Surges and/or Chuggles
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
DEFINITION: Engine
power variation under steady throttle or cruise. Feels like the vehicle speeds
up and slows down with no change in the accelerator pedal.
|
1
| Was the
Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 2
| Go to the
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
|
2
|
- Perform a bulletin search.
- If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found, correct the
condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 3
|
3
| Was visual/physical check performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 4
| Go to Visual/Physical Checks
.
|
4
| Be sure
driver understands Transaxle torque converter clutch and A/C compressor operation
as explained in the owner's manual Inform customer how TCC and the A/C clutch
operates
Is the customer experiencing a normal condition?
| --
| System OK
|
Go to Step 5
|
5
|
- Start the engine.
- Observe the HO2S 1 voltage display on the scan tool while modulating
the throttle.
- If the HO2S 1 voltage does not respond quickly to changes in throttle
position, check for a contaminated HO2S. Refer to
Notice: Contamination of the oxygen sensor can result from the use of an inappropriate
RTV sealant (not oxygen sensor safe) or excessive engine coolant or oil consumption.
Remove the HO2S and visually inspect the portion of the sensor exposed to
the exhaust stream in order to check for contamination. If contaminated, the
portion of the sensor exposed to the exhaust stream will have a white powdery
coating. Silicon contamination causes a high but false HO2S signal voltage
(rich exhaust indication). The control module will then reduce the amount
of fuel delivered to the engine, causing a severe driveability problem. Eliminate
the source of contamination before replacing the oxygen sensor.
.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 6
|
6
|
- Check fuel pressure. Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Test
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 7
|
7
| Monitor Long Term Fuel Trim on the scan tool.
Is Long Term Fuel Trim significantly in the negative range (Rich condition)?
| --
|
Go to Step 8
|
Go to Step 9
|
8
|
- Check items that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 10
|
Go to Step 22
|
9
|
- Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in
DTC P0171 Fuel Trim System Lean
.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 10
|
Go to Step 22
|
10
|
- Check for proper ignition coil output voltage with a J 26792
spark tester:
| • | Clip the spark tester to engine ground. |
| • | Connect one end of a spark plug wire to the spark tester; connect
the other end of the spark plug wire to the coil being tested. |
| • | Connect one end of another spark plug wire to the other coil tower;
connect the other end of the spark plug wire to ground. |
| • | Crank the engine while observing the spark tester; a crisp blue
spark should be observed. |
| • | Repeat the above steps for each coil. |
- If adequate spark is not present at all coils, replace coil(s)
as necessary. Refer to
Ignition Control Module Replacement
.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 11
|
11
|
- Check for loose ignition control module ground. Refer to Ground
Distribution in Electrical Diagnosis.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 12
|
12
|
Important: Spraying the secondary ignition wires with a light mist of water may
help locate an intermittent problem Ignition components will arc to ground
when a secondary component is faulty.
- Visually/Physically inspect secondary ignition wires. Check for the
following conditions:
| • | Check all ignition wire resistances; should be less than the specified
value. |
| • | Ignition wires for cross firing. |
| • | Ignition wires arcing to ground. |
| • | Ignition wires for improper routing. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| 30,000 ohms (30K ohms)
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 13
|
13
|
- Inspect the ignition coils for cracks or carbon tracking.
- If a problem is found, replace coil(s) as necessary. Refer to
Ignition Control Module Replacement
.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 14
|
14
|
- Check ignition coil secondary resistance.
- Replace any coil(s) which are not within the specified resistance
values. Refer to
Ignition Control Module Replacement
.
Was a problem found?
| 5000 - 8000 ohms
(5-8K ohms)
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 15
|
15
|
Notice: Determine the cause of the oil or gas fouled spark plugs in order to
avoid damage to the new spark plugs.
- Remove the spark plugs.
- Check for wet plugs, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes,
or heavy deposits.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 16
|
16
|
- Check the injector connections.
- If any of the injector connectors are connected to an incorrect
cylinder, correct as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 17
|
17
|
- Check PCM grounds for being clean, tight and in the proper locations.
Refer to Ground Distribution in Electrical Diagnosis.
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 18
|
18
|
- Check MAF sensor connections.
- If a problem is found, replace faulty terminals as necessary.
Refer to Wiring Repair in Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 19
|
19
|
- Visually/physically check vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and
proper connections and routing as shown on the Vehicle Emission Control Information
label.
| • | All with VIN 1 (RPO L67) except Bonneville - Refer to
C/H-Car with VIN 1
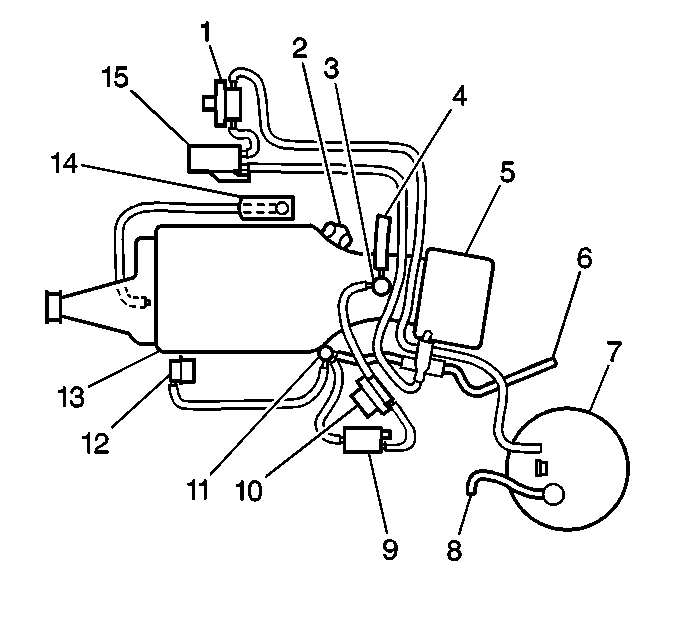
|
| • | Bonneville with VIN 1 (RPO L67) - Refer to
Pontiac H-Car with VIN 1
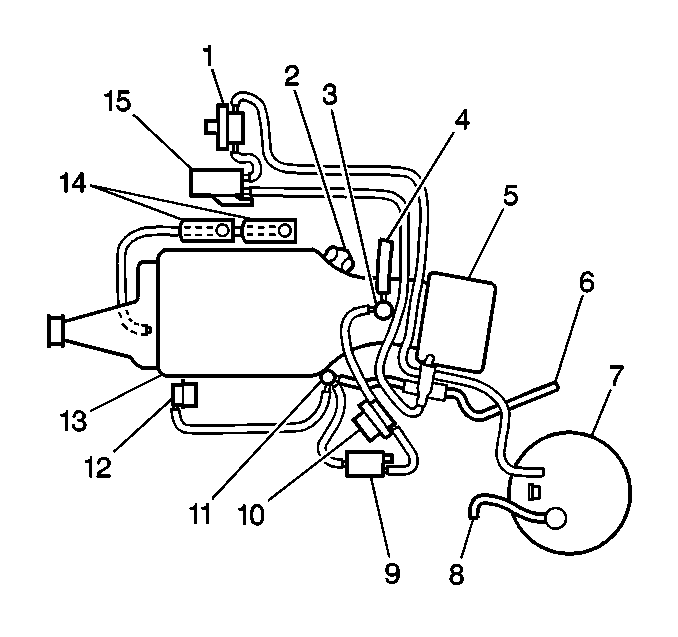
|
| • | C-Car with VIN K (RPO L36) - Refer to
C-Car with VIN K
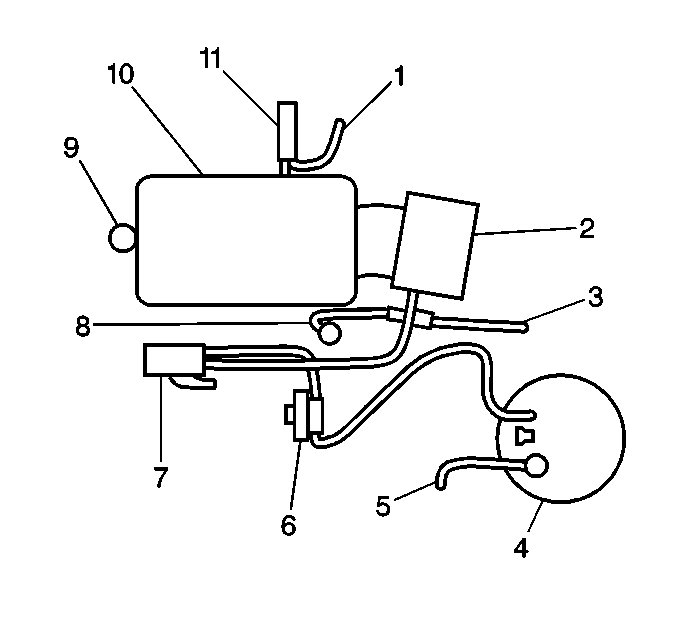
|
| • | H-Car with VIN K (RPO L36) - Refer to
H-Car with VIN K
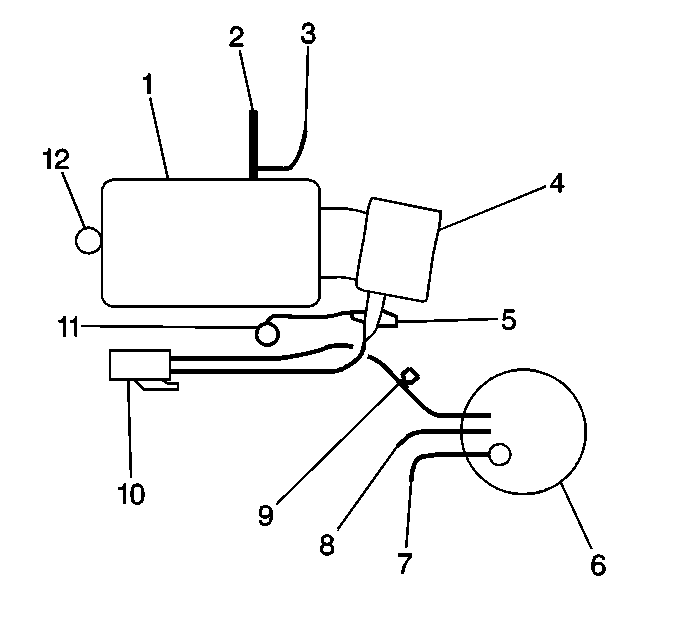
|
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 20
|
20
|
- Check exhaust system for possible restriction:
| • | Inspect exhaust system for damaged or collapsed pipes. |
| • | Inspect muffler for heat distress or possible internal failure. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
|
Go to Step 21
|
21
|
- Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
- If all procedures have been completed and no malfunctions have
been found, review/inspect the following:
| • | Visual/physical inspection. Refer to Visual/Physical
Checks
. |
| • | Freeze Frame data/Failure Records data. |
| • | All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system. |
- If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
| --
|
Go to Step 22
| Review technical bulletins
|
22
| Operate the vehicle to duplicate
conditions present when the original symptom was noted.
Is symptom still present?
| --
|
Go to Step 3
| System OK
|




