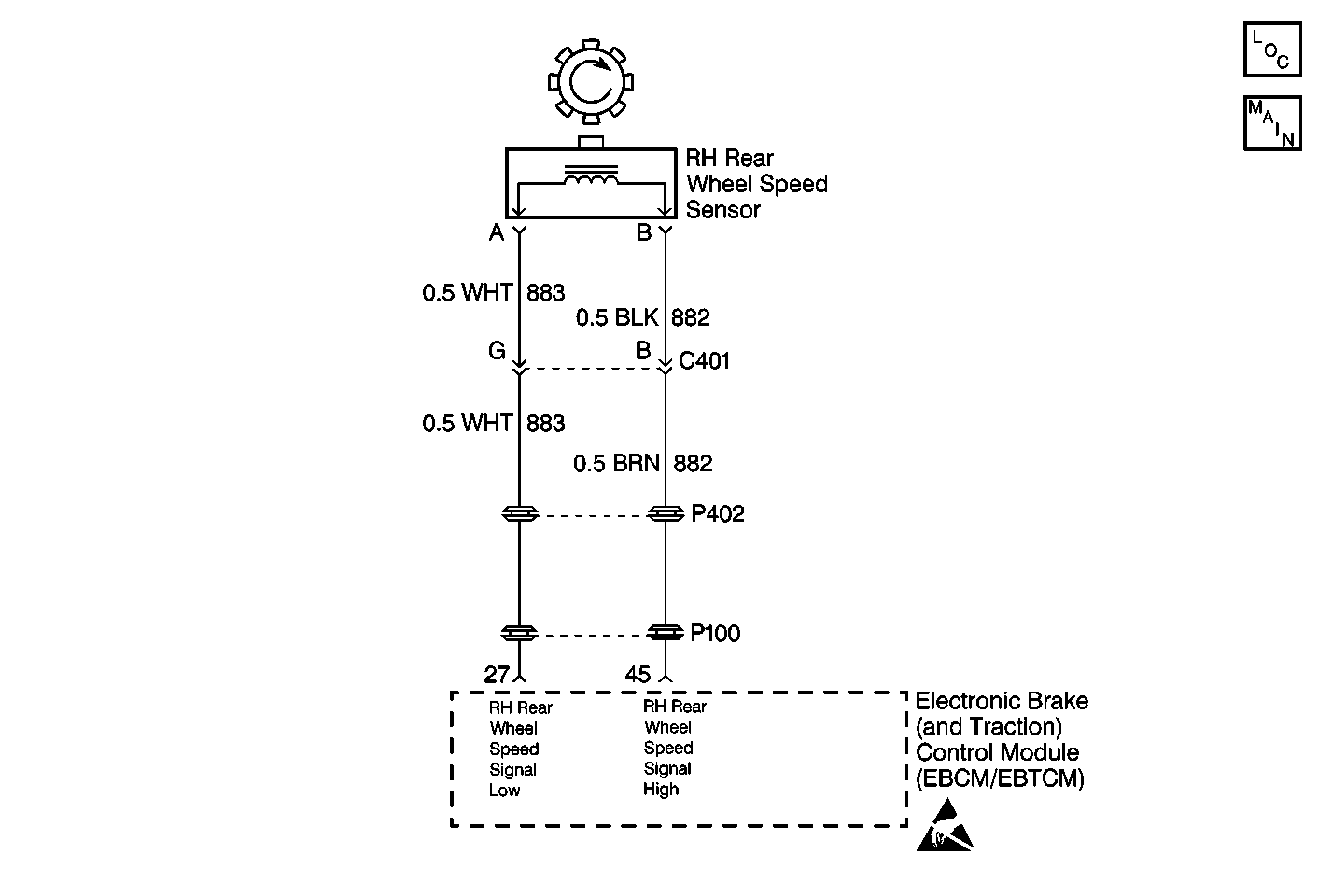
Circuit Description
The wheel speed sensor creates an AC voltage as each wheel turns. The frequency of the voltage is proportional to the wheel speed.
The voltage is magnetically induced. It is caused by a toothed sensor ring (mounted on the drive axle) which passes the stationary pickup coil of the wheel speed sensor.
The EBCM/EBTCM uses the wheel speed sensor signal to calculate the following values:
| • | The vehicle reference speeds |
| • | The speed of each wheel |
| • | The acceleration |
| • | The slip values |
Use these values in order to determine when antilock or traction control (when equipped) is required.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The DTC C1232 sets when the EBCM/EBTCM detects electromagnetic interference (noise) in a wheel speed sensor signal.
The following components may be sources of interference:
| • | The accessory motors |
| • | The wiper motors |
| • | The ignition circuits |
| • | Any add-on or after market equipment |
The DTC C1232 also sets when the EBCM/EBTCM determines that a wheel speed signal is erratic. (An example of an erratic signal is a signal which indicates that a wheel is accelerating faster than physically possible.)
An intermittent or a short to the ground in a wheel speed sensor may also cause the EBCM/EBTCM to set a DTC.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The following actions will be taken when the DTC sets:
| • | A malfunction DTC is stored. |
| • | The ABS is disabled. |
| • | The ANTILOCK indicator lamp is turned ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The DTC will be cleared under following conditions:
| • | Conditions for the malfunction are no longer present. Use the scan tool clear DTCs function. |
| • | 100 ignition switch key cycles have passed with no malfunctions detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
One of the following condition may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | A rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A wire that is broken inside the insulation |
Inspect any suspect circuitry for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table:
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
2 |
Is the sensor or the wiring physically damaged? | -- | ||
3 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 850-1350 ohms | ||
With the J 39200 DMM still connected, select the mV AC scale. Is the AC voltage greater than the specified value? | 100 mV | |||
5 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||
6 | Reconnect all of the connectors. Test drive the vehicle above 24 km/h (15 mph) for at least 30 seconds while monitoring the scan tool for ABS/TCS DTCs. Does the DTC C1232 reset? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
7 |
Does the DTC C1232 reset? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
8 | Replace the right rear wheel speed sensor. Refer to Rear Wheel Bearing and Hub Replacement in Rear Suspension. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Repair the short between CKT 883 and CKT 882. Refer to Rear Wheel Bearing and Hub Replacement in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Replace the EBCM/EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake and Traction Control Module Replacement in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Test drive the vehicle above 24 km/h (15 mph) for at least 30 seconds while monitoring the scan tool for ABS/TCS DTCs. Does the DTC C1232 reset? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
