Distributor Ignition System
The primary components of the distributor ignition (DI) system are:
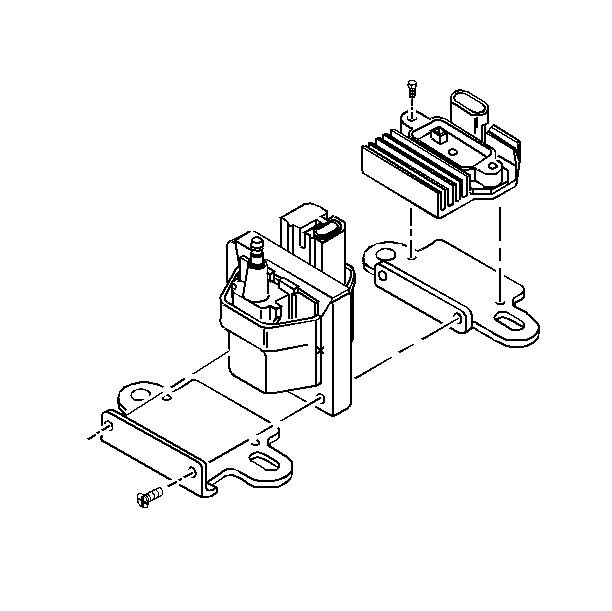
| • | The ignition control module (ICM) |
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) |
| • | The PCM timing control circuits |
| • | The vacuum harness primary wiring |
| • | The vacuum harness secondary wiring |
| • | The camshaft position (CMP) sensors |
| • | The crankshaft position sensor |
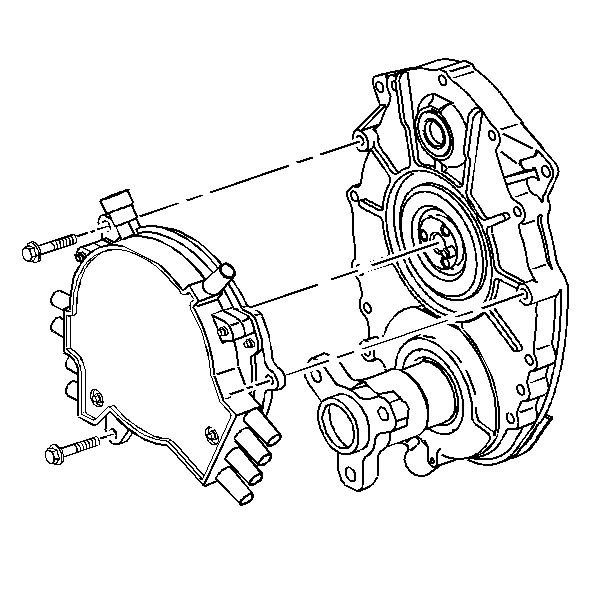
The distributor is mounted directly to the front cover behind the water
pump. The distributor directs the spark from the ignition coil to the proper
spark plug secondary wire through a rotor. The spark plug secondary wire connectors
in the cap are arranged in a way that eases in the routing of the spark plug
wire harnesses. A cylinder number is molded on each distributor cap next to
each spark plug secondary wire connector.
The distributor contains a signal disk and two optical camshaft position
(CMP) sensors that send signals to the PCM for timing control. The PCM controls
all ignition timing. Thus, there is no bypass mode built into the ICM. One
CMP sensor senses 360 equally spaced slots in the signal disk in order to
provide 720 signals per camshaft revolution for high resolution timing control.
The second CMP sensor senses eight disk slots of varying lengths, providing
a low resolution signal which tells the PCM which of the spark plugs is being
fired.
The PCM determines if one of the timing inputs is not being received
by comparing the two inputs. If the PCM detects one timing pulse without detecting
the other, DTC 16 or 36 will set. Power for the optical CMP sensors, the system
ground, and the two CMP sensor signals is transferred between the PCM and
the distributor through a shielded harness on the four terminal distributor
connector.
The reference signals toggle between 0-5 Volts as the camshaft
turns. Therefore, any of the following situations can prevent the voltage
from pulsing at the PCM:
- An open circuit
- A short to voltage
- A short to ground
- A defective sensor

The ignition coil and the ICM provide a spark to the distributor, timed
by the PCM signals. Power for the ignition coil primary circuit and the ICM
is supplied through the ignition switch. The PCM combines the CMP information
supplied by the distributor with other system parameters. The PCM then calculates
the required spark advance. The PCM signals the ICM, which turns on the primary
circuit to the ignition coil by grounding the primary circuit, and then turns
it off by removing the ground. When the primary circuit current flow stops,
high voltage induced in the ignition coil secondary winding becomes the spark
voltage for the spark plug. The spark voltage is delivered to the distributor
through the secondary coil output wire, and then directed to the proper spark
plug connector by the distributor rotor.
Electronic Ignition System
The electronic ignition (EI) system controls fuel combustion by providing
a spark to ignite the compressed air/fuel mixture at the correct time. The
powertrain control module (PCM) controls the distributor spark advance and
retard (timing). The EI system provides improved engine performance, fuel
economy, and control of exhaust emissions.
The EI system has the following advantages over a mechanical distributor
system:
- No moving parts
- Low maintenance
- Remote mounting capability
- No mechanical load
- More coil cool down time between firing events
- No mechanical timing adjustments
- Increased available ignition coil saturation time




