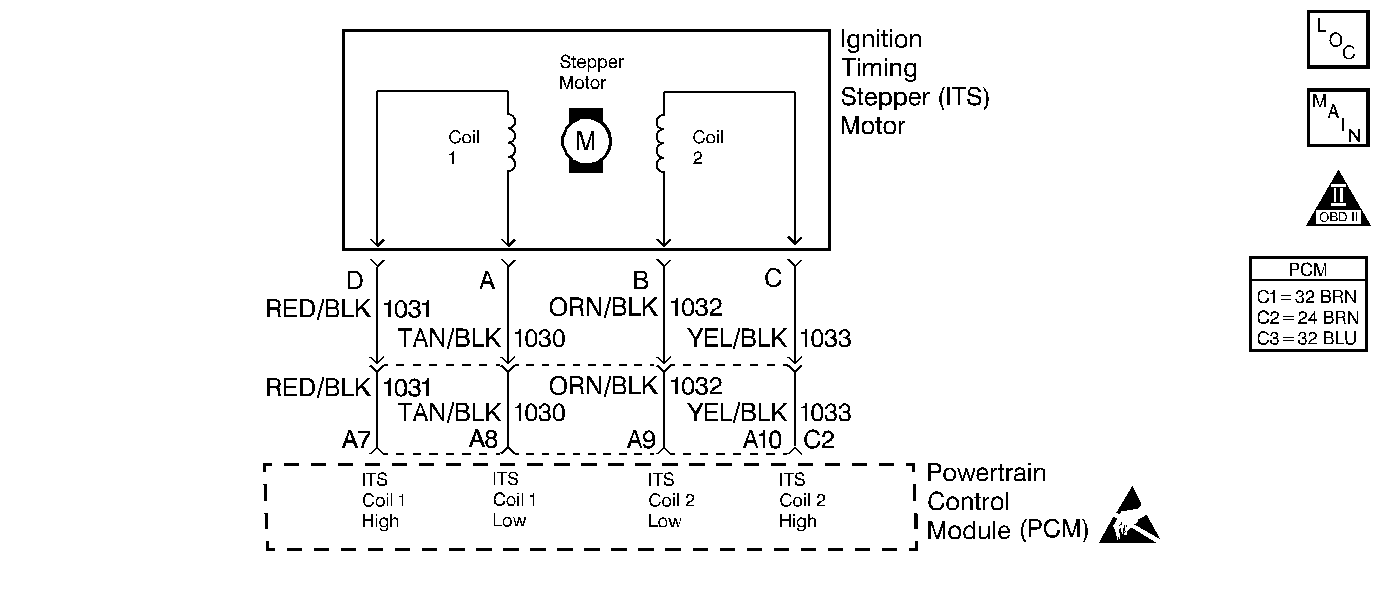
Circuit Description
The timing of the combustion event is accomplished by delivering a pulse of fuel into the combustion chamber at a desired degree of piston travel. This desired degree (desired timing) defines the current position of the piston in relationship of top dead center (TDC). This test compares the desired timing to the measured timing when certain conditions have been met. In order to retard the injection timing, the PCM extends the Stepper motor. To advance the injection timing, the PCM retracts the Stepper motor.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine speed has not changed more than 56 RPM for 20.8 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
A 5 degree difference between the Act. Inj. Time and Des. Inj. Time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the Failure Records store this information. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the Freeze Frame records the operating conditions at the time of failure and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL off after three consecutive trips without a fault condition. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emmision related diagnostic does not report any failures. |
| • | Use of a scan tool will clear the DTC codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by the following:
| • | Poor connections |
| • | A rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
A hard start and a possible poor performance condition might exist. The Act. Inj. Time will freeze at the point of the fault. DTC P0216 will possibly set if the injection timing is not set correctly. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Timing Adjustment for the correct procedure.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step determines if DTC P0216 is a hard failure or an intermittent.
-
This step checks for an open or short in the injection timing coil circuit 1.
-
This step checks for an open or short in the injection timing coil circuit 2.
-
The important thing in this step is that the PCM is sending a varying voltage [voltage may vary between 1 and 12 (usually you will see voltage vary between 5 and 6 when engine is idling)], this will indicate that the PCM is OK and that there is a problem with the injection timing stepper motor. If there is a steady voltage present on any circuit, this will indicate a problem with the PCM or a circuit shorted to voltage.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
Does the scan tool display a difference greater than or equal to the specified value between Actual Inj Time and Desired Inj Time at idle or at 2700 RPM? | 5° | |||||||||
3 | The DTC is intermittent. If no additional DTCs are stored, refer to Diagnostic Aids. If additional DTCs were stored refer to those table(s) first. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids
| ||||||
Is the resistance within the specified value? | 10 - 60 Ohms | |||||||||
Measure the resistance between coil 2 low and coil 2 high at the PCM harness. Is the resistance within the specified value? | 10 - 60 Ohms | |||||||||
Does the voltage vary on all circuits? | -- | |||||||||
7 |
Is the resistance within the specified value? | 950 -1050 Ohms | ||||||||
8 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||||||||
10 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||||||||
11 | Check for a proper electrical connection at the injection timing stepper motor. Did any terminals require replacement? | -- | ||||||||
12 | Check the non-varying circuit for a short to ground, short to voltage, or a proper connection at the PCM. If a problem is found , repair the problem as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||||||||
13 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||||||||
14 | Replace the crankshaft position sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . After replacing the sensor, the PCM must be programmed with a new offset. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Top Dead Center Offset Adjustment . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
15 |
Important: The new injection pump must be timed. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Timing Adjustment . Replace the injection pump. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
16 |
Important: The new PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
17 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||||||||
18 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
