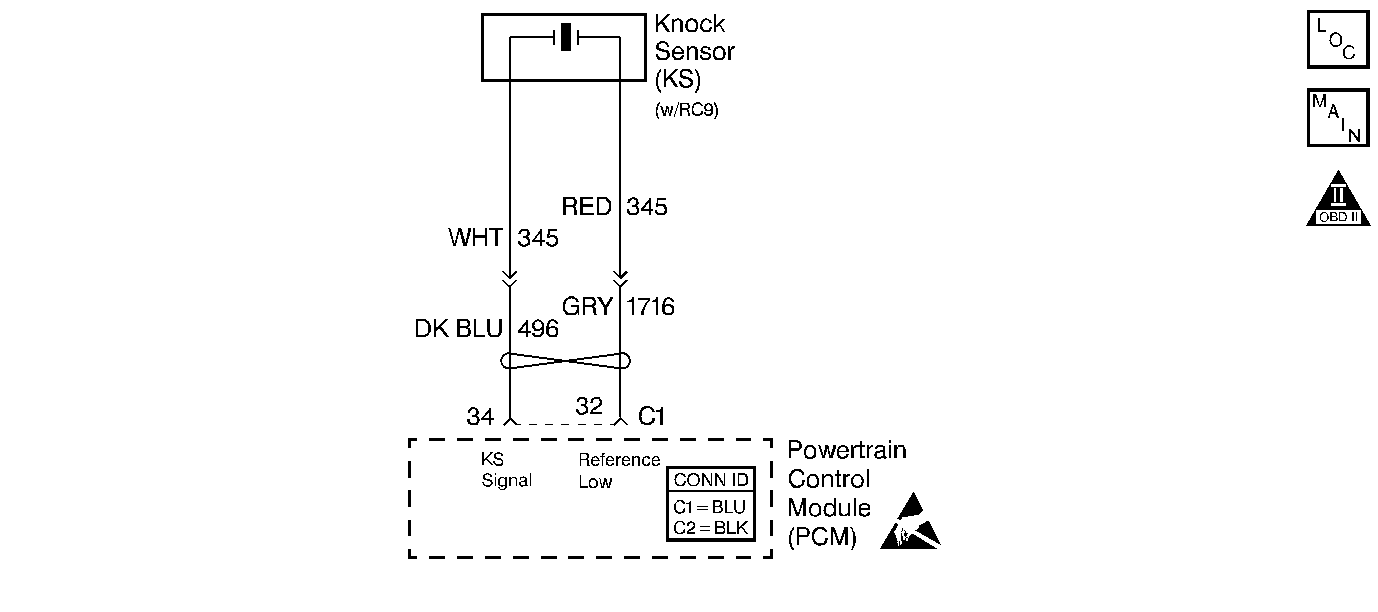
Circuit Description
The knock sensor system detects for an engine detonation. The knock sensor produces an AC voltage signal. The amplitude and the frequency of the AC voltage signal is dependent upon the knock level being detected. This signal then travels to the KS module that is an internal part of the PCM. If knock is detected, the PCM will retard the spark timing based on the signal from the knock sensor. The Knock Sensor (KS) does not contain an internal 100 kohms resistor as the Knock Sensors did in the past. The resistor is now internal of the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Engine run time is greater than 20 seconds. |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than 70°C (158°F). |
| • | Engine speed is between 1800-2400 RPM. |
| • | MAP is greater than 35 kPa. |
| • | Engine vacuum is between 33-45 kPa. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The KS voltage and variation is not within normally expected ranges. |
| • | The above conditions are present for greater than 15 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time when the diagnostic fails. This information stores in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before using the diagnostic table. |
| • | Thoroughly check any suspected circuitry for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed connectors |
| - | Damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| - | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | Check the knock sensor and knock sensor mounting location for the following conditions: |
| - | The knock sensor must be torqued correctly to 25 N·m (19 lb ft). |
| - | The knock sensor mounting location between the sensor head and the engine mounting face is free of the following conditions: |
| - | Burrs |
| - | Casting flash |
| - | Foreign material |
| - | The knock sensor head is clear from contacting any of the following items: |
| - | Hoses |
| - | Brackets |
| - | Engine electrical wiring |
| • | Check the knock sensor wiring for the correct twisting of the wiring. The wiring for the knock sensor should have a minimum of 9 twists per foot. This twisting of the wiring, reduces electrical noise on the knock sensor circuit lessening the chance of erratic signals to the PCM. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when this DTC is set. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
If the engine has an internal knock or an audible noise that causes a knocking type of noise on the engine block, this is an indication that the knock sensor may be responding to the noise.
-
This step checks the internal resistance of the PCM or the wiring to the knock sensor electrical connector.
-
Thoroughly check any suspected circuitry for the following conditions:
-
Reprogram the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learning procedure. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn for the crankshaft position variation learning procedure.
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||
Is a knock or audible noise present? | -- | |||||||||
3 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
4 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
Is the resistance between the specified values? | 95K -105K ohms | |||||||||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
7 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
10 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | ||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||
12 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||
13 | Check to see if any DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
