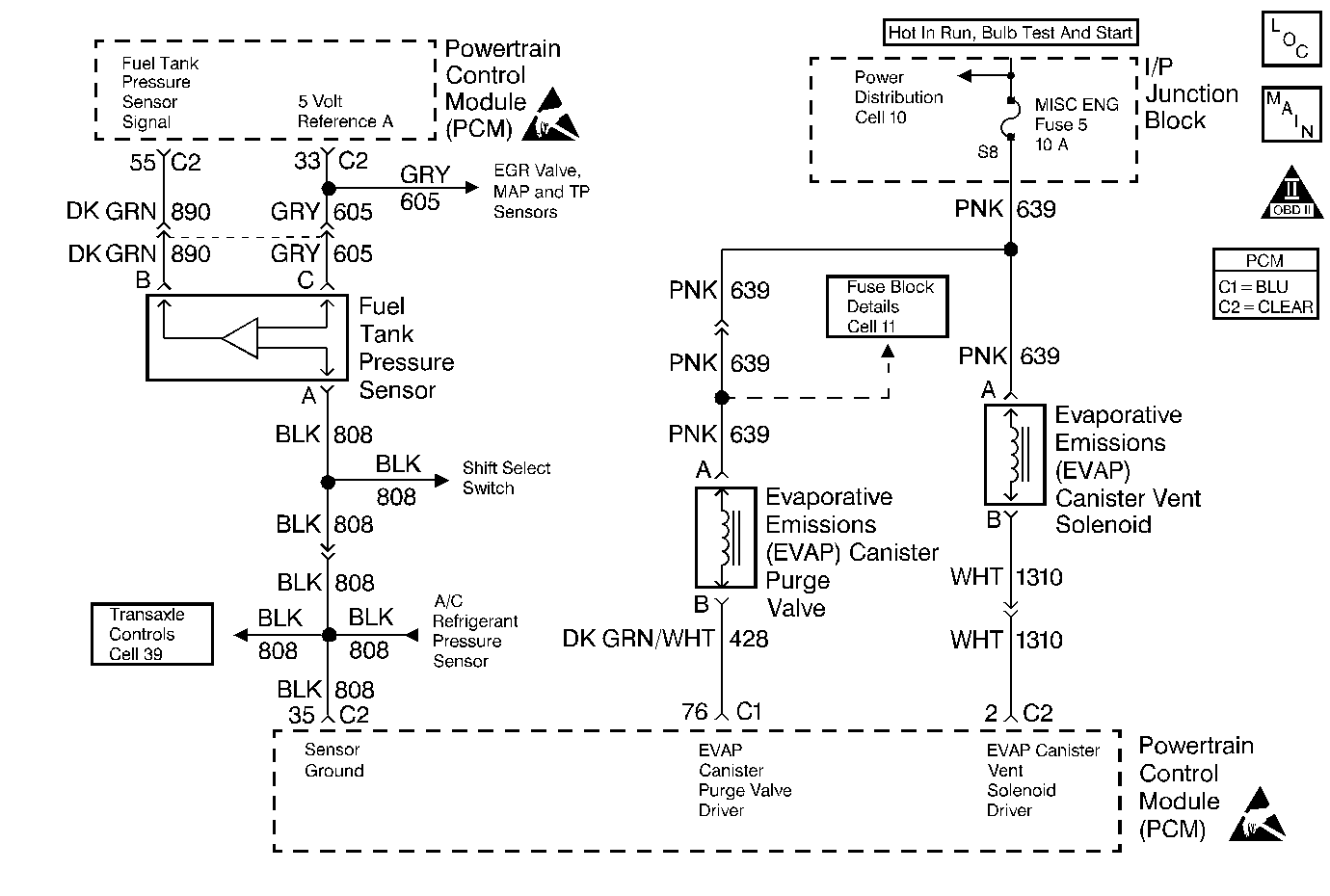
Circuit Description
The EVAP purge valve allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a ground to energize the EVAP purge valve (purge ON). The EVAP purge valve control is Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) or turned ON and OFF several times a second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by engine operating conditions including load, throttle position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature. The duty cycle is calculated by the PCM and the output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have been met:
| • | Engine coolant temperature above 25°C (77°F). |
| • | After the engine has been running about 2 1/2 minutes on a cold start or 30 seconds on a warm start. |
| • | The vehicle is operating in closed loop fuel control. |
Canister purge commanded duty cycle varies according to operating conditions determined by mass air flow, fuel trim, and intake air temperature.
Canister purge operation is also affected by throttle position.
| • | VIN K -- Canister purge will be disabled if TP angle increases to above 70 percent. Canister purge will be re-enabled when TP angle decreases below 66 percent |
| • | VIN 1 -- Canister purge will be disabled if TP angle increases to above 33 percent. Canister purge will be re-enabled when TP angle decreases below 29 percent |
The EVAP vacuum switch is a normally closed switch positioned in the purge line between the canister and the EVAP purge valve. The EVAP vacuum switch will open when vacuum increases to greater than 5 inches of water (in. H2O) in the purge line. The PCM monitors the EVAP vacuum switch signal to determine if the evaporative emission control system is working properly. If the switch is open (purge flow detected) when the PCM is not commanding the EVAP purge valve ON, DTC P1441 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No active TP sensor, IAT sensor, MAP sensor, or ODM DTC(s) set. |
| • | The BARO reading is greater than 70 kPa. |
| • | Engine speed is between 650 RPM and 5000 RPM. |
| • | Intake Air Temperature is between 10°C (50°F) and 70°C (158°F). |
| • | The difference between Engine Coolant Temperature and Intake Air Temperature is less than 10°C (18°F). |
| • | EVAP Canister Purge is less than 3 percent. |
| • | The EVAP vacuum switch circuit signal indicates purge flow. |
| • | The above conditions are present for longer than 4 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at the PCM. |
| Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. |
| Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| • | If the harness appears to be OK, connect the
|
| • | Incorrect vacuum line routing. |
| Verify that the source vacuum line routing to the EVAP purge valve is correct and that the EVAP purge and source vacuum lines to the EVAP purge valve are not switched. |
| • | Malfunctioning or damaged canister. |
| A malfunctioning canister may intermittently allow charcoal into the EVAP purge valve, EVAP vacuum switch, and associated lines causing a DTC to be set. Use the following procedure to check for a carbon release condition: |
| 1. | Turn OFF the ignition switch. |
| 2. | Remove the EVAP purge valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . |
| 3. | Lightly tap the EVAP purge valve and (if applicable) the vacuum switch on a clean work area looking for carbon particles exiting either of the vacuum ports. |
| 4. | If no carbon release is evident, reinstall the components and continue with the DTC P1441 table. If carbon is being released from either component, continue with this service procedure. |
| 5. | Remove the EVAP canister from the vehicle. |
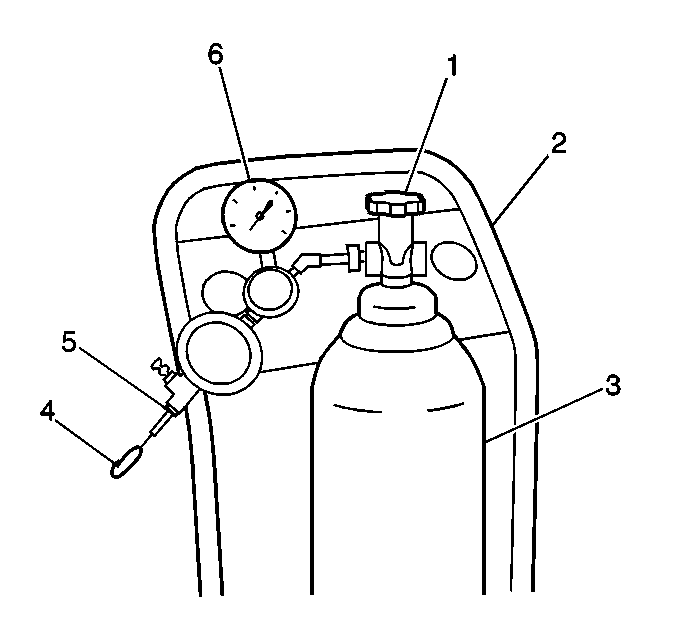
| 6. | Ensure that the main cylinder valve is turned off on the

|
| 7. | Disconnect the black hose that connects the nitrogen cylinder to the EVAP purge/pressure diagnostic station at the pressure regulator by unscrewing the knurled nut on the regulator. No tools are required to remove the black hose from the regulator. |
| 8. | Using a section of vacuum line, connect one end over the open threaded fitting of the EVAP purge/pressure diagnostic station pressure regulator. |
| 9. | Connect the remaining end to the EVAP purge valve end of the EVAP purge line at the vehicle and turn on the main nitrogen cylinder valve. Continue to blow any debris from the purge line for 15 seconds. |
| 10. | Return the EVAP Pressure/Purge Diagnostic Station to its original condition by re-installing the black hose that was disconnected in step 7. |
| 11. | Replace the following components: |
| - | The EVAP purge valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . |
| - | The EVAP canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Replacement |
| 12. | Proceed with the DTC P1441 diagnostic table. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
If an EVAP purge valve electrical malfunction is present, the purge system will not operate correctly. Repairing the electrical malfunction will very likely correct the condition that set DTC P1441.
-
Checks the Fuel Tank Pressure sensor at ambient pressure.
-
Checks for a stuck open EVAP purge valve.
-
Verifies that the fuel tank pressure sensor accurately reacts to EVAP system pressure changes.
-
If the EVAP purge and engine vacuum lines are switched at the EVAP purge solenoid, the solenoid valve will leak vacuum.
-
The PCM will command the EVAP purge and EVAP canister vent valves closed with the scan tool Seal System EVAP output control function activated. Fuel tank pressure should not decrease under this condition.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||
Was DTC P1676 also set? | -- | -- | ||
Is Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 0 in. H2O | |||
|
Important:: Before continuing with diagnosis, zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum
(inches of H2O) gauges on the
Can the specified value be achieved? | 5 in. H2O | |||
Is Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 5 in. H2O | |||
Check the EVAP purge and source vacuum line routing and connections at the EVAP purge valve. Refer to Emission Hose Routing Diagram . Are the EVAP purge and source vacuum lines connected correctly at the EVAP purge valve? | -- | |||
7 |
Does the EVAP purge valve maintain vacuum at the specified value? | 15 in. Hg | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
8 |
Important: Check for carbon release into the EVAP system. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Replace the EVAP purge valve. Go to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Correct the EVAP purge and source vacuum line routing and connections. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
Does vacuum remain at the specified value while the scan tool Seal System function is activated? | 0 in. H2O | System OK |
