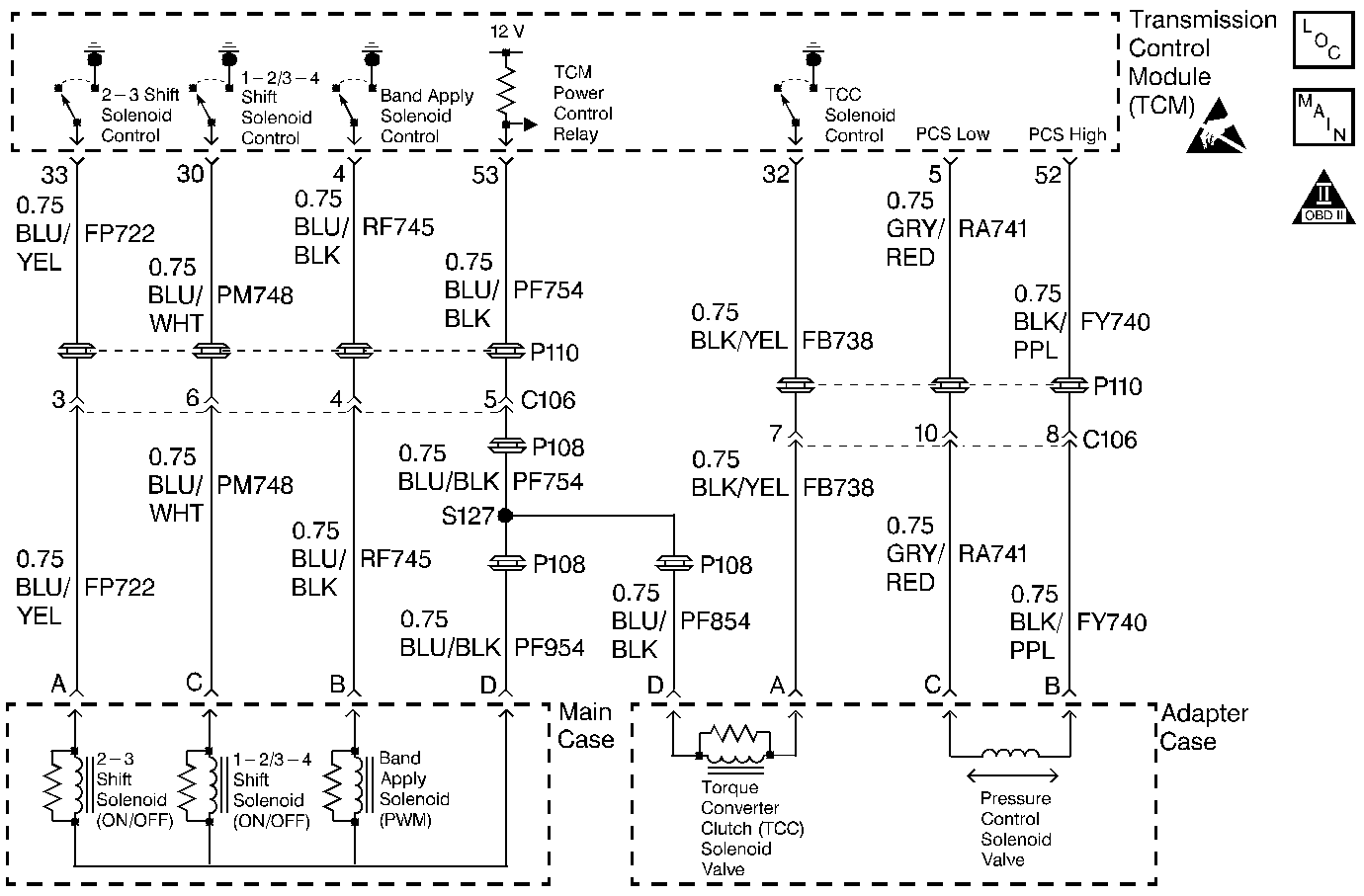
Circuit Description
The shift solenoids, the band apply solenoid, and the TCC solenoid are supplied power via the transmission power relay (internal to the TCM) on TCM terminal 53. The pressure control solenoid is also supplied power via the transmission power relay (internal to the TCM) but on TCM terminal 52. TCM terminals 52 and 53 are connected within the TCM. The TCM controls the solenoids by grounding the appropriate control circuit via internal solid state devices called drivers. The driver circuits have their own fault detection abilities that identify conditions with individual solenoids/circuits. The TCM also has fault detection circuitry for the power supply circuit that powers all of the solenoids in the transmission. If the TCM detects a condition with this circuit, DTC P1800 will set, and the TCM will shut off the transmission power relay. Any time a TCM DTC is set that requires the transmission to operate in default mode, the TCM turns off the power relay, effectively disabling all of the transmission components. Any time the default mode is in effect, the transmission line pressure is at maximum, the transmission starts in 4th gear, TCC is inhibited and the transmission adapt shift function is disabled.
When the TCM detects a power supply interrupt on TCM terminals 52 and 53, then DTC P1800 sets. DTC P1800 is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition switch is in the RUN position. |
| • | No 1-2/3-4 SS valve DTC P0753. |
| • | No 1-2/3-4 SS valve DTC P0758. |
| • | No TCC enable solenoid circuit- Electrical DTC P0743. |
| • | Band apply solenoid circuit DTC P1850. |
Condition for Setting the DTC
Power supply to TCM terminals 52 and 53 is interrupted.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Early production - The TCM illuminates the service transmission lamp (STL) and sends a MIL request to the ECM on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | Late production - The TCM flashes the Sport Mode Lamp and sends a MIL request on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The TCM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | The ECM records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame at the time of the MIL request from the TCM. |
| • | The transmission operates in the default mode (maximum line pressure, command 4th gear, inhibit TCC, freeze shift adapts). |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | Early production - The TCM turns off the STL as soon as the fault is no longer present. |
| • | Late production - The TCM stops flashing the sport mode lamp as soon as the fault is no longer present. |
| • | The ECM turns off the MIL after three consecutive drive trips during which the TCM sends no MIL request. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are present by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
| • | The TCM cancels the DTC default mode actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is Off long enough in order to power down the TCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Vehicles equipped with Fuel Cap Lamps utilize the Sport Mode lamp to indicate a transmission malfunction. In these vehicles, the Sport Mode Lamp flashes at 200 millisecond intervals when the TCM commands the lamp ON.
Vehicles not equipped with Fuel Cap Lamps are equipped with a dedicated Service Transmission Lamp (STL) on the Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC). The STL illuminates steadily when the TCM commands the lamp ON.
Use the J 35616-A connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the TCM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the TCM or at the component. Inspect the harness connectors for any backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems for proper procedure. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving any related connectors and any wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help to locate the fault. |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
3 | With the J 35616-200 connected to B+, probe the transmission power relay output circuit (terminals 52 and 53) in the TCM harness connector. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
4 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
5 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
Use a DMM J 39200 in order to check the harness for continuity of the transmission power relay output circuit (terminals 52 and 53) from the TCM harness connector to either the Main Case or Adapter Case harness connector. Is continuity indicated? | -- | |||
7 | Repair the power relay output circuit shorted to B+. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Repair the power relay output circuit shorted to ground. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Repair the open/high resistance power relay output circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Repair the transmission power relay output circuit shorted to ground in the adapter case. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Repair the transmission power relay output circuit shorted to ground in the main case. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Check the TCM harness connector for a poor connection or poor terminal tension. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis . Was a condition found and corrected? | -- | -- | |
13 |
Is DTC P1800 set? | -- | System OK |
