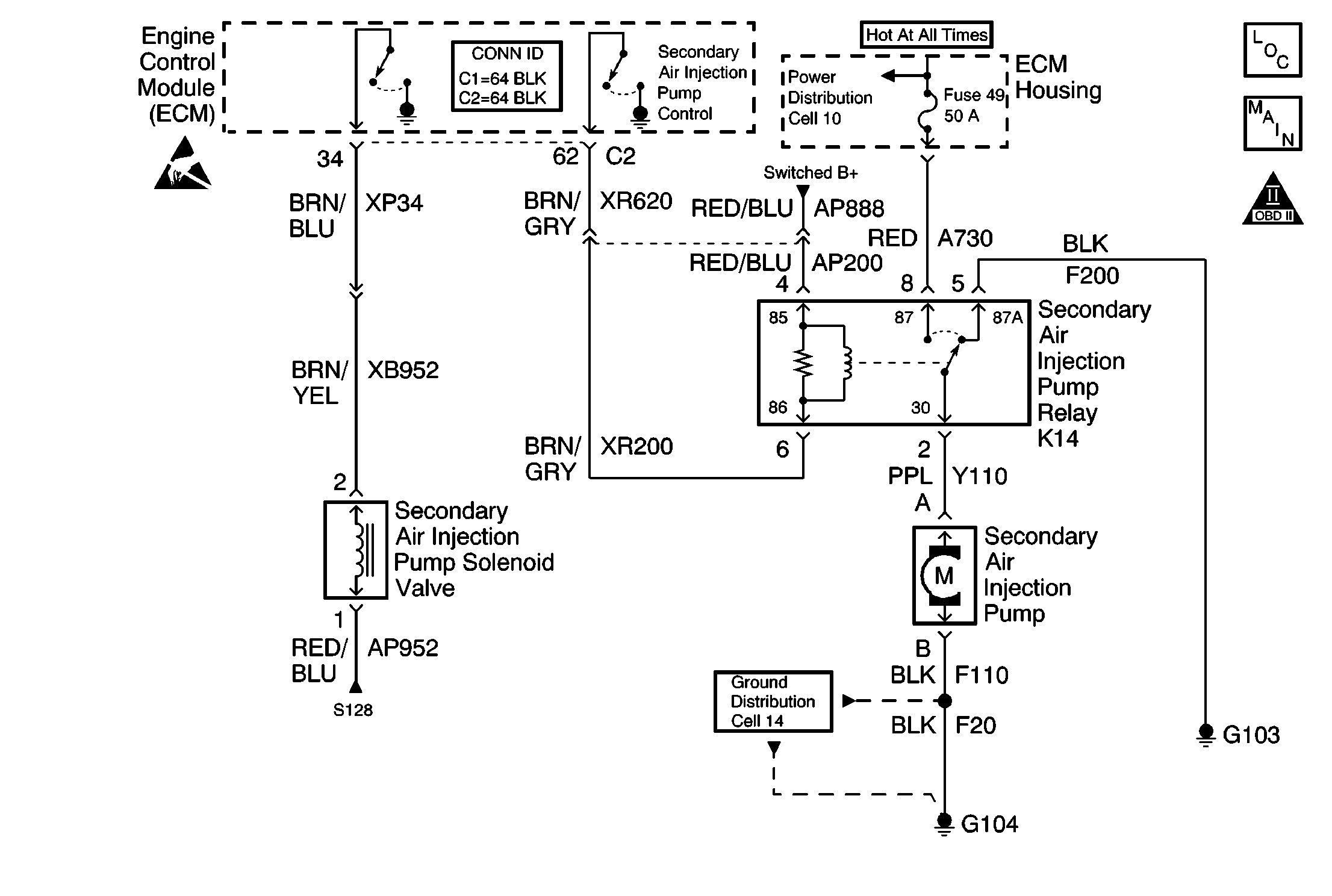
Circuit Description
The purpose of the Secondary Air Injection (AIR) system is to reduce the hydrocarbon (HC), the carbon monoxide (CO), and the oxides of nitrogen (NOx) exhaust emissions by causing any combustible gases in the exhaust to re-burn. This also causes the catalytic converters and the heated oxygen sensors to reach the normal operating temperatures more quickly, thus the Closed Loop operation occurs earlier.
When the engine is started, the ECM commands the AIR pump relay and the AIR cutoff valve vacuum control solenoid on, injecting clean air into the engine exhaust ports. The ECM switches the AIR system off when the oxygen sensors become active. The AIR cutoff valve prevents air from being drawn into the system when the AIR pump is off. The vacuum to the valve is controlled by the AIR cutoff valve vacuum control solenoid. A check valve close to the engine prevents hot exhaust gases from backing up into the AIR system.
The Secondary Air Injection Pump Solenoid Valve receives power from the engine controls power relay (Switched B+). The engine control module (ECM) controls the solenoid by grounding the control circuit via an internal solid state device called a driver. The primary function of the driver is to supply the ground for the component being controlled. Each driver has a fault line that is monitored by the ECM. When the ECM commands a component on, the voltage of the control circuit should be low (near 0 volts). When the ECM commands a component off, the voltage potential of the control circuit should be high (near battery voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage other than what is expected, this DTC will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine speed is more than 40 RPM. |
| • | The battery voltage is between 7.5-15 volts. |
| • | The above conditions are present for 300 ms (0.3 seconds). |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
A short to ground, an open circuit, or a short to battery voltage detected on the control circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Using the J 35616-A Connector Test Adapter Kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Use the J 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the ECM or at the component--Inspect the harness connectors for any backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the battery ground cables. The cables should be clean and tight. The secondary air pump is grounded through this circuit. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for any damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving the related connectors and the wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help in order to locate the fault. |
Refer to Intermittent Conditions for the Intermittents.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Listen for an audible click when the solenoid operates. Repeat the commands as necessary.
-
This check can detect a partially shorted solenoid coil which would cause an excessive current flow. Leaving the circuit energized for 2 minutes allows the coil to warm up. When warm, the coil may open, the amps drop to 0, or short, go to above 0.20 amp.
-
Perform the Idle Learn Procedure when replacing the ECM or the throttle body.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Does the AIR solenoid turn ON and OFF with each command? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 5 | |
Does the current draw measure within the range shown? | 100-750 mA | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 4 | |
4 |
The DMM should display an infinite resistance. Does the DMM display an infinite resistance? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
5 |
The test lamp should illuminate. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 12 |
6 |
The test lamp should NOT illuminate. Is the test lamp OFF? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 10 |
7 | Using an unpowered test lamp connected to BATTERY POSITIVE, probe the Secondary Air Injection (AIR) solenoid valve control circuit in the solenoid harness connector. The test lamp should NOT illuminate. Is the test lamp OFF? | -- | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 11 |
8 |
Does the current draw measure within the range shown? | 100-750 mA | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 9 |
9 |
Was a wiring repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 13 |
10 | Repair the Secondary Air Injection (AIR) solenoid valve control circuit for a shorted to B+ condition. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- |
11 | Repair the Secondary Air Injection (AIR) solenoid valve control circuit for a shorted to ground condition. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- |
12 | Repair the switched B+ circuit to the secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid valve. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- |
13 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 14 |
14 | Replace the secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid valve. Refer to Secondary Air Cutoff Valve Vacuum Solenoid Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- |
15 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 16 |
|
Important: This vehicle is equipped with a Theft Deterrent System which interfaces with the Engine Control Module (ECM). Program the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 17 | -- | |
17 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the diagnostic Passed? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 2 |
18 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
