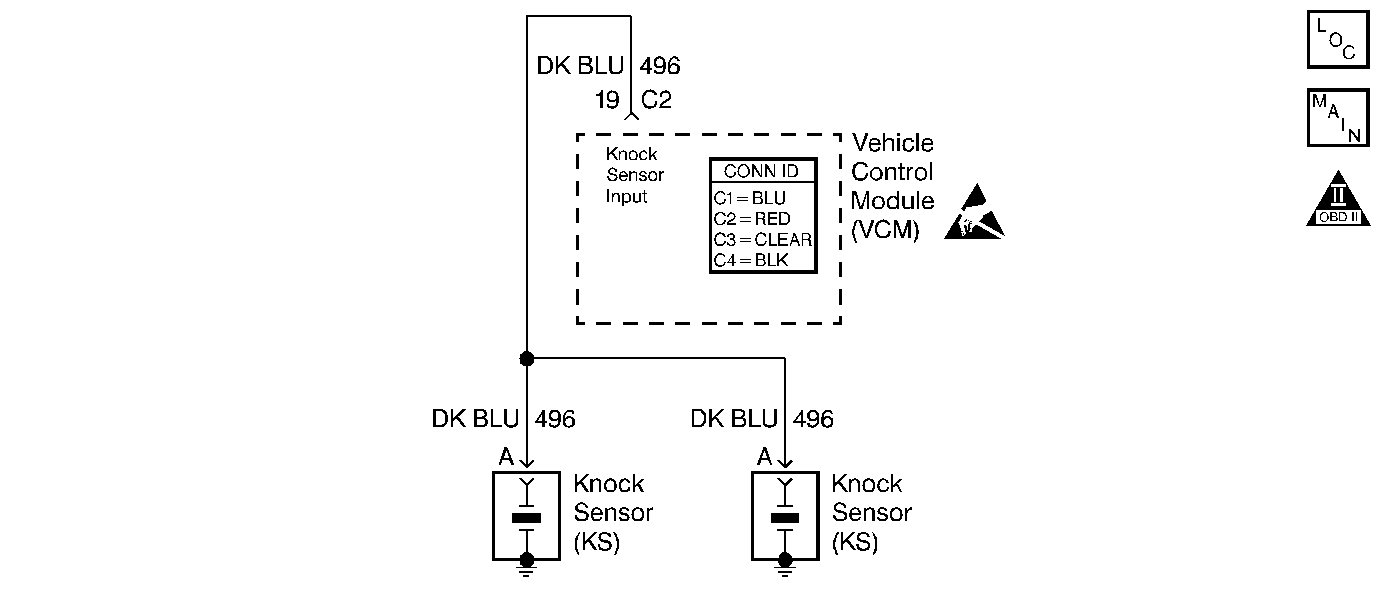
Circuit Description
The control module uses the knock sensors (KS) in order to detect engine detonation. Ignition control (IC) spark timing is retarded based on the KS signal input when spark knock is detected.
The control module monitors normal engine background noise during warm engine operation. It stores these noise values for comparison to the current knock sensor signal in order to help discriminate between normal engine noise and knock. If the amount of noise is below the minimum stored noise value, this diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active ECT sensor DTCs |
| • | No active TP sensor DTCs |
| • | The timing retard is 0° or less. |
| • | System voltage is between 10 and 17.1 volts |
| • | The ECT is greater than 60°C (140°F) |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 2 minutes |
| • | The knock sensor noise is less than 3 counts |
| • | The engine speed is between 2,000 and 3,000 RPM |
| • | The throttle position is greater than 6% |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The difference between the actual noise value and the learned minimum noise value is less than 50 counts or more than 200 counts
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The VCM illuminates the MIL during the second consecutive drive cycle in which the diagnostic reports a fail. |
| • | The VCM will set the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The VCM stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection at the VCM -- Inspect the knock sensor and the VCM connectors for the following items: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | A misrouted harness -- Inspect the knock sensor harness in order to ensure that it is not routed too close to high voltage wires such as spark plug leads. |
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
| • | Improper knock sensor torque specification. Torque the knock sensor to 19 N·m (14 lbs ft). |
Review the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed in order to help determine how often the conditions that caused the DTC to set occur. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the insulation.
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, then refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Ensures that the condition is present.
-
Ensures that the knock sensor is capable of detecting detonation. Striking the lift bracket with a non-metallic object should produce a signal that the knock sensor should detect.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference because the data will be lost when the Clear Info function is used. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool indicate the DTC P0327 failed this ignition? | -- | |||
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate the DTC P0327 Failed This Ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
4 |
Is the voltage above the specified value at both sensors? | 4.5 V | ||
5 | Measure the resistance of each knock sensor by connecting the J 39200 DMM between the KS terminal and the engine block. Is the resistance of each knock sensor near the specified value? | 8K ohms | ||
Are any signals indicated on the J 39200 DMM while tapping on the engine lift bracket? | -- | |||
7 | Check the KS signal circuits for a poor terminal connection at the knock sensor. Repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
8 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
9 | Probe the KS harness connector with a test lamp to the B+ terminal. Is the test lamp ON. | -- | ||
10 | Repair the short to ground in the KS signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Replace the Knock Sensor/s that did not produce a signal. Refer to Knock Sensor Replacement Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
13 | Check the Knock Sensor Module for incorrect terminal mating and make sure it is fully seated. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
14 | Replace the Knock Sensor Module. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
16 |
Refer to Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
17 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
18 | Display the Capture Info and the Review Capture Info functions with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
