- Use a charger, with an end voltage of 16 V, equipped with a voltmeter that is accurate to within 1 percent.
- The ambient temperature should be 15-38°C (60-100°F). A battery that is extremely cold will not accept measurable current for several hours after starting the charger.
- Ensure that the charging area is well ventilated.
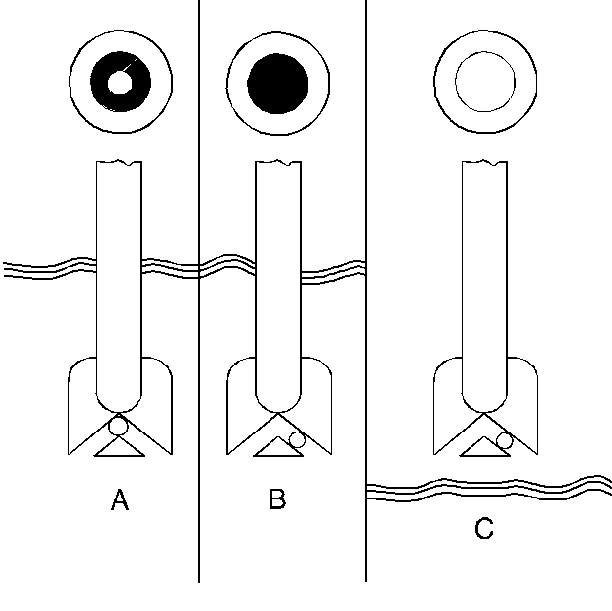
- Do not charge the battery when the built in hydrometer is clear or yellow (C). Replace the battery if there is a cranking problem.
- Do not charge a battery that appears to be frozen. Replace the battery.
- Batteries showing a green dot in the hydrometer (A) do not need to be charged unless the battery has just been discharged (such as cranking the engine).
Charging Time Required
The time required to charge a battery will vary depending upon the following factors:
- The size of the battery
- The temperature
- The charging capacity
- The state-of-charge
A completely discharged, heavy-duty battery requires more than twice as much recharging time as a completely discharged, light duty battery.
More time is required in order to recharge a cold battery. When a fast charger is connected to a cold battery, the current accepted by the battery is very low at first. Then, as the battery warms, the battery accepts a higher rate of current.
Higher amperage chargers require less time to charge a battery.
A completely discharged battery requires more than twice as much charge time as a half charged battery. Because the electrolyte is nearly pure water and a poor conductor in a completely discharged battery, the battery accepts very low current at first. Later, as the charging current causes the electrolyte acid content to increase, the charging current also increases.
Charging Procedure
Tools Required
Notice: Turn OFF the ignition when connecting or disconnecting the battery cables, the battery charger or the jumper cables. Failure to do so may damage the PCM or other electronic components.
- Do not charge a battery with a green hydrometer dot unless the battery has just been discharged, such as by cranking.
- When charging side-terminal batteries on-vehicle, use the following procedure:
- When charging side-terminal batteries out of vehicle, install battery side terminal adapters, GM P/N 12303040.
- Ensure that all of the battery terminals are clean and tight.
- Best results occur when charging a battery that is at room temperature. A battery that is extremely cold may not accept current for several hours.
- Charge the battery until the hydrometer has a green dot.
- Inspect the battery every 30 minutes after starting the battery charger.
- Tap the hydrometer lightly in order to dislodge any air bubbles. The bubbles may cause a false indication.
- After charging the battery, load test the battery.
| 2.1. | Turn off the charger. |
| 2.2. | Connect the charger positive lead to the positive cable terminal located in the engine compartment on the right side. |
| 2.3. | Connect the negative charger lead to a solid engine ground, such as the generator mounting bracket. |

Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Tighten
Tighten the battery side terminal adapters to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
