DTC 38 TCC Brake Switch High Input L57 MFI
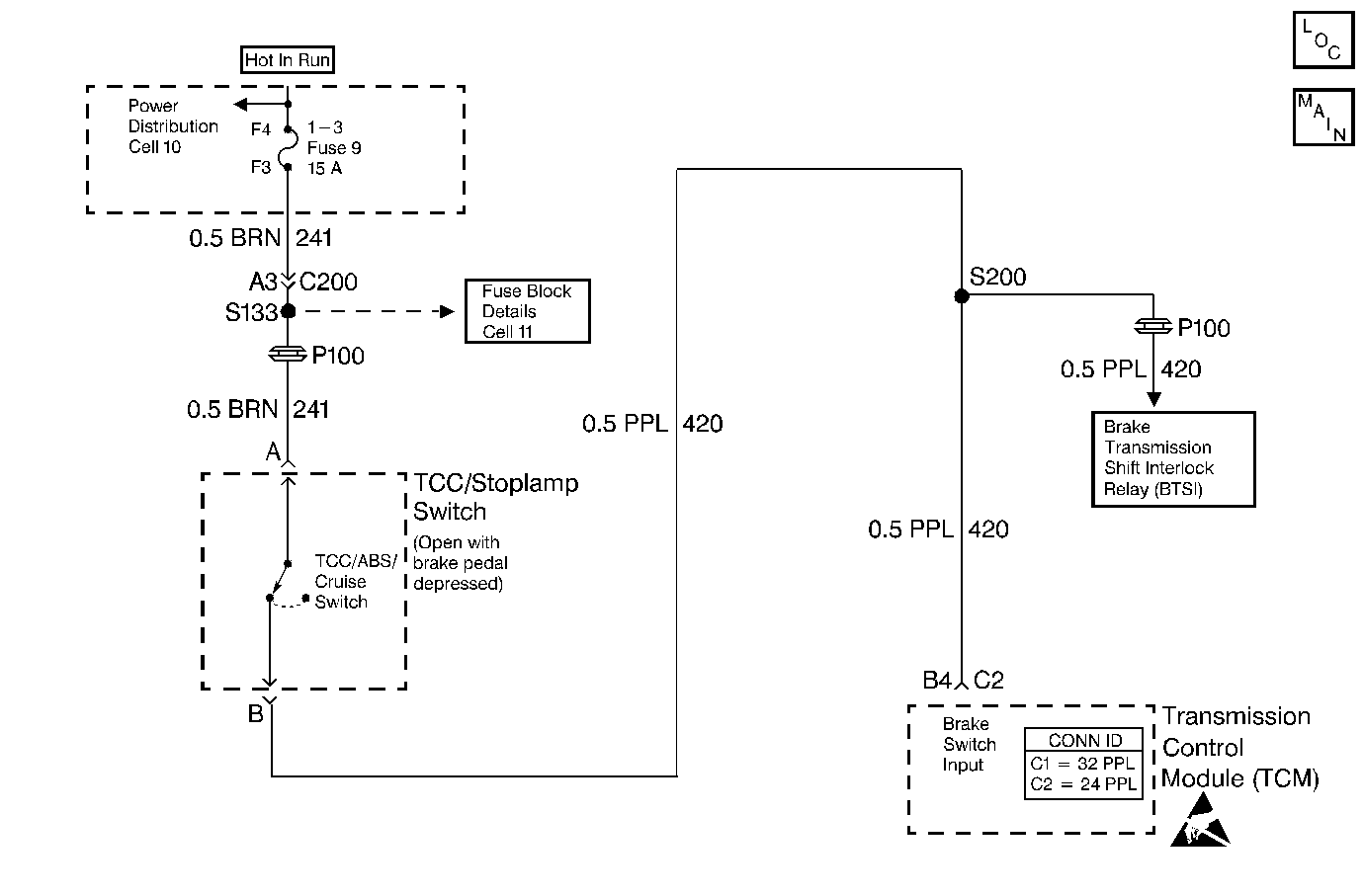
Circuit Description
The TCC stoplamp switch indicates the brake pedal status. The normally-closed TCC stoplamp switch supplies a B + signal on circuit 420 to the transmission control module (TCM). The signal voltage circuit opens when the brakes are applied. The TCM uses the open signal voltage circuit in order to de-energize the torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve when the brakes are applied.
If the TCM detects a closed TCC stoplamp switch circuit during accelerations, then DTC 38 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The following sequence of events occurs:
| • | The vehicle speed is greater than 32 km/h (20 mph) for 6 seconds. |
| • | Then the vehicle speed is 8-32 km/h (5-20 mph) for 6 seconds. |
| • | Then the vehicle speed is less than 8 km/h (5 mph). |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | All conditions are met for seven occurrences. |
| • | The TCM detects a closed TCC stoplamp brake switch/circuit (12 volts) for 2 seconds during decelerations. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The TCM does not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The TCM inhibits TCC. |
| • | The TCM will inhibit 4th gear if in hot mode. |
| • | The TCM stores DTC 38 in TCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A scan tool clears the DTC from TCM history. |
| • | The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive key cycles without a diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The TCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the TCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect the wiring at the TCM, the TCC stoplamp switch connector and all other circuit connecting points for the following conditions: |
| - | A backed out terminal |
| - | A damaged terminal |
| - | Reduced terminal tension |
| - | A chafed wire |
| - | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| - | Moisture intrusion |
| - | Corrosion |
| • | When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open, massage the wiring harness while watching the test equipment for a change. |
| • | Ask about the customer's driving habits and any unusual driving conditions he or she might have, such as stop and go traffic or expressway driving. |
| • | Inspect the TCC stoplamp switch for proper mounting and adjustment. |
| • | Inspect for the most current calibration ID and the latest bulletins. |
| • | Inspect for any transmission DTCs that may have reset. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step isolates the TCC stoplamp switch as a source for setting the DTC.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Important:: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Failure Records from the TCM. Did the TCC brake switch status change from CLOSED to OPEN? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Did the TCC brake switch status change from CLOSED to OPEN? | -- | |||
4 | Replace the TCC stoplamp switch. Refer to Stoplamp Switch Replacement in Hydraulic Brakes. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
5 | Inspect circuit 420 (PPL) for a short to B+. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was a short to B+ condition found? | -- | ||
6 | Replace the TCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming in Engine Controls. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Repair the wiring as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Does the Scan Tool TCC brake switch status change from CLOSED to OPEN? | -- | System OK |
