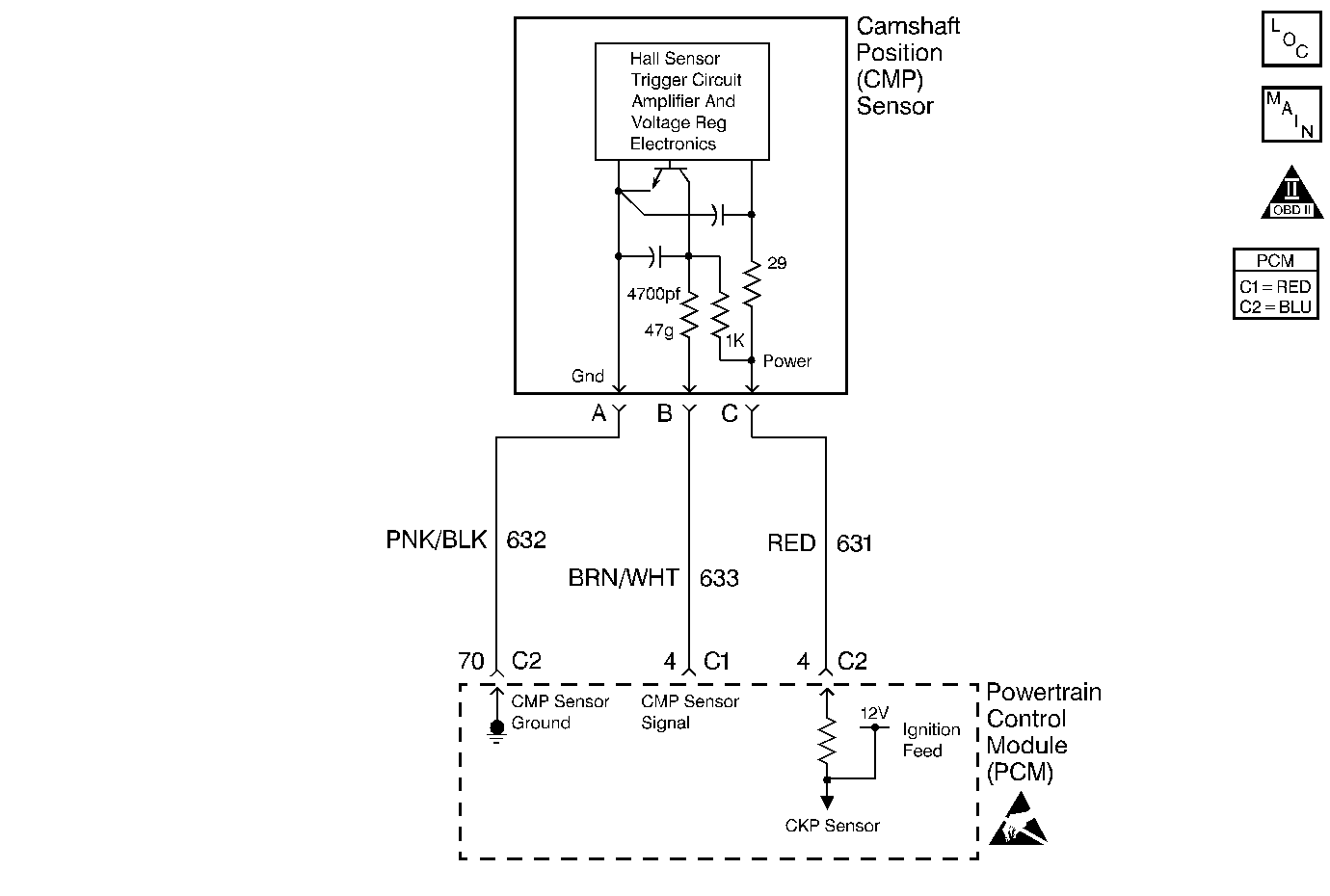
Circuit Description
The Camshaft Position sensor is mounted through the top of the engine block at the rear of the valley cover. The CMP sensor works in conjunction with a 1X reluctor wheel on the camshaft. The reluctor wheel is inside the engine immediately in front of the rear cam bearing. The PCM provides a 12 volt power supply to the CMP sensor as well as a ground and a signal circuit.
The CMP sensor determines whether a cylinder is on a firing stroke or on an exhaust stroke. As the camshaft rotates, the reluctor wheel interrupts a magnetic field produced by a magnet within the sensor. The sensors internal circuitry detects this and produces a signal which the PCM reads. The PCM uses this 1X signal in combination with the Crankshaft Position sensor 24X signal in order to determine crankshaft position and stroke. This diagnostic for the Camshaft Position sensor checks for a loss of Camshaft Position sensor signal.
Observe that as long as the 24X signal is available, the engine starts even if there is no Camshaft Position sensor signal. The PCM can determine when a particular cylinder is on either a firing or exhaust stroke by the 24X signal alone, but the PCM requires the cam signal in order to determine which (firing or exhaust). The system attempts synchronization and looks for an increase in MAF signal indicating the engine started. If the PCM does not detect a MAF increase, the PCM assumes it incorrectly synchronized to the exhaust stroke and re-syncs to the opposite cam position. A slightly longer cranking time may be a symptom of this condition.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | System voltage is between 5.0 volts and 17.0 volts. |
| • | Engine speed is less than 4000 RPM. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects that a CMP to CKP mis-match has occurred for 10 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, this information will be stored in Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the operating conditions at the time of failure will be written to Freeze Frame and the Failure record will be updated. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles (coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 70°C (160°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear Information function. |
| • | Disconnect the PCM battery feed for 30 seconds. |
Diagnostic Aids
A poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation may cause an intermittent.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections or |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | Camshaft reluctor wheel damage. |
| • | Camshaft reluctor wheel damage. |
| • | Check for improperly installed camshaft position (CMP) sensor. |
Refer to Symptoms .
Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can be useful in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that were noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step verifies that the malfunction is present.
-
This step checks for EMI (Electro Magnetic Interference) on the CMP sensor circuits.
-
Vertical lines across the face of the sensor could indicate foreign material passing between the CMP sensor and the reluctor wheel. This condition would cause this DTC to set.
-
Damage to the reluctor wheel would affect the CMP sensor output. If this condition exists, refer to Engine/Engine Mechanical for Camshaft replacement.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P0341 failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||
4 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Engine/Engine Mechanical | ||||||||
Inspect the CMP reluctor wheel for damage. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||
8 | Replace the CMP sensor. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||
10 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
