Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
DEFINITION: Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine speed; usually
more pronounced as engine load increases.
|
1
| Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 2
| Go to the
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
.
|
2
|
- Perform a bulletin search.
- If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found, correct the
condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
| --
|
Go to Step 13
|
Go to Step 3
|
3
| Was visual/physical check performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 4
| Go to Visual/Physical Checks
|
4
|
- Check PCM grounds for being clean, tight and properly routed.
Refer to Ground Distribution
in Electrical Diagnosis.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 5
|
5
| Observe Long Term Fuel Trim Bn1 and Bn2 on the scan tool.
Is Long Term Fuel Trim Bn1 or Bn2 significantly in the negative range
(Rich condition)?
| --
|
Go to Step 6
|
Go to Step 7
|
6
|
- Check for conditions that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer
to
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 1
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 9
|
7
| Is Long Term Fuel Trim Bn1 or Bn2 significantly in the positive range (Lean
condition)?
| --
|
Go to Step 8
|
Go to Step 9
|
8
|
- Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to
DTC P0171 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 1
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 9
|
9
|
- Check for incorrect idle speed. Ensure that the following conditions
are present:
- Using a scan tool, monitor IAC position.
Is IAC position between the specified values?
| 5-50
|
Go to Step 11
|
Go to Step 10
|
10
|
- Visually/physically inspect for the following conditions:
| • | Throttle body tampering (throttle shaft stop screw turned). |
| • | Restricted air intake system. Check for a possible collapsed air
intake duct, restricted air filter element, or foreign objects blocking the
air intake system. |
| • | Throttle body. Check for the following conditions: |
| - | Excessive deposits in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate. |
| - | Objects blocking the IAC passage or throttle bore. |
| - | Excessive deposits in the IAC passage or on the IAC pintle. |
| • | Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that can cause a large
vacuum leak, such as an incorrectly installed or faulty PCV valve or brake
booster hose disconnected. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 8
|
11
| Check the injector connections. Refer to
Fuel Injectiors
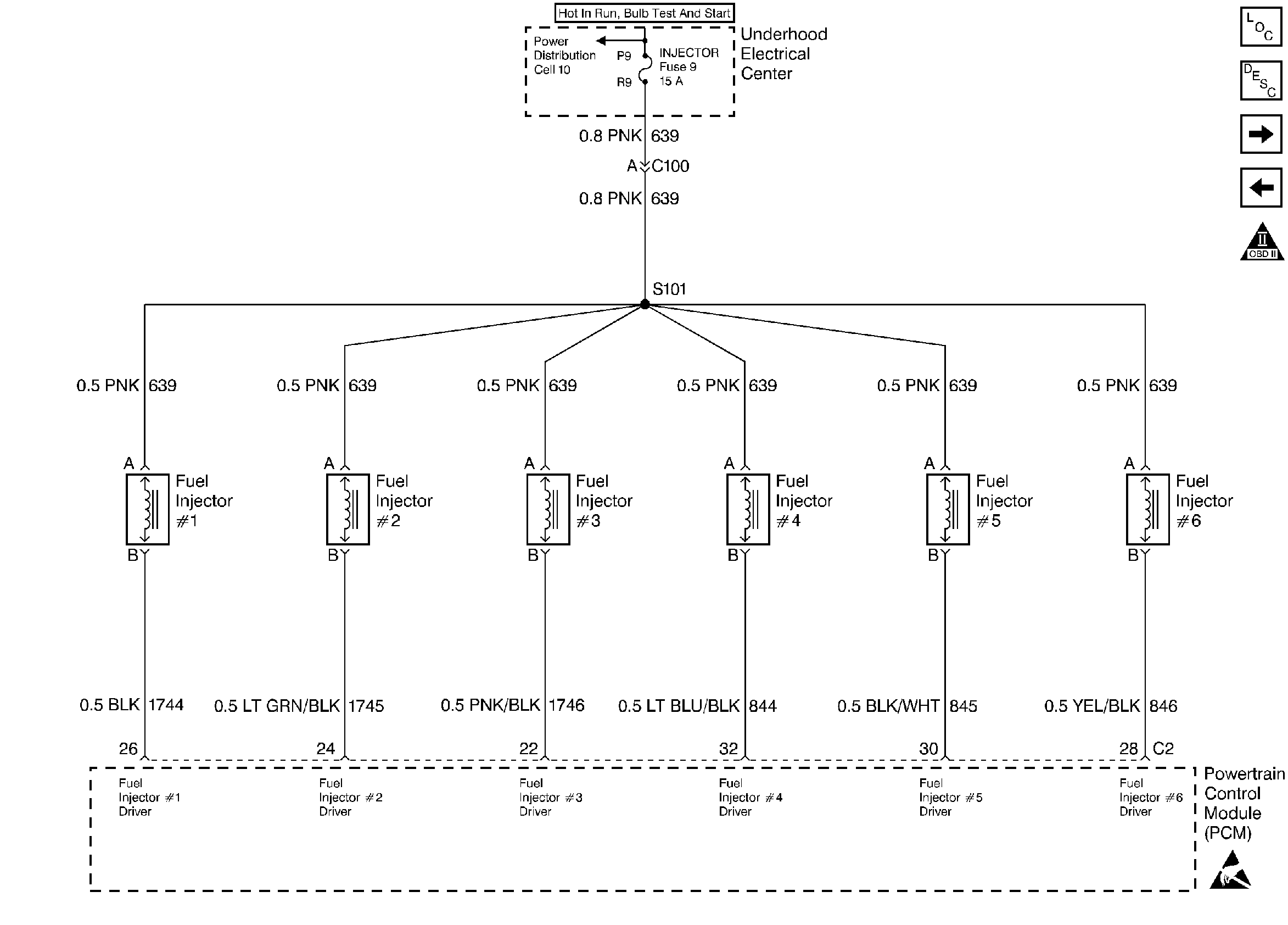
. If any of the injectors are connected
to an incorrect cylinder, correct as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 12
|
12
|
- Check for correct injector operation. Refer to
Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 13
|
13
|
- Check for fuel in pressure regulator vacuum hose.
- If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator assembly.
Refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement
.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 14
|
14
|
- Check for proper ignition coil output voltage with a J 26792
Spark Tester:
| • | Clip the spark tester to engine ground. |
| • | Connect one end of a spark plug wire to the spark tester; connect
the other end of the spark plug wire to the coil being tested. |
| • | Connect one end of another spark plug wire to the other coil tower;
connect the other end of the spark plug wire to ground. |
| • | Crank the engine while observing the spark tester; a crisp blue
spark should be observed. |
| • | Repeat the above steps for each coil. |
- If adequate spark is not present at all coils, replace affected
coil(s) as necessary. Refer to
Ignition Control Module Replacement
.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 15
|
15
|
- Remove the spark plugs.
Important: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of the fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs in order to avoid damage to
the new spark plugs.
- Check for wet plugs, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes,
or heavy deposits.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary. Refer to On-Vehicle Service
in Ignition System.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 16
|
16
|
- Check for a loose ignition control module ground. Refer to Ground Distribution
in Electrical Diagnosis.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 17
|
17
|
- Check ignition coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
- If a problem is found, replace affected coil(s) as necessary.
Refer to
Ignition Control Module Replacement
.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 18
|
18
| Using a scan tool, monitor TP angle with the engine idling.
Is TP angle at the specified value and steady?
| 0%
|
Go to Step 19
| Go to
DTC P0123 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Circuit High Voltage
|
19
|
- Check PCV valve for proper operation. Refer to
Crankcase Ventilation System
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 20
|
20
|
- Check the Transmission pressure switch manifold circuits. Refer
to 4L60-E Transmission Diagnosis
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 21
|
21
|
- Check for the following conditions:
| • | Damaged or bent crankshaft harmonic balancer interrupter rings. |
| • | Loose or damaged crankshaft position sensor. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary. Refer to
Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 22
|
22
|
- Refer to Engine General Information and Mechanical Diagnosis to
check for the following conditions:
| • | Sticking or leaking valves. |
| • | Incorrect valve timing. |
| • | Broken valve springs. Refer to Valve Train Diagnosis. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 23
|
23
|
- Check for faulty motor mounts.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 24
|
24
|
- Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
- If all procedures have been completed and no malfunctions have
been found, review/inspect the following:
| • | Visual/physical inspection. Refer to Visual/Physical Checks
. |
| • | Freeze Frame data/Failure Records Data. |
| • | All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
| Review technical bulletins
|
25
| Operate the vehicle
to duplicate conditions present when the original symptom was noted.
Is symptom still present?
| --
|
Go to Step 3
| System OK
|

