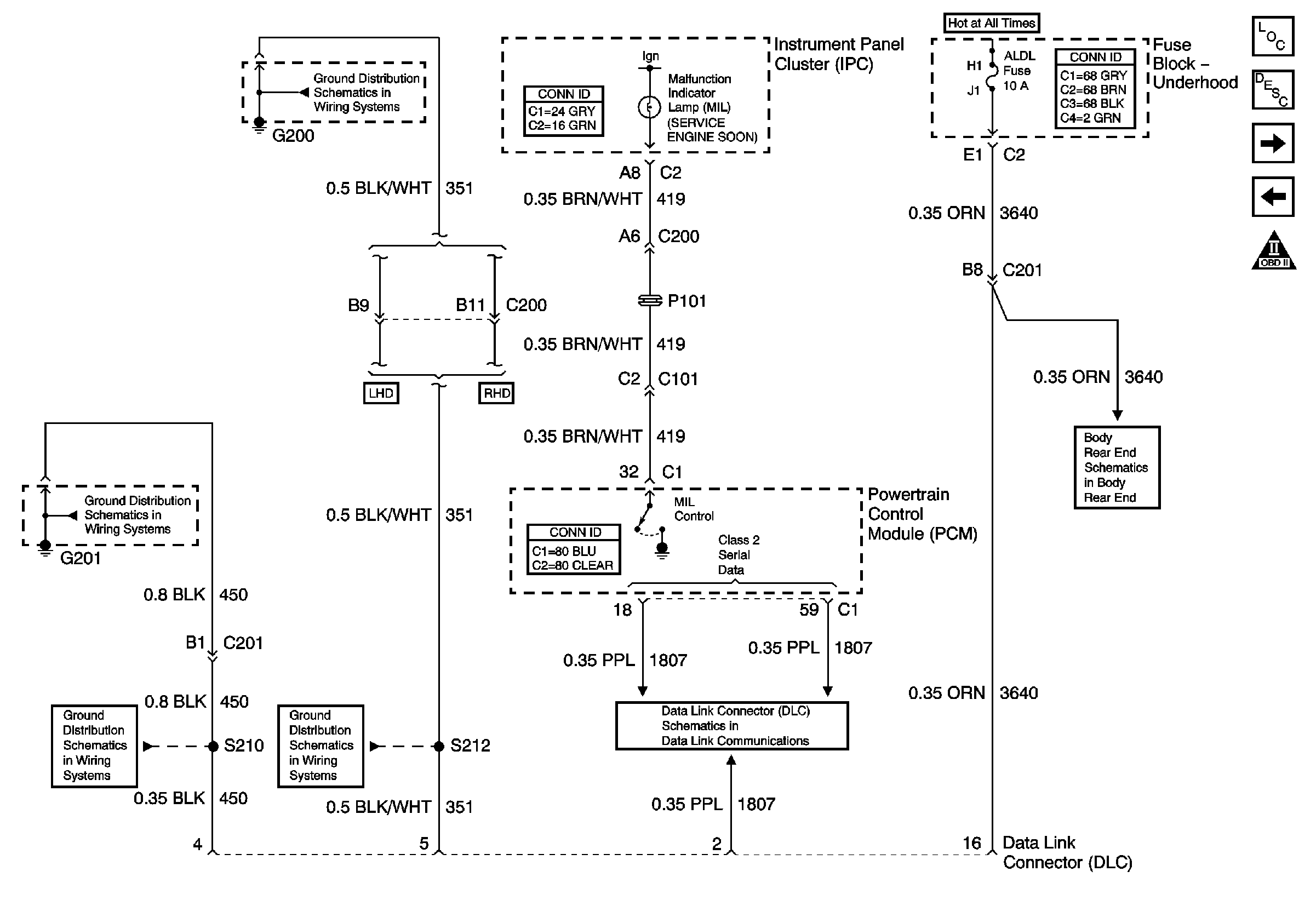
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) uses output driver modules (ODMs) to control many functions of the engine, and the transaxle. The ODMs supply the ground path for the PCM controlled device when the PCM commands the device ON. Each ODM is able to control several outputs. Unlike the quad driver modules (QDMs) used in earlier model years, the ODMs are able to diagnose each output circuit. The PCM monitors the ODMs for circuit conditions that are incorrect for the commanded state of the ODM. If the PCM detects an improper circuit condition in the ODM that controls the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0650 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The system voltage is between 8-16 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM detects an improper voltage level on the output circuit that controls the MIL. |
| • | The condition exists for at least 10 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
In order to determine whether an improper voltage level exists on the output circuit, the PCM compares the voltage level to the commanded state. For example, a failure condition exists if the PCM detects a low voltage level when the device is commanded OFF, or a high voltage level when the device is commanded ON.
Step | Action | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
Schematic
Reference:
| |||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Is the MIL ON? | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 5 |
3 | Use the scan tool in order to command the MIL OFF. Is the MIL OFF? | Go to Intermittent Conditions | Go to Step 4 |
4 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
5 |
Is the test lamp ON? | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 |
6 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 |
7 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF? | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 9 |
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 |
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 |
10 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 13 | -- |
12 | Replace the IP cluster. Refer to Instrument Cluster Replacement in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console. Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 13 | -- |
13 |
Does the DTC run and pass? | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 2 |
14 | With a scan tool, observe the stored information, Capture Info. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | System OK | |