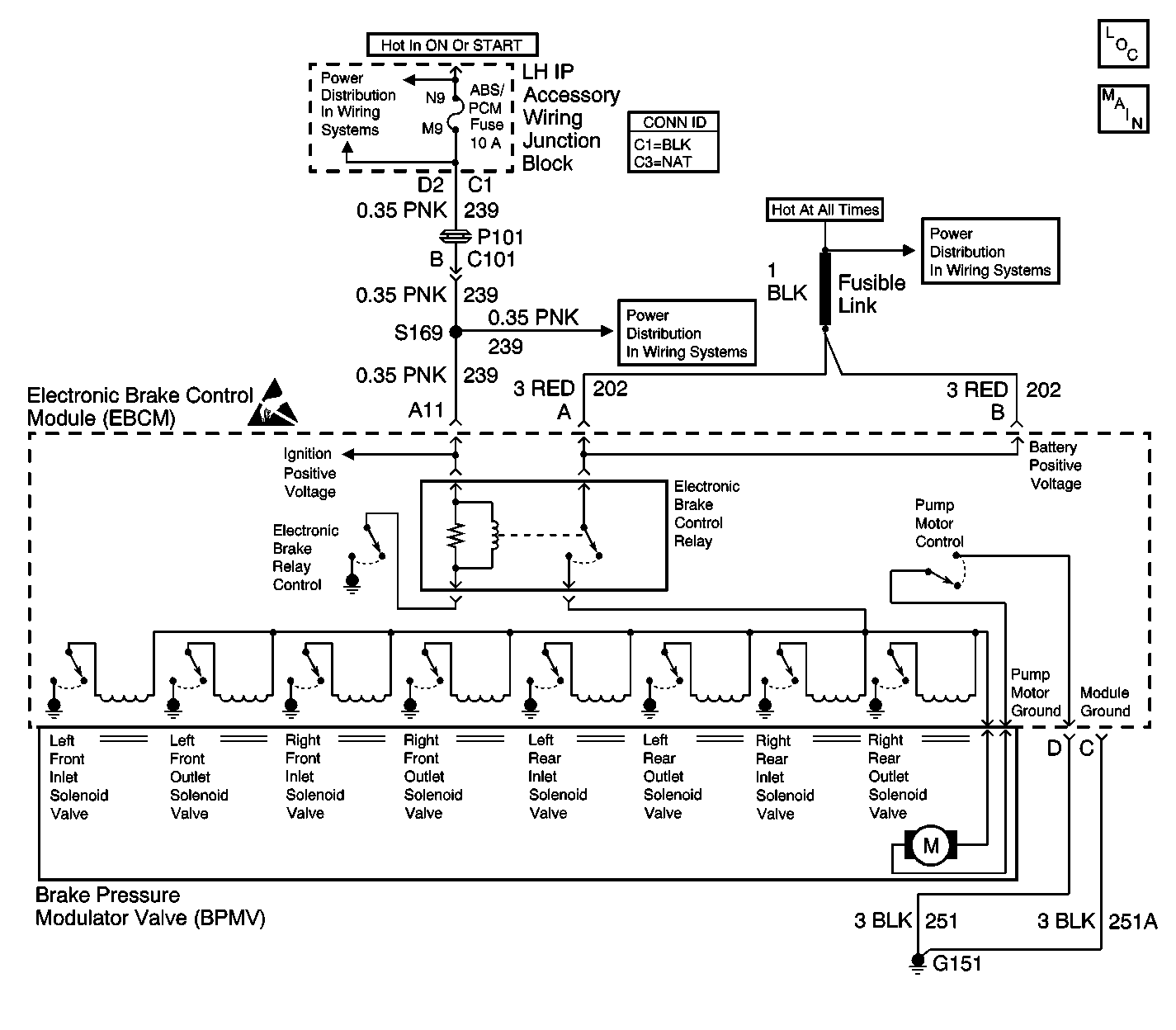
Circuit Description
The pump motor is an integral part of the Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV). The electronic brake control relay supplies power to the solenoid valves and pump motor. This voltage is referred to as the system voltage. The electronic brake control relay, located in the EBCM, is activated whenever the ignition switch is in the RUN position and no faults are present. The electronic brake control relay remains engaged until the ignition switch is turned off or a failure is detected.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The pump motor is ON for at least 0.3 seconds. |
| • | The electronic brake control relay is ON. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The EBCM determines that the pump motor is turning slowly or not at all.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
If equipped, the following actions occur:
| • | The EBCM disables the ABS/TCS for the duration of the ignition cycle. |
| • | The ABS indicator turns ON. |
| • | The Traction Off indicator turns ON. |
| • | The message center displays the Service Traction System message. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Condition for DTC is no longer present and scan tool clear DTC function is used. |
| • | 100 ignition cycles have passed with no DTCs detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Possible causes for DTC C1243 to set are: |
| - | The pump motor has high resistance. |
| - | The pump motor jammed (seized). |
| - | The pump motor turns too slowly (due to corroded pump motor or contaminated pump circuit). |
| • | The pump motor is part of Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) and is not serviceable separately. |
| • | The solenoid valve control relay is integral to the EBCM and is not serviceable separately. |
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the ABS Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Is the connector OK and cavity free of brake fluid? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 3 |
3 |
Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 7 | -- |
4 | Replace the BPMV. Refer to Brake Pressure Modulator Valve Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 5 | -- |
5 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 6 | System OK |
6 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 6 | -- |
7 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
