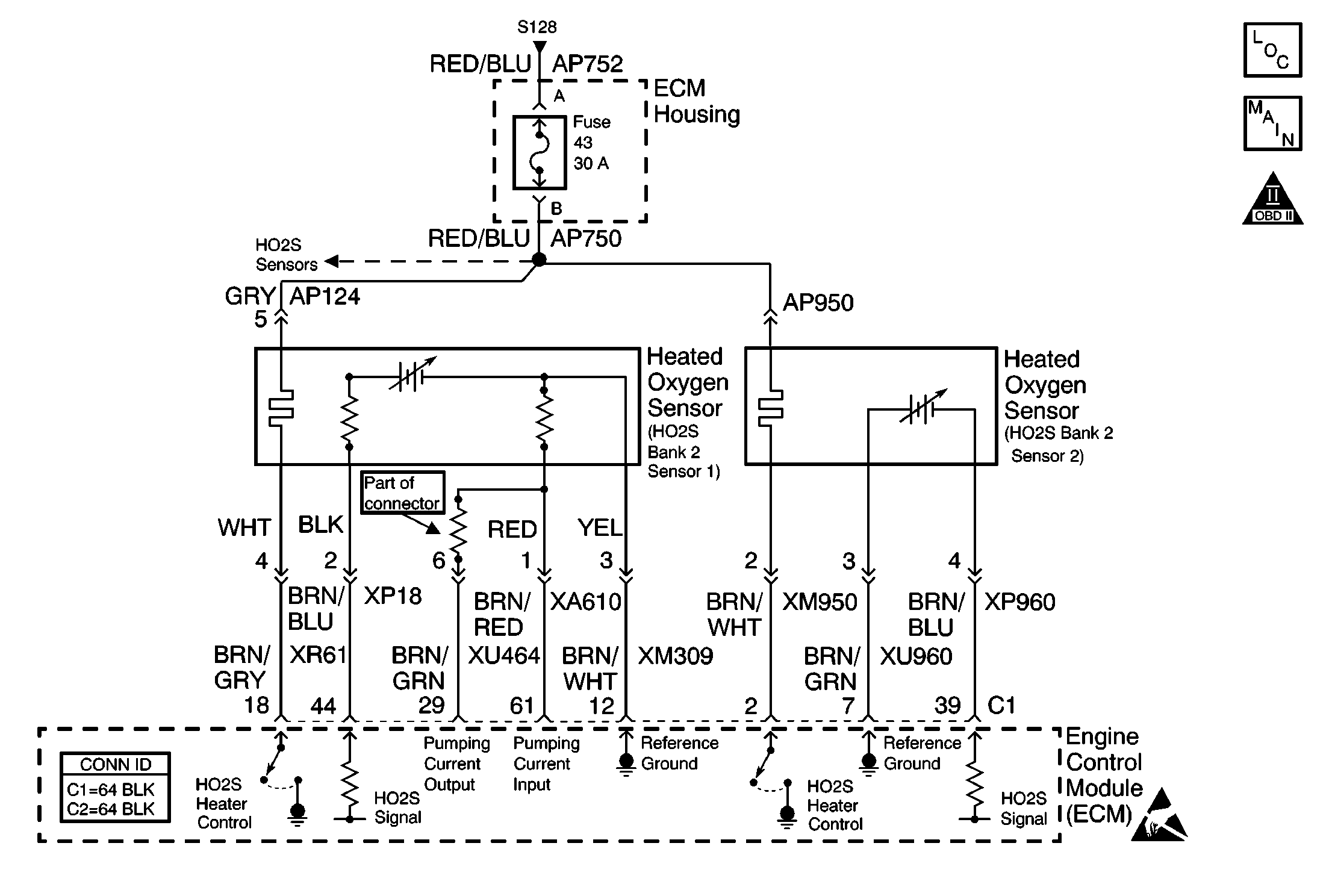
Circuit Description
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) produces a voltage that varies between 100 mV and 900 mV under normal operating conditions. The engine control module (ECM) produces a bias voltage on the HO2S signal circuit of 420 to 480 mv. The reference ground for the sensor is provided through the ECM. The ECM monitors the signal voltage to determine if the exhaust is lean or rich. The oxygen sensor voltage is high when the exhaust is rich, and low when the exhaust is lean. The ECM constantly monitors the HO2S signal during the Closed Loop operation.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No evaporative emissions (EVAP) DTCs are set. |
| • | The rear HO2S are in Closed Loop. |
| • | The AIR system is not operating. |
| • | No AIR DTCs are set. |
| • | The secondary AIR diagnostic is not running. |
| • | The engine run time is more than 10 minutes. |
| • | Low fuel is not indicated. |
| • | The battery voltage is more than 11 volts. |
| • | The catalytic converter temperature is less than 800°C (1472°F). |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The HO2S signal voltage is less than 40 mv.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the J 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector.
If the conditions to set this DTC are not present, check for the following conditions:
| • | Heated oxygen sensor wiring--Check for the following conditions: |
| - | A signal wire intermittently shorted to ground |
| - | A reference ground wire intermittently shorted to ground |
| - | The sensor pigtail or the harness may be mis-positioned and contacting the exhaust system. |
| - | An oxygen supply inside of the HO2S is necessary for a proper operation. This supply of oxygen is provided through the HO2S wires. All of the HO2S wires and connections should be inspected for breaks or contamination. If any wiring requires repair, refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| - | Inspect the connectors for the following conditions: |
| • | Proper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Corrosion and water intrusion |
| • | An intermittent lean engine condition such as the following: |
| - | Incorrect fuel pressure, refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| - | Lean fuel injectors |
| - | Vacuum leaks--Check for any disconnected or damaged vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake manifold, the throttle body, and the crankcase ventilation system. |
| - | An inaccurate mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| - | Exhaust leaks--An exhaust leak may cause the outside air to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the HO2S, causing this DTC to set. Check for any exhaust leaks near the HO2S. |
| - | Fuel contamination--Water, even in small amounts, can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can cause a lean exhaust to be indicated. Excessive alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. Refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis for the procedure. |
| • | Poor ECM grounds |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The engine must be at the normal operating temperature before performing this test.
-
Using the Freeze Frame data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be duplicated, review the information in the Freeze Frame. Try to operate the vehicle within the same Freeze Frame conditions, the RPM, the MAF, the vehicle speed, the temperature, etc., that were noted. This process may help in recreating the conditions that set the DTC.
-
The ECM provides the reference ground for the oxygen sensor. A short to engine or chassis ground on this circuit will cause the signal voltage to shift.
-
Monitor the HO2S voltage for the opposite bank sensor. If the voltage activity of the opposite bank sensor is similar to the voltage activity of the suspect sensor, check for a lean condition that would affect both cylinder banks. An opposite bank sensor with normal HO2S voltage activity indicates a lean condition exists only on the suspect cylinder bank or a fault in the circuit.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||
Does the HO2S voltage remain below the specified value? | 85°-95°C (185°-203°F) 40 mV | |||||||||||||||||
Is this DTC set? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||||||
4 |
Does the scan tool indicate an HO2S voltage within the specified range? | 420-480 mV | ||||||||||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | ||||||||||||||||
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | |||||||||||||||||
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | |||||||||||||||||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||
9 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | ||||||||||||||||
10 |
Important: This vehicle is equipped with a Theft Deterrent System which interfaces with the Engine Control Module (ECM). Program the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||
11 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||
12 | Does the scan tool indicate any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
