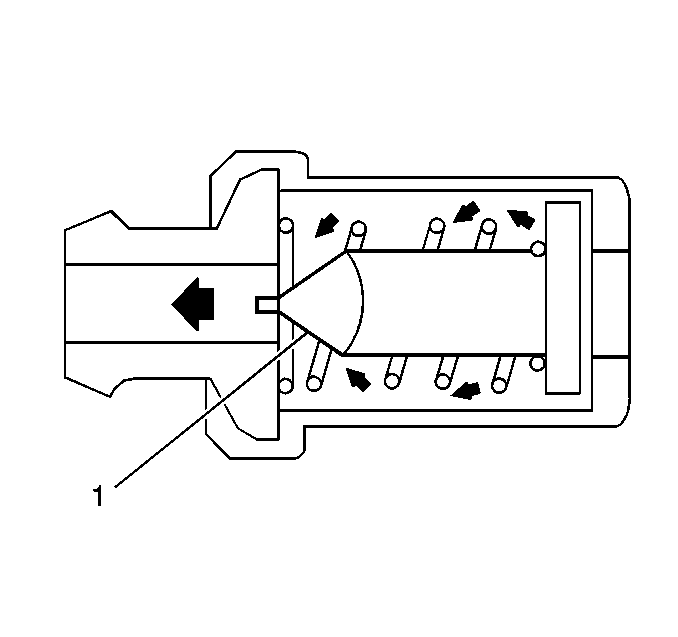
Purpose
In gasoline engines, a small amount of combustion gas leaks past the
piston rings, and into the crankcase. These blow-by gases pollute the air,
and reduce the quality of the engine oil. The positive crankcase ventilation
(PCV) system is used to circulate fresh air into the crankcase. The PCV
system removes the blow-by gases, and prevents them from entering the atmosphere.