Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is used to reduce the amount of
nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by combustion temperatures exceeding 816°C
(1,500°F). It does this by introducing small amounts of exhaust gas back into
the combustion chamber. The exhaust gas absorbs a portion of the thermal energy produced
by the combustion process and thus decreases combustion temperature. The EGR system
will only operate under specific temperature, barometric pressure and engine load
conditions in order to prevent drivability concerns and to increase engine performance.
Linear EGR Valve
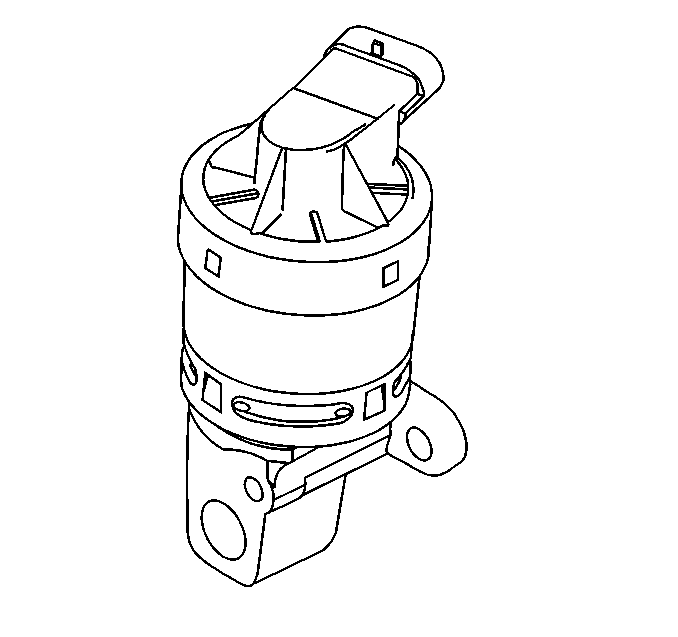
The linear EGR valve consists of the following:
| • | The EGR valve position sensor |
| • | The EGR valve position sensor cap |
| • | The bobbin and coil assembly |
| • | The armature and base assembly |
| • | The exhaust gas inlet port |
| • | The exaust gas outlet port |
Linear EGR Control
The linear EGR valve is controled by a high side driver within the PCM. The
high side driver provides 12 volts that is pulse width modulated (PWM) by a
duty cycle via the high control circuit of the EGR valve . The ground path is provided
by the low control circuit of the EGR valve. The PCM calculates the amount of EGR
needed based on the following inputs:
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | The barometric pressure (BARO) |
| • | The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor |
| • | The throttle position (TP) sensor |
| • | The mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
EGR Diagnostics
The PCM tests the EGR flow during deceleration by momentarily commanding the
EGR valve to open while monitoring the signal of the manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor. When the EGR valve is opened, the PCM will expect to see a predetermined increase
in MAP. If the expected increase in MAP is not detected, the PCM records the amount
of MAP difference that was detected and adjusts a calibrated fail counter towards
a calibrated fail threshold level. When the fail counter exceeds the fail threshold
level, the PCM will set a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Normally, the PCM will only allow one EGR Flow Test Count during an ignition
cycle. To aid in verifying a repair, the PCM allows eighteen EGR Flow Test Counts
during the first ignition cycle following a code clear or a battery disconnect. Between
nine and eighteen EGR Flow Test Counts should be sufficient for the PCM to determine
adequate EGR flow and pass the EGR flow test. If the PCM detects an EGR flow error,
a DTC will set.
The PCM monitors the position of the EGR valve pintle via the EGR position sensor.
If the PCM detects a calibrated variance between the Desired EGR Position parameter
and the EGR Position Sensor parameter, actual position, for a calibrated amount of
time a DTC will set.
The PCM also monitors the EGR soleniod high control circuit and
the EGR soleniod low control circuit for electrical faults. If an EGR control circuit
fault is detected for a calibrated amount of time a DTC will set.

