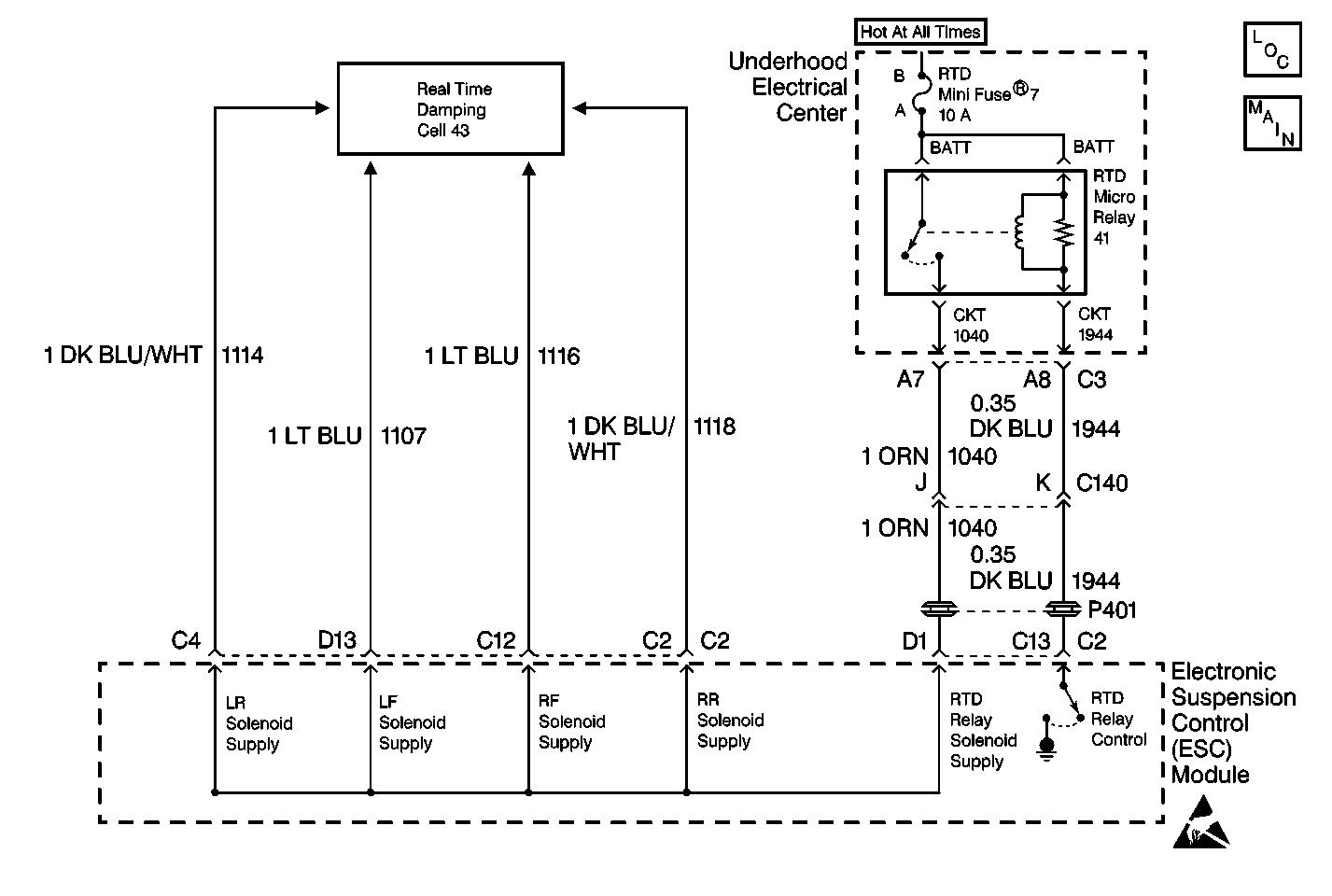
Circuit Description
Solenoid supply voltage is applied to the ESC module through the RTD relay circuit. The ESC module controls the RTD relay by grounding CKT 1944. This closes the relay contacts providing each shock absorber solenoid with supply voltage through the ESC module's internal solenoid supply circuitry. Each individual solenoid drive then controls the operation of the corresponding shock absorber. The ESC module monitors the RTD relay control/solenoid supply circuits for any malfunction conditions.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The ESC module detects low voltage (an open or a short to ground) on the RTD relay control CKT 1944. |
| • | Detection for this DTC can only be accomplished during the OFF (relay not applied) state. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Stores a DTC C1787 in the ESC memory. |
| • | Commands 0% PWM duty cycle in order to disable all four solenoids. |
| • | Sends a message to the IPC to display the SERVICE RIDE CONTROL and the SHOCKS INOPERATIVE messages. |
| • | Sends a message to the PCM to limit the speed. The PCM then sends a massage to the IPC to display the MAXIMUM SPEED 129 km/h (80 mph) message. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The ignition must be cycled before this DTC can change from current to history even if the malfunction is no longer present. |
| • | The ESC module no longer detects low voltage (an open or a short to ground) on the RTD relay control CKT 1944 with the relay OFF. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 100 consecutive ignition cycles if the condition for the malfunction is no longer present. |
| • | The IPC clearing DTCs feature. |
| • | Using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction: |
| - | An open or a short to ground on the RTD relay control CKT 1944. |
| - | An open RTD relay coil or high resistance condition. |
| - | An open RTD relay fuse #7. |
| - | A short to ground on any shock absorber solenoid supply circuit. |
| - |
| • | The RTD relay may be installed in the underhood electrical center in two directions and still function properly. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for electrical center identification. |
| • | The RTD relay provides supply voltage to all four shock absorber solenoids. Therefore, multiple shock absorber solenoid open or short to ground DTCs may also be stored along with a DTC C1786. Diagnose a DTC C1787 first before attempting to diagnose multiple shock absorber solenoid DTCs. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
This step checks the underhood electrical center supply voltage.
-
This step checks for a short to ground on the RTD relay control CKT 1944.
-
This step measures the resistance of the RTD relay coil.
-
This step checks for an open on the RTD relay control CKT 1944.
-
This step checks for an intermittent malfunction and requests a thorough inspection of the related RTD relay circuit wiring and connectors.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the RTD Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||
Is the voltage indicated over the specified value? | 10.0 V | |||
Is there continuity? | -- | |||
Measure the resistance of the RTD relay coil between terminals 1 and 2 (or 85 and 86). Is the resistance reading within the specified value? | 75-105 ohms | |||
Was the voltage indicated over the specified value? | 10.0 V | |||
Check the RTD relay circuit for an intermittent malfunction. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Was an intermittent malfunction found and repaired? | -- | |||
7 | Locate and repair the short to ground in the underhood electrical center or CKT 1944. Is the circuit repair complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Locate and repair the open in CKT 1040. Is the circuit repair complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Locate and repair the open in the underhood electrical center, the RTD open fuse, or the power feed to the underhood electrical center. Is the circuit repair complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Replace the RTD relay. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Replace the ESC module. Refer to Electronic Suspension Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- |
