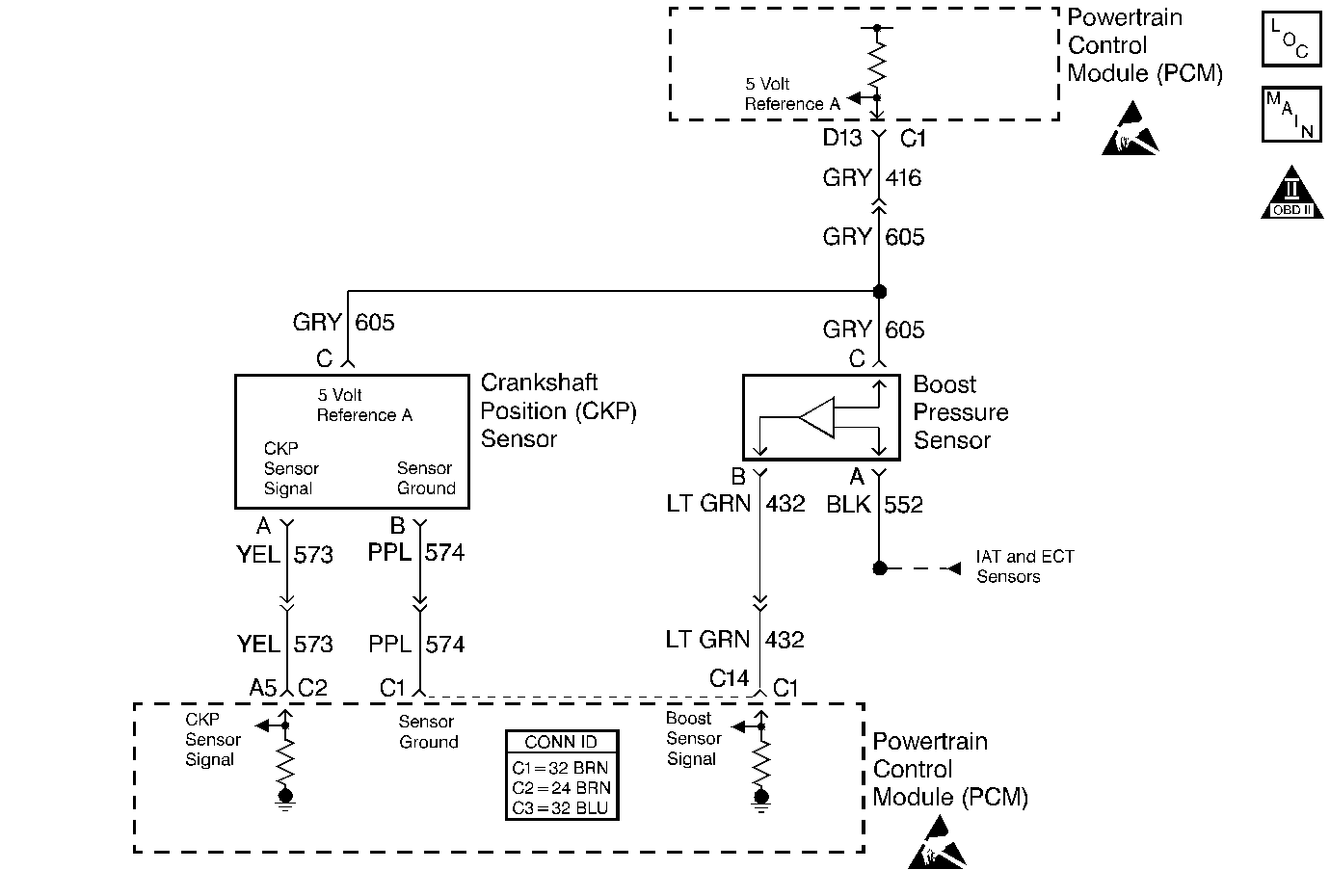
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position sensor is a Hall-effect type of sensor which monitors the crankshaft position and the speed. There are four teeth 90 degrees apart on the front of the crankshaft sprocket which induce a pulse in the sensor which is transmitted to the PCM. There is a physical one to one correspondence between the pump cam and the crankshaft.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is operating.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Eight consecutive crank pulses are missing. |
| • | An average of eight consecutive crank pulses are missing. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the first drive trip the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, this information is stored in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL off after three consecutive trips without a fault condition. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive engine warm up cycles, if this or any other emmision related diagnosic does not report any failures. |
| • | Use of a scan tool will clear the DTC codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
When the PCM is in backup fuel, long crank times, fast idle and poor performance conditions will exist. Check for a good connection at the crankshaft position sensor and at the PCM. Many intermittent problems are caused by poor electrical connections or wiring. When attempting to diagnose an intermittent problem, always begin by trying to reproduce the conditions under which the failure occurs. This usually involves raising the engine to a higher temperature or operating the engine near the RPM where the problem occurs. Since heat and vibration are often the cause of the intermittent, this may bring out the failure.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step will determine if DTC P0335 is the result of a hard failure or an intermittent condition.
-
This step checks the 5 volt reference circuit (the 5 volt reference may vary slightly).
-
This step checks the ground circuit.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool display the specified value? | 8 | |||
3 | The DTC is intermittent. If no additional DTCs are stored, refer to the Applicable DTC Table(s) first. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.8-5.2 V | |||
Probe the sensor ground circuit using a J 35616-200 unpowered test lamp connected to B+. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | |||
6 |
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 4.2-4.5 V | ||
7 | Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 4.2-4.5 V | ||
8 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||
9 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||
10 | Check the CKP 5 volt reference circuit for a proper connection at the PCM and replace the terminal if necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did the terminal require replacement? | -- | ||
11 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||
12 |
Is there voltage present on the CKP sensor signal circuit? | -- | ||
13 | Repair the short to voltage on the CKP sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Check the CKP signal circuit for a proper connection at the PCM and replace the terminal if necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did the terminal require replacement? | -- | ||
15 | Replace the Crankshaft position sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . After replacing the sensor, the PCM must be programmed with a new TDC Offset. Refer to Fuel Injection Pump Top Dead Center Offset Adjustment . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 |
Important: The new PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
17 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
18 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
