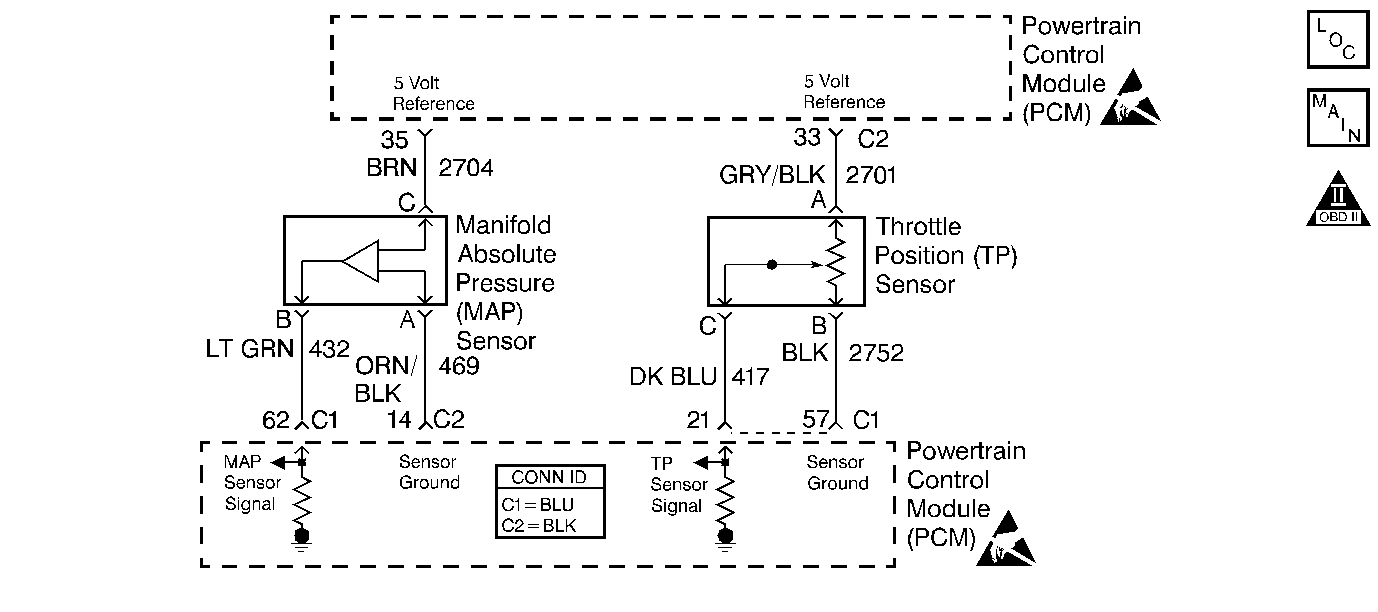
Circuit Description
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a 5.0-volt reference signal and a ground to both the throttle position (TP) sensor and the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. The TP sensor sends a voltage signal back to the PCM relative to the throttle plate opening, and the MAP sensor sends a voltage signal back to the PCM relative to the intake manifold pressure. The PCM can detect if the TP sensor or the MAP sensor are out of range by comparing the two values against the high and low limits and engine speed defined within the engine calibration. If the TP or the MAP are not within the expected limits of the engine calibration, a DTC P0105 is set. During the DTC P0105 test, the actual MAP value is compared to a high limit threshold and low limit threshold for any speed and load in which the vehicle is operated. If the actual MAP value is more than the high limit, or less than the low limit, a malfunction is indicated.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0171, P0172, P0200, P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0325, P0341, P0342, P0440, P0442, P0502, P0506, P0507, P1441 not set.
| • | Engine run time is greater than 40 seconds. |
| • | Engine speed is between 600 RPM and 6375 RPM. |
| • | Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) is stable to within 2.5 percent. |
| • | Engine speed is stable to within 50 RPM. |
| • | IAC valve is stable to within 5 counts. |
| • | The TP sensor is stable to within 2 percent |
| • | The above conditions are present for 1.5 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The MAP sensor is out of an expected range defined on the engine calibration. for 14 out of 16 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | With the ignition turn ON and the engine stopped, the manifold pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will be high. This information is used by the PCM as an indication of the vehicle barometric pressure. Comparison of this reading with a known good vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the same +/-0.4 volt. |
| • | The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thoroughly checked for restrictions at the intake manifold. |
| • | A TP sensor that is stuck will attempt an auto zero every time the engine runs. |
| • | If a DTC P0105 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame/Failure Records data can be useful. Use the scan tool DTC information data in order to determine the status of the DTC. |
- A DTC P0105 may set due to any condition that may cause an unreasonably high or low map value including the following engine conditions:
- A TP sensor that is stuck may attempt to auto zero every time the engine runs. An indication if this happens is the TP percentage will be 0 percent and TP voltage will be high.
- Using a DMM in order to check 5.0 volt reference circuits may not detect small amounts of resistance within the malfunctioning circuit. Connecting a jumper wire from the 5.0 volt reference circuit to the signal circuit detects the small amounts of resistance.
- Certain conditions can produce normal results when probed, but can cause a bad reading when connected. Check for the following conditions on the TP and MAP sensor electrical connectors:
- The MAP sensor needs a dedicated vacuum source. Check the MAP sensor and the MAP sensor vacuum source for the following conditions:
| • | Incorrect cam timing |
| • | Restricted exhaust |
| • | Worn piston rings |
| • | Low fuel pressure |
| - | Spread terminals |
| - | Poor electrical terminal connections |
| - | Vacuum leak |
| - | Split vacuum hose |
| - | Shared vacuum source |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the malfunction occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
A DTC P0507 may also set under Last Test Failed if a vacuum leak is present. Refer to DTC P0507 Idle Speed High .
-
The TP sensor has an auto zeroing feature. If the voltage reading is between 0.2 to 0.9 volts, the PCM will assume the TP sensor is at a closed throttle position (0%). If the reading is out of the auto zeroing range at closed throttle, look for a binding or damaged linkage. Additional information can be found in the Engine Scan Tool Data Definitions .
-
Normal TP voltage when the throttle plates are fully closed is near 0.50 volts. A sensor will display a higher voltage when the sensor is stuck or a circuit is malfunctioning.
-
A MAP sensor that displays a BARO value that does not appear normal for the altitude, the sensor is considered to be malfunctioning. Additional information can be found in the Engine Scan Tool Data Definitions
-
While starting the engine, the MAP sensor should detect any changes in the manifold pressure. This test is to determine if the MAP sensor is stuck at a value. Additional information can be found in the Engine Scan Tool Data Definitions .
-
A normal MAP sensor will react as quickly to the throttle changes as they can be made. A MAP sensor should not appear to be lazy or catch up with the throttle movements.
-
A sensor that cannot maintain a steady value, should be checked for a poor connection or chaffed wiring. If no wiring malfunction is found, Replace the malfunctioning sensor.
-
This step checks if the reason for a no MAP change was due to a malfunctioning sensor or a poor vacuum source to the sensor.
-
The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thoroughly checked for restrictions. A drill bit can be used to clean out any casting flash that may exist in the vacuum port.
-
A disconnected TP sensor should not display a voltage reading on the scan tool. An amount less than the specified value is normal.
-
When the test light is connected to the ground circuit, the test light should glow brightly if the ground circuit may be OK but could have a small amount of resistance in the circuit.
-
Important: The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) uses a single 5.0 volt power supply to supply power to all the engine control components. If one component shorts its 5.0 volt reference circuit to ground or battery voltage, the other 5.0 volt reference circuits will also have a low or high voltage.
Disconnecting other sensors that are connected to the 5.0 volt reference circuits internally to the PCM determines if the 5.0 volt reference circuit is shorted or if one of the sensors is causing a short on the 5.0 volt reference circuit.
-
Replacement PCMs must be reprogrammed and the crankshaft position system variation procedure must be preformed. Refer to the latest Techline information for programming procedures and also refer to the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn .
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||
Does the TP angle value increase steadily when the accelerator pedal is depressed to greater than the first specified value and decrease steadily returning to the second specified value when the pedal is released? | 98% 0% | |||||||||
Does the scan tool display a TP voltage below the specified value when the throttle is fully closed? | 0.90 V | |||||||||
Compare the BARO reading with a known good vehicle. Is the BARO reading normal for your altitude? | -- | |||||||||
Start the engine while watching the MAP sensor value with the scan tool. Does the MAP sensor value change while starting the engine? | -- | |||||||||
With the engine still running, snap the throttle while watching the MAP sensor display on the scan tool. Does the MAP sensor value change rapidly when the throttle position changes? | -- | |||||||||
Does the MAP sensor perform correctly through the ranges? | -- | |||||||||
9 | Does the TP sensor perform correctly through the ranges? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
10 |
Does the scan tool read the specified value? | 0.0 V | ||||||||
11 |
Does the DMM read the specified voltage? | 5.0 V | ||||||||
12 |
Does the scan tool read the specified value? | 5.0 V | ||||||||
13 |
Does the DMM read a voltage greater than the specified value? | 0.5 V | ||||||||
Does the MAP sensor value on the scan tool change? | 15 in Hg | |||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||
16 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
17 | Does the MAP sensor 5.0 reference circuit read near the specified value on the DMM? | 12 V | ||||||||
18 |
Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
19 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
20 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
21 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
22 |
Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
23 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
24 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
25 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
Does the scan tool read the specified value? | 0.0 V | |||||||||
27 |
Does the DMM read the specified voltage? | 5.0 V | ||||||||
28 |
Does the scan tool read the specified value? | 5.0 V | ||||||||
Does the DMM read a voltage greater than the specified value? | 0.5 V | |||||||||
30 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
31 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
32 |
Does the DMM display a voltage near the specified value? | 5.0 V | ||||||||
Does the DMM display a voltage near the specified value? | 5.0 V | |||||||||
34 |
Is the action complete? | 5.0 V | -- | |||||||
35 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
36 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
37 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
38 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||
40 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||
41 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
