Tools Required
| • | J 38758 Parasitic Draw Test Switch Tool |
| • | J 39200 Digital Multimeter (DMM) |
Notice: Do not turn the parasitic draw test switch to the OFF position with the engine running. Damage will occur to the vehicle's electrical system.
Notice: The test switch must be in the ON position when removing the fuses in order to maintain continuity in the electrical system. This avoids damaging the digital multimeter due to accidental overloading, such as a door being opened to change a fuse.
Important: The switch knob on the J 38758 is marked ON and OFF. When the switch knob is in the ON position, the circuit is closed and electrical current will pass through the switch. When the switch knob is in the OFF position, the circuit is open and electrical current will not pass through the switch.
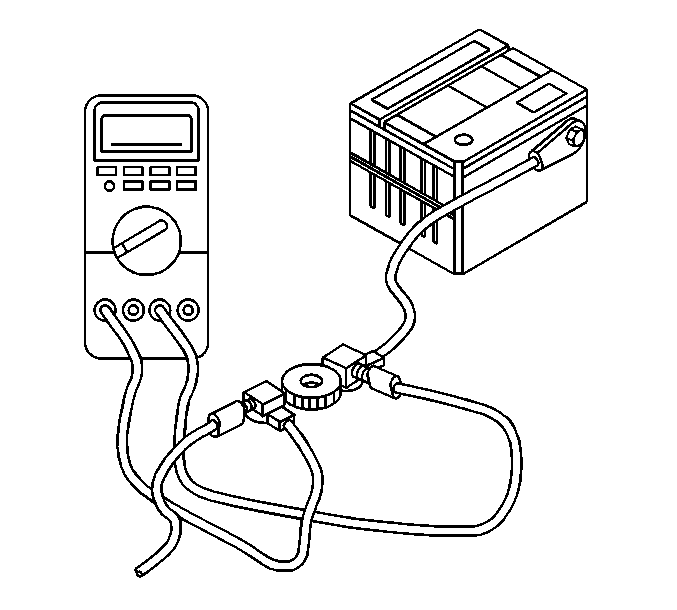
- Disconnect the battery (ground) negative cable from the battery negative terminal.
- Install the male end of the J 38758 to the battery ground (negative) terminal.
- Turn the J 38758 knob to the OFF position.
- Install the battery (ground) negative cable to the female end of the J 38758 .
- Turn the J 38758 knob to the ON position.
- Road test the vehicle and activate all of the accessories, including the radio and the air conditioning.
- Park the vehicle. Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position and remove the ignition switch key.
- Set a DMM to the 10 A scale.
- Connect the DMM to the test switch tool terminals.
- Turn the J 38758 knob to the OFF position. The current to flows through the DMM.
- Wait one minute. Check and record the current reading.
- Turn the J 38758 knob to the OFF position. Wait 10 minutes.
- Check and record the current reading.
- Note the battery reserve capacity. Refer to Battery Usage .
- Check the charging system if the vehicle has an acceptable amount of current drain and the vehicle battery was weak or failed a load test. Refer to Generator Not Operating Properly .
- When the vehicle has an unacceptable amount of parasitic current drain, remove each fuse one at a time until the current drain falls to an acceptable level. This will indicate which circuit is causing the drain. Refer to Power Distribution in Wiring Systems to diagnose exactly which part of the suspect circuit is causing the parasitic drain. In some cases a non-fused circuit or component, such as a generator, is the cause of excessive parasitic current drain.
- Repeat the parasitic current drain test procedure after any repair has been completed to make sure that the parasitic current drain is at an acceptable level.
- When the cause of the excessive current draw has been located and repaired, remove the J 38758 .
- Connect the battery (ground) negative cable to the battery negative terminal. Tighten to 15N·m (11 lb ft).
| • | When there is a current reading of 2 A or less, turn the J 38758 knob to the ON position. Continuity is maintained in the electrical system. |
| • | Then, switch the DMM down to the 2 A scale for a more accurate reading when the J 38758 knob is turned OFF. |
| • | Divide the reserve capacity by 4. |
| • | Compare this to the multimeter milliampere reading taken in the previous step. |
| • | The parasitic current drain should not exceed this number. |
| • | Example: If a battery has a reserve capacity of 100 amperes, the current drain should not exceed 25 minutes. |
Notice: The test switch must be in the ON position when removing the fuses in order to maintain continuity in the electrical system. This avoids damaging the digital multimeter due to accidental overloading, such as a door being opened to change a fuse.
Component | Approximate Current Draw (mA) Typical | Approximate Current Draw (mA) Maximum |
|---|---|---|
ALC (After 7 Minute Time Out) | -- | 1.0 |
Blower Control Module (C68 or CJ2) | 1.0 | 2.0 |
Compact Disc (CD) Player | 1.8 | 3.5 |
Electronic Brake (& Traction) Control Module (After 4 Minute Time Out) | 1.0 | 1.5 |
Generator | 2.0 | 2.0 |
Heated Seat Control Module | 0.5 | 1.0 |
HVAC Programmer | 0.5 | 0.75 |
Instrument Cluster | 4.0 | 6.0 |
Lamp Control Module | 0.5 | 1.0 |
Lamp Monitor Control Module | 0.5 | 1.0 |
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) | 5.0 | 7.0 |
Remote Function Actuator (RFA) Module | -- | 3.8 |
Radio | 7.0 | 8.5 |
Theft Deterrent Module | 0.75 | 1.0 |
If the current draw in the parasitic load test is above 30 millilamps the load can either be that a module on the Class 2 serial data line is not going to "sleep" or that the load is related to a traditional excessive current draw such as lumbar seat switch stuck on.
Diagnosing Class 2 Serial Data Line
- Pull the COMFORT, IGN0 BODY, and BATT fuse(s). If the draw goes away the most likely cause is that a module on the Class 2 serial data line is keeping the body control module (PZM) "awake." Do not replace the PZM until the whole test is complete. If the current draw does not go away, refer to the traditional excessive current draw in this procedure.
- Reinstall the COMFORT fuse. This will "wake up" the Class 2 serial data line.
- Wait 20 minutes.
- When the PZM goes back to sleep, monitor the current draw using a DMM. If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to a component that receives power from the COMFORT fuse or a component that is powered by the controlled power relay. If no change is noted in the current draw, proceed to the next step.
- Disconnect the RFA module.
- Monitor the current draw using a DMM. If the excessive current draw is removed, then the parasitic drain can be isolated to the RFA module and its related circuits.
- Disconnect the CD changer, if equipped.
- Monitor the current draw using a DMM. If the excessive current draw is removed, then the parasitic drain can be isolated to the CD changer and its related circuits.
- Disconnect the ACM.
- Wait 20 minutes.
- When the PZM goes back to sleep, monitor the current draw using a DMM. If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to the ACM and its related circuits.
- Do not replace the PZM until all of the components powered by the controlled power relay have been diagnosed.
- Reinstall the IGN0 BODY fuse (equipped with a climate control panel CCP).
- Monitor the current draw using a DMM. If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to a component that receives power from the IGN0 BODY fuse. If no change is noted in the current draw, proceed to the next step.
- Reinstall the BATT fuse.
- Monitor the current draw using a DMM. If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to a component that receives power from the BATT fuse. If no change is noted in the current draw, proceed to the next step.
- When cause of excessive current draw has been located and repaired, remove the parasitic load test switch and connect the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal.
Tighten
Tighten the negative battery cable to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
