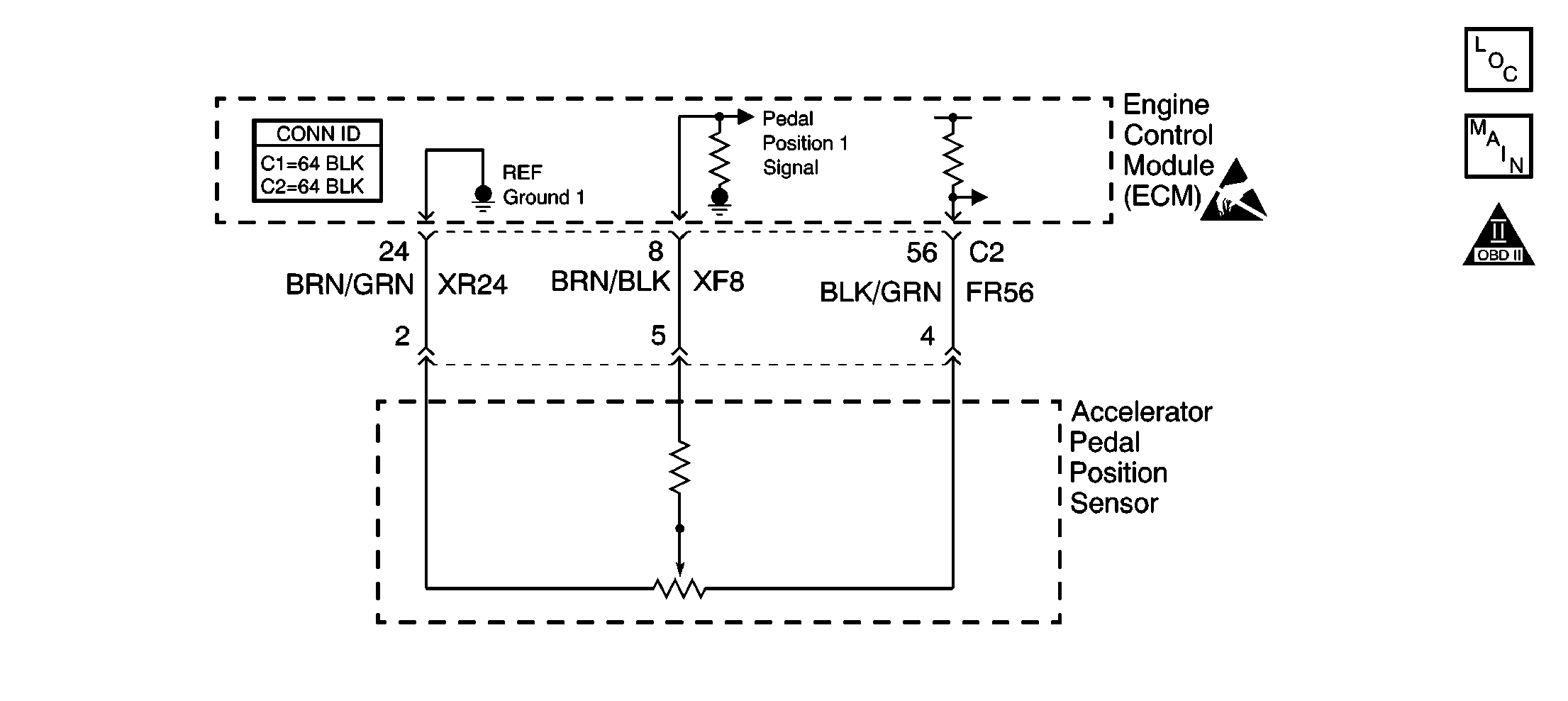
Circuit Description
The accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor is made up of 2 sensors that are housed inside one assembly. The APP sensor is located on a bracket above the accelerator pedal. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a separate 5 volt reference and the ground circuit for each of the sensors. The 5 volt reference for APP sensor 1 is supplied from the same source in the ECM as the 5 volt reference for the mass air flow sensor and the fuel tank pressure sensor. The 5 volt reference for APP sensor 2 is supplied from the same source in the ECM as the 5 volt reference for the throttle position sensors. The 5 volt reference voltage for all of the sensors is supplied on separate ECM terminals, but the terminals are connected internally to the shared voltage supply. The APP sensor sends a signal from each of the sensors to the ECM indicating the acceleration demand of the driver. The ECM actuates the throttle plates based on this information.
The APP sensor 1 signal voltage increases as the throttle opens, from about 0.4 volt at closed throttle to above 3.5 volts at wide open throttle. The APP sensor 2 signal voltage also increases as the throttle opens, but at a slightly different rate. The APP sensor 2 signal voltage increases from about 0.2 volt at closed throttle to about 1.8 volts at wide open throttle. The APP sensor 1 is the main control of the system. The APP sensor 2 is used for comparison of the APP sensor 1. The ECM constantly monitors these two sensors and if the sensors are not within a calibrated value, a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The battery voltage must be more than 7 volts.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The APP sensor 1 voltage is more than 4.8 volts or less than 0.2 volt. |
| or |
| • | The voltage of APP sensor 2 is 0.2 volt more than expected in part throttle range or 1.0 volt more than expected in full throttle range. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the first drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
The ECM compares the signal of each of the accelerator pedal position sensor to each other throughout the entire range of operation. Clear the DTCs and actuate the throttle through the entire range with the ignition ON and the engine OFF. If the DTC resets, check all of the circuits to the APP sensors for high resistance. Resistance as low a 2 ohms in the APP sensor circuits can affect the operation of the sensors.
With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, view the APP sensor 1 and the APP sensor 2 with a scan tool. Slowly depress the accelerator pedal, if one sensor value changes and the other does not, test the sensor circuits for high resistance or shorts. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. If the circuits are OK, replace the APP sensor.
Use the J 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems for Intermittent conditions.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The APP sensor 1, the mass air flow sensor, and the fuel tank pressure sensor all share the same 5 volt source inside the ECM. A short to ground or voltage on the 5 volt reference of any of these sensors will affect the operation of APP sensor 1. The diagnosis of these circuit faults is located in the diagnostic table for the mass air flow sensor. P0450 for the fuel tank pressure sensor may be set in addition to the P0100.
-
The ECM performs a comparison of the signals from both APP sensors during the entire range of operation. If the DTC does not set with the key ON and the accelerator pedal released, actuating the throttle may cause the DTC to set.
-
This step tests the integrity of the APP sensor 1 signal circuit. The APP sensor 1 data parameter on the scan tool should read near 5 volts when connected to the 5 volt reference circuit.
-
Part of the diagnosis for the APP sensors include comparing the signal of each sensor throughout the entire range of operation. A 5 volt reference circuit for APP sensor 2 that is shorted to voltage may cause the ECM to set a DTC for APP sensor 1.
-
The 5 volt reference for the TP sensors and APP sensor 2 are connected inside the ECM. A short to voltage on the TP sensor 5 volt reference circuit will affect the operation of APP sensor 2.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Using the scan tool, view the DTC Information. Is DTC P0100 also set? | -- | Go to Step 3 | ||
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the APP sensor 1 parameter is within the specified range? | 0.2-0.5 volts | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 6 |
4 |
Does the harness movement cause this DTC to reset? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 5 |
Does this DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 6 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
6 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the APP sensor 1 parameter is less than the specified value? | 0.2 volts | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 16 |
7 | Measure the voltage between the 5 volt reference circuit of the APP sensor 1 and battery ground using a DMM. Does the voltage measure within the specified value? | 4.8-5.2 volts | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 12 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the APP sensor 1 parameter is more than the specified value? | 4.8 volts | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 15 | |
9 |
Important: Make sure the ECM has shut down prior to measuring the reference ground circuit resistance. This can be verified by the loss of communication on the scan tool. Important: Do not use a test lamp to test the continuity of the reference ground. Damage to the ECM will result. Does the resistance measure less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 10 |
10 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Measure the resistance from the ground stud at the ECM bracket to battery ground. Is the resistance of the circuit less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 21 |
12 | Is the voltage less than the specified value? | 5 volts | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 13 |
13 | Test the 5 volt reference circuit of the APP sensor 1 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 25 |
14 | Test the 5 volt reference circuit of the APP sensor 1 for a short to ground, a high resistance, or an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 23 |
15 | Test the signal circuit of the APP sensor 1 for a short to ground, high resistance, or an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 23 |
16 | Test the signal circuit of the APP sensor 1 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 25 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 5.2 volts | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 22 | |
18 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 19 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 25 | |
20 | Repair the harness or connections as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 26 | -- |
21 | Repair the open or high resistance in the ECM ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 26 | -- |
22 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the APP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 24 |
23 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the engine control module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 25 |
24 | Replace the APP sensor. Refer to Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 26 | -- |
25 |
Important: Perform the Idle Learn Procedure when replacing the ECM or the throttle body. Important: This vehicle is equipped with a theft deterrent system that interfaces with the engine control module (ECM). Program the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 26 | -- |
26 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 2 |
27 | Does the scan tool display any additional, undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
