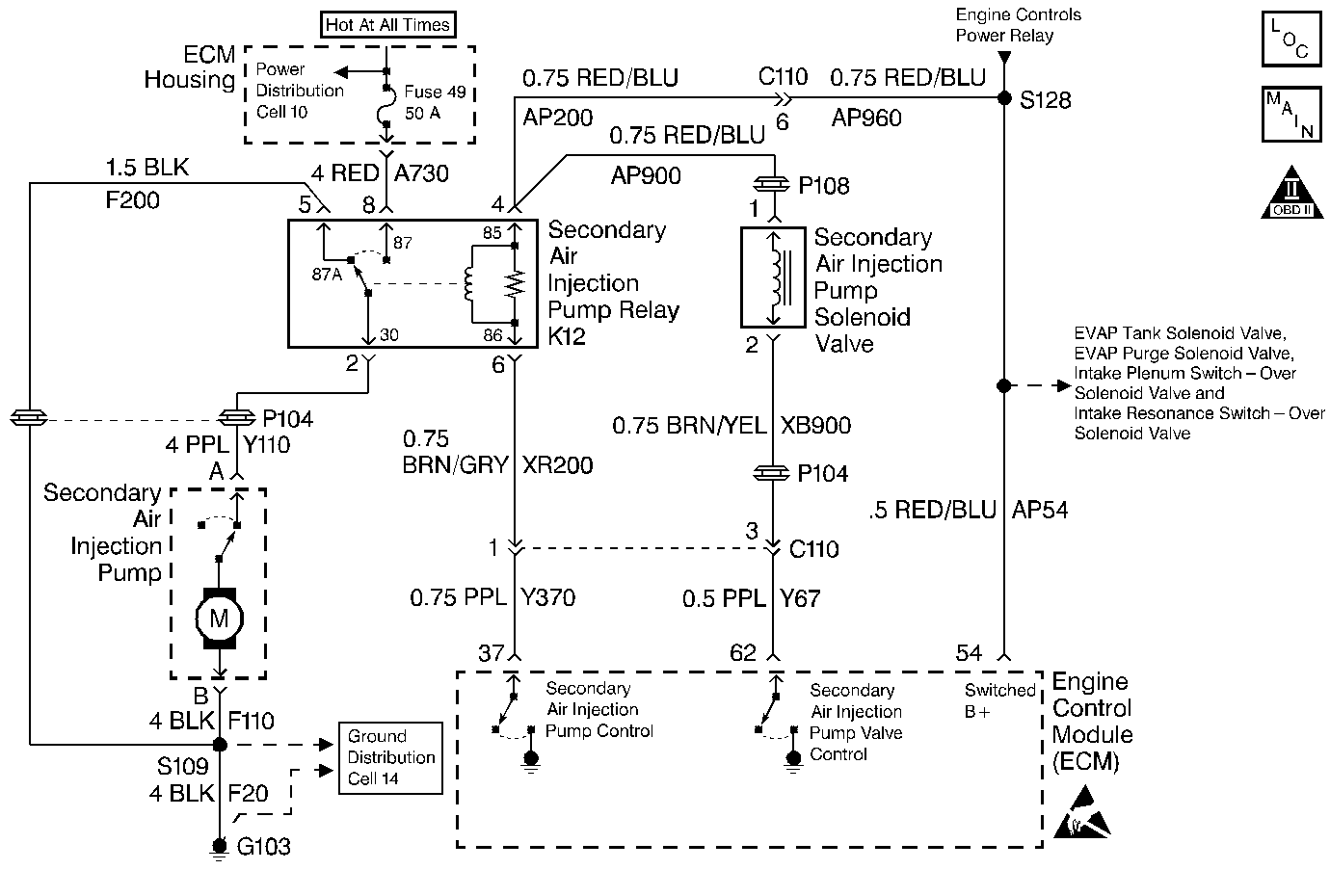
Circuit Description
The purpose of the Secondary Air Injection (AIR) system is to reduce Hydrocarbon (HC), the Carbon Monoxide (CO), and the Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) exhaust emissions by causing any combustible gases in the exhaust to re-burn. This also causes the catalytic converters and the heated oxygen sensors to reach the normal operating temperatures more quickly, thus Closed Loop operation occurs earlier.
When the engine is started, the ECM commands the AIR pump relay and the AIR Cutoff Valve Vacuum Control solenoid on, injecting clean air into the engine exhaust ports. The ECM switches the AIR system off when the oxygen sensors become active. The AIR Cutoff Valve prevents air from being drawn into the system when the AIR pump is off. The vacuum to the valve is controlled by the AIR Cutoff Valve Vacuum Control solenoid. A check valve close to the engine prevents hot exhaust gases from backing up into the AIR system.
The ECM uses the Short Term Fuel Trim in order to diagnose the AIR system. When the AIR system is enabled, the ECM monitors the Short Term Fuel Trim. If the Short Term Fuel Trim goes below a threshold, the ECM interprets this as an indication that the AIR system is operational. When the AIR pump is disabled, the Short Term Fuel Trim should return to normal.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | One or more of the following DTCs are not set: P0100, P0110, P0115, P0116, P0120, P0133, P0153, P0171, P0172, P0174, P0175, P0300 thru P0306, P0560, P0440, P0441, or P0443. |
| • | The Closed Loop is enabled |
| • | The EVAP purge disabled. |
| • | The IAT is greater than 5.3°C (41.5°F). |
| • | The ECT is greater than 18.8°C (65.8°F). |
| • | The engine is at idle. |
| • | Vehicle speed=0 miles/h. |
| • | The short term fuel trim is above the minimum limit of approximately -25%. |
| • | The start up ECT is between 0° and 36°C (32° and 97.0°F). |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The Short term fuel trim does not increase to the expected value within 6 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616 for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals. |
| • | Using the Freeze Frame data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be duplicated, review the information in the Freeze Frame. Try to operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (the RPM, the MAF, the vehicle speed, the temperature, etc.) that were noted. This process may help in order to recreate the malfunction. |
| • | Inspect the AIR pump connector for corrosion and proper terminal tension. Inspect the AIR ground connection. It must be clean and tight. A small amount of resistance over one ohm in the AIR pump supply circuit or AIR pump ground circuit may cause low AIR pump performance resulting in low airflow conditions. Perform voltage drop tests on these circuits to accurately diagnose these circuits. |
| • | Inspect the AIR pump check valve for a restriction or damage. |
| • | Refer to Symptoms for the Intermittents |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
The air pump may have an in-rush current draw of up to 90 amps when first operating the pump. This is considered normal. The current should stabilize to about 20 amps once the pump is running. The air pump on the Catera is equipped with an internal circuit breaker designed to protect it from overheating. Using a heavy jumper wire to activate the air pump will not damage the system. However, prolonged operation of the pump may cause the circuit breaker to open, rendering the pump inoperative. This can occur if the relay were to stick closed or if the pump is operated for extended periods during diagnosis. DO NOT replace the pump if this occurs. The pump will resume normal operation as soon as it sufficiently cools.
-
The AIR pump has a filter element on the inlet side. Check for a blocked pump inlet filter before replacing the pump.
-
Inspect the check valve. A check valve that is stuck closed can cause no air flow. Check the hoses after the check valve for evidence of heat damage. A heat damaged hose indicates that the check valve is stuck open allowing exhaust gas back into the AIR system.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | ||||||||
2 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF? | -- | ||||||||
3 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
4 | Probe the Switched B+ circuit to the relay with the test lamp connected to ground. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
5 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: The air pump on the Catera is equipped with an internal circuit breaker designed to protect it from overheating. Prolonged operation of the pump may cause the circuit breaker to open, rendering the pump inoperative. This can occur if the relay were to stick closed or if the pump is operated for extended periods during diagnosis. DO NOT replace the pump if this occurs. The pump will resume normal operation as soon as it sufficiently cools. Use a heavy gauge jumper wire in order to jumper the B+ circuit to the AIR pump feed circuit in the relay connector. Does the AIR pump turn ON and run? | -- | |||||||||
7 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
8 | Probe the AIR pump ground circuit in the harness connector with the test lamp connected to B+. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
| 0.6V | ||||||||
10 | Measure the voltage from the AIR pump ground circuit of the AIR pump harness connector to a good ground. | 0.6V | ||||||||
11 |
Is continuity indicated? | -- | ||||||||
12 |
Is the vacuum displayed on the gage more than the specified valve? | 33 kPa (10 in Hg) | ||||||||
13 |
Is the vacuum displayed on the gage more than the specified valve? | 33 kPa (10 in Hg) | ||||||||
Is manifold vacuum present at the cutoff valve? | -- | |||||||||
Is the valve open? | 33 kPa (10 in Hg) | |||||||||
16 |
Is airflow present at the AIR pump outlet when the pump is running? | -- | ||||||||
17 | Inspect for the following conditions between the AIR pump and engine:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
18 | Repair the B+ supply circuit to the relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
19 | Repair the Switched B+ circuit to the relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
20 | Repair the AIR pump feed circuit between the AIR pump and the AIR pump relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
21 | Repair the open or high resistance in the AIR pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
22 | Repair the open or high resistance in the relay control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
23 | Repair the vacuum supply hose or plugged vacuum source. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
24 | Repair the vacuum hose to the cutoff valve. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
25 | Replace the secondary AIR cutoff valve vacuum solenoid, refer to Secondary Air Cutoff Valve Vacuum Solenoid Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
26 | Replace the AIR cutoff valve, refer to Secondary Air Injection Cut Off Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
27 | Test for a poor connection or poor terminal tension at the relay connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. If a repair is necessary, refer to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
28 | Replace the relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
29 | Test for a poor connection or poor terminal tension at the AIR pump harness connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. If a repair is necessary, refer to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
30 | Inspect the AIR pump inlet filter for a restriction. Replace as necessary. Did the inlet filter require replacement? | -- | ||||||||
31 | Replace the AIR pump, refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
32 | Test for a poor connection or poor terminal tension at the ECM harness connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring systems. If a repair is necessary, refer to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
33 |
Important: This vehicle is equipped with a Theft Deterrent System which interfaces with the Engine Control Module (ECM). Program the new ECM with the frequency code of the theft deterrent module that is currently on the vehicle. Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
34 |
Is this DTC set? | -- | ||||||||
35 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
