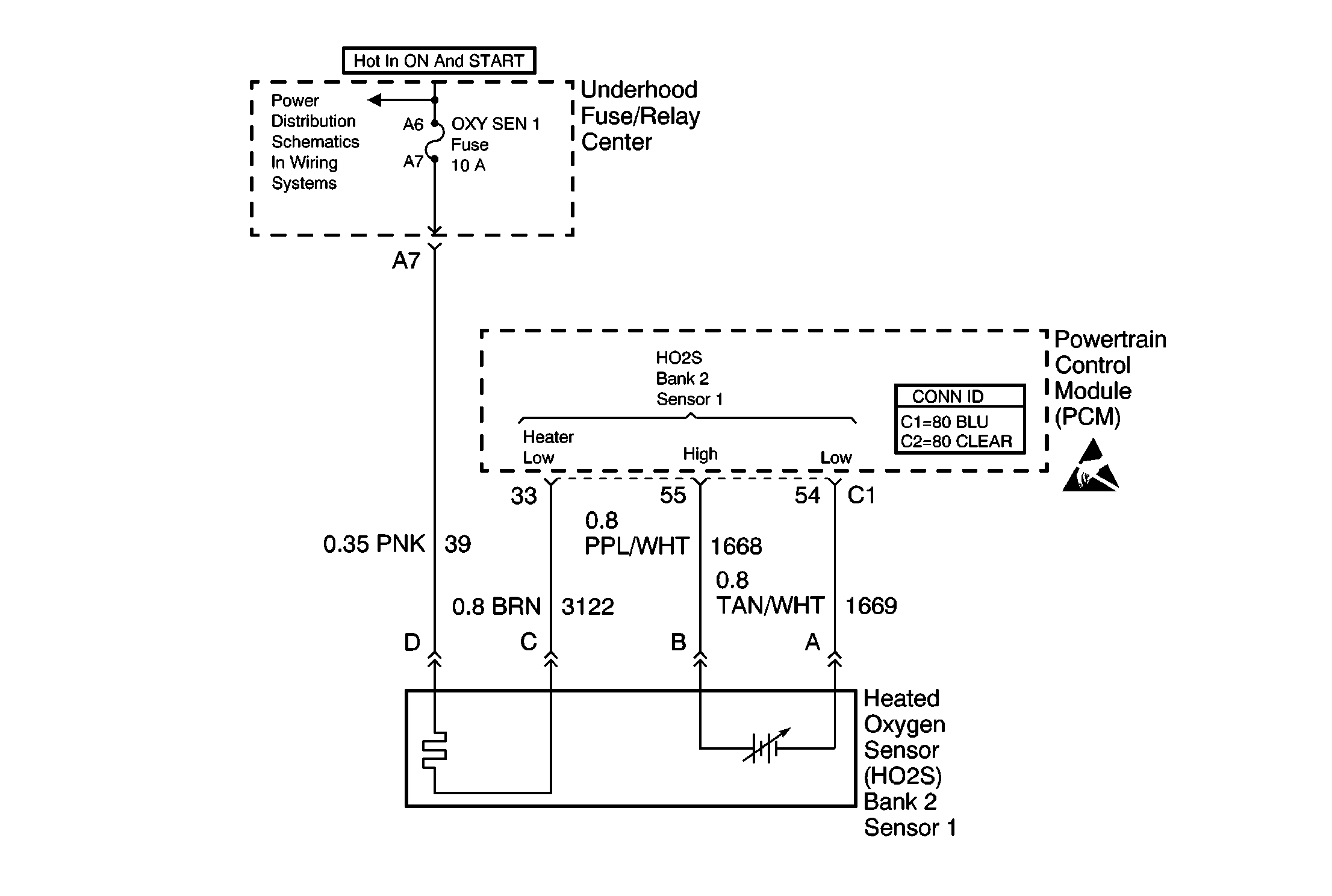
Circuit Description
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is a sensor used to detect oxygen-content in the exhaust. The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies the sensor with a signal circuit and a ground circuit. The PCM supplies a bias voltage between the circuits. The sensor varies the voltage based on the oxygen content in the exhaust. When the exhaust stream is lean (more oxygen), the sensor produces a low voltage signal. When the exhaust stream is rich (less oxygen), the sensor produces a high voltage signal.
The PCM continuously monitors the sensor (HO2S) signal for a calibrated period of time. During the monitoring period, the PCM counts the number of times that a rich to lean and lean to rich response occurs. Then, the PCM adds the amount of time it took to complete all transitions. The PCM detects a rich to lean transition when the HO2S voltage changes from more than 600 mV to less than 300 mV. The PCM detects a lean to rich transition when the HO2S voltage changes from less than 325 mV to more than 625 mV. The PCM uses the data to determine an average time for each transition. If the PCM determines that the average response time is too slow for HO2S bank 2 sensor 1, DTC P0153 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No TP sensor, MAF sensor, MAP sensor, IAT sensor, ECT sensor, EVAP system, AIR system (if equipped), fuel injector, misfire, or HO2S Heater DTCs are set. |
| • | DTC P1153 is not set |
| • | EGR Flow test inactive |
| • | AIR System test inactive (if equipped) |
| • | Catalyst test inactive. |
| • | System voltage is between 9-18 volts. |
| • | Engine run time is more than 202 seconds (approximately 3.5 minutes). |
| • | Engine speed is between 1200-2300 RPM. |
| • | Coolant temperature is more than 75°C (167°F). |
| • | TP angle is more than 3 percent. |
| • | MAF is between 15-35 g/s. |
| • | Closed loop fuel control active. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | HO2S bank 2 sensor 1 lean to rich average transition response time during the sample period was more than 100 milliseconds. |
| OR |
| • | HO2S bank 2 sensor 1 rich to lean average transition response time during the sample period was more than 200 milliseconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM stores the conditions present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
If the condition is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions in Symptoms.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Verifies that the malfunction is currently present the average rich/lean and lean/rich transition times. With the ignition turned ON, the scan tool indicates the results of the last test for this diagnostic. The test conditions must be met in order for the scan tool to update the results of test for this ignition cycle.
-
HO2S transition time, ratio, and switching DTCs set for multiple sensors indicate probable contamination. Before replacing the sensors, isolate and correct the source of the contamination to avoid damaging the replacement sensors.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||
|
Important: If any DTCs are set, except P0133, P1134, or P1154, refer to those DTCs before proceeding with this diagnostic table. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List/Type to diagnose the applicable DTC.
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P0153 failed last test? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||
Does the scan tool also indicate DTC P1154 failed last test? | -- | |||||||||||||
4 | Visually/physically inspect for the following items:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
6 |
Important: Correct the source of the oxygen sensor contamination before replacing
the sensor in order to prevent future contamination. Typical contamination
sources include the following:
Replace the sensor sensor. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 2 . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
7 |
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P0153 passed? | -- | System OK |
